A supply chain is a system of organizations, people, activities, information and resources involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer. The company's supply chain illustrates the total process of transforming raw materials into a finished product, and then selling that finished product to consumers .
Supply Chain
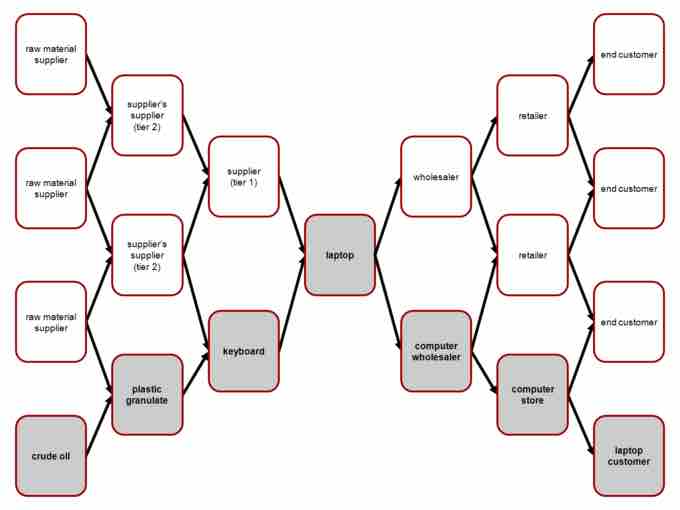
This represents the typical supply chain for a computer. The right half of the chart represents the steps it takes from producing the final product to the consumers.
The purpose of a supply chain is to act as an integrating function that links major business functions and processes into a cohesive business model. When designed well, a supply chain is able to respond to shifts in demand and changes in the marketplace. Based on these shifts, the supply chain is able to alter production levels accordingly so that supply can meet demand so that the firm is able to maximize its profit.
Supply chains vary based on industry, the resources of the manufacturer, and market conditions. Some typical elements and actors in a supply chain include:
- Extraction/Acquisition of Raw Materials or Components. Before the production of a good can be initiated, you need to have all of the necessary elements. These elements could be unrefined raw materials that the company transforms into components or pre-assembled parts. A firm may have subsidiaries or divisions that obtain raw materials or it might acquire those elements from a third party.
- Production. This is the process that transforms the elements acquired from the prior step into the finished good. Economic actors involved in this step include product designers, assembly-line workers, and floor management.
- Inventory. Once the good is completed, it is generally placed into a centralized inventory location while decisions are made by inventory managers and a firm's sales division.
- Transportation. Finished goods must be transported to stores and other locations where consumers can obtain the good. Depending on the type of business, goods may be transferred to smaller regional inventory depots, merchants, or directly to a consumer.
- Wholesaler. A wholesaler is someone who sells a good to smaller stores, who in turn sells the good to consumers.
- Retailer. The retailer buys the product in bulk and sells individual or smaller groups of units to the end consumer.