Chapter 11
Monopoly
By Boundless

Control over a natural resource that is critical to the production of a final good is one source of monopoly power.

Economies of scale and network externalities discourage potential competitors from entering a market.

There are two types of government-initiated monopoly: a government monopoly and a government-granted monopoly.

The government creates legal barriers through patents, copyrights, and granting exclusive rights to companies.
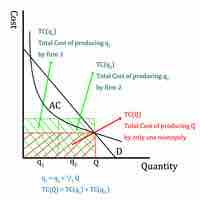
Natural monopolies occur when a single firm can serve the entire market at a lower cost than a combination of two or more firms.

Firms gain monopolistic power as a result of markets' barriers to entry, which discourage potential competitors.

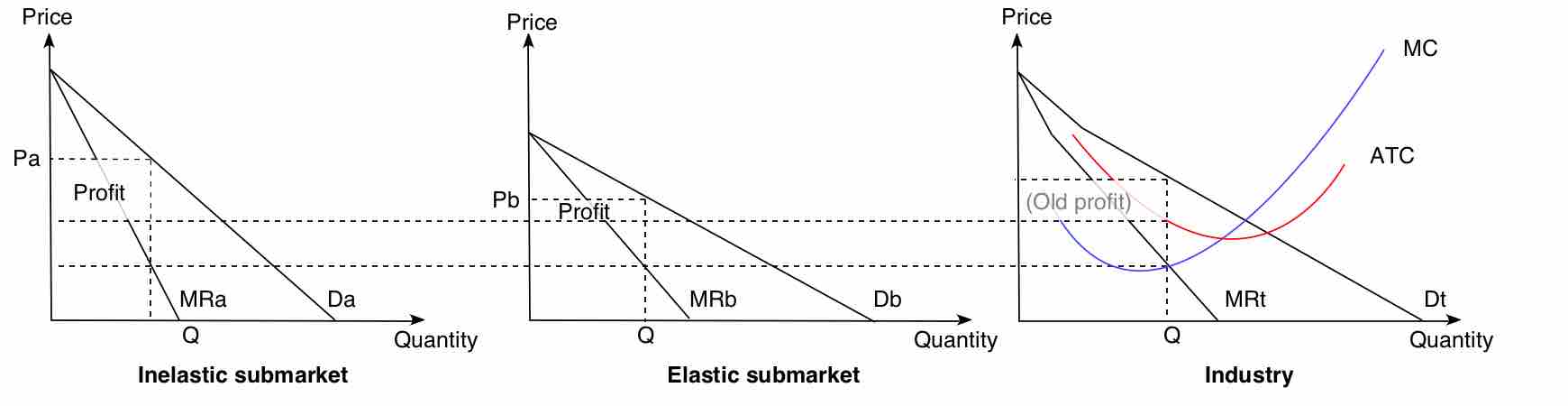
Monopolies, as opposed to perfectly competitive markets, have high barriers to entry and a single producer that acts as a price maker.
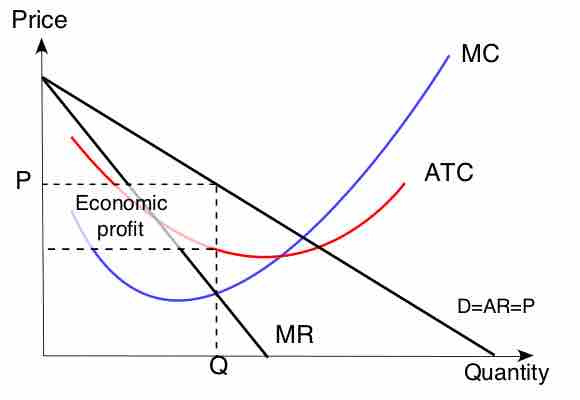
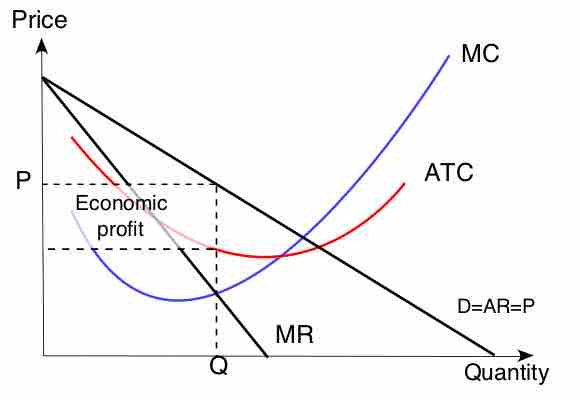
For monopolies, marginal cost curves are upward sloping and marginal revenues are downward sloping.
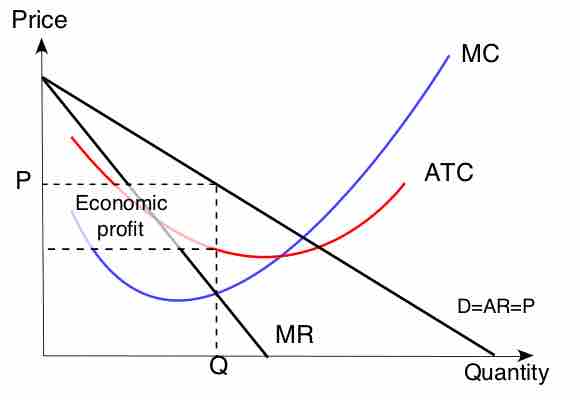
Monopolies set marginal cost equal to marginal revenue in order to maximize profit.
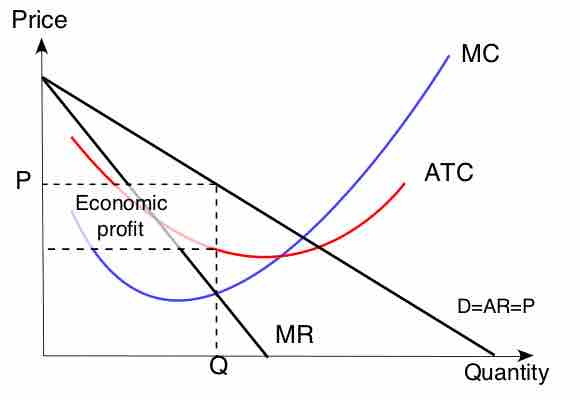
To maximize output, monopolies produce the quantity at which marginal supply is equal to marginal cost.
Monopolies can influence a good's price by changing output levels, which allows them to make an economic profit.
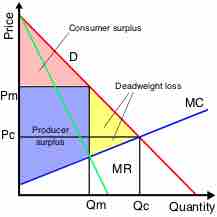
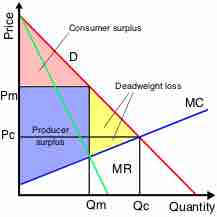
A monopoly generates less surplus and is less efficient than a competitive market, and therefore results in deadweight loss.

In economics, deadweight loss is a loss of economic efficiency that occurs when equilibrium for a good or service is not Pareto optimal.
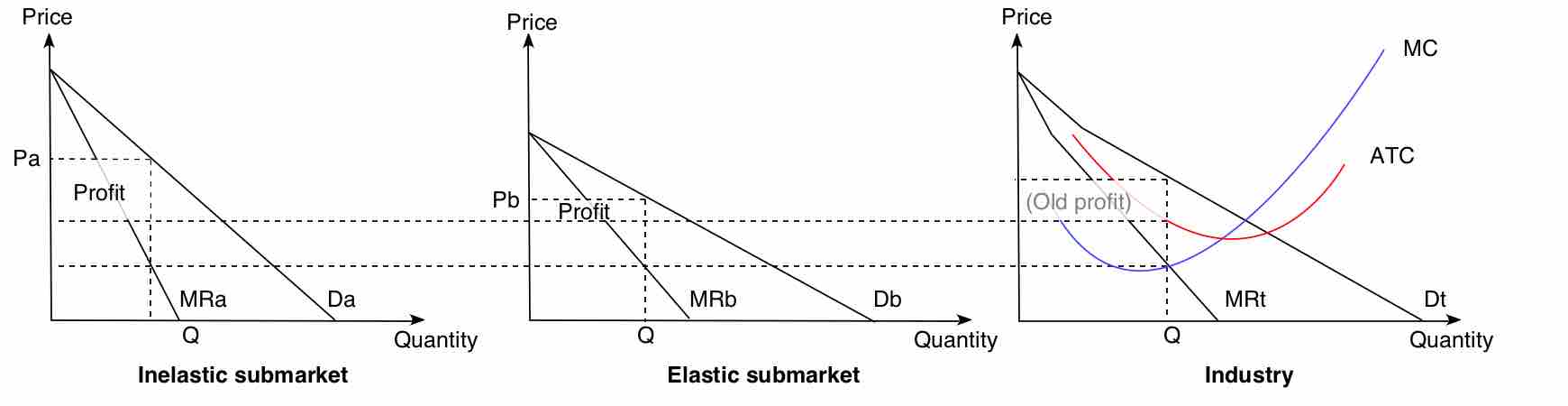
In a competitive market, price discrimination occurs when identical goods and services are sold at different prices by the same provider.
Price discrimination is present in commerce when sellers adjust the price on the same product in order to make the most revenue possible.
The purpose of price discrimination is to capture the market's consumer surplus and generate the most revenue possible for a good.

A monopoly can diminish consumer choice, reduce incentives to innovate, and control supply to enforce inequitable prices in a society.
Antitrust laws ensure that competitive environments are preserved in order to maintain an efficient and equitable capitalistic system.
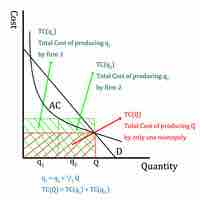
Natural monopolies are conducive to industries where the largest supplier derives cost advantages and must be regulated to minimize risks.
