Chapter 24
Aggregate Demand and Supply
By Boundless
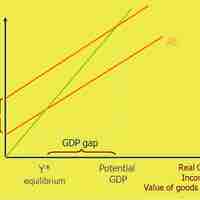
Aggregate expenditure is the current value of all the finished goods and services in the economy.
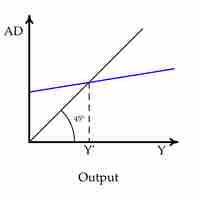
An economy is said to be at equilibrium when aggregate expenditure is equal to the aggregate supply (production) in the economy.
An economy is said to be at equilibrium when the aggregate expenditure is equal to the aggregate supply (production) in the economy.
When the fiscal multiplier exceeds one, the resulting impact on the national income is called the multiplier effect.

In the short run, output fluctuates with shifts in either aggregate supply or aggregate demand; in the long run, only aggregate supply affects output.

Classical theory, the first modern school of economic thought, reoriented economics from individual interests to national interests.

Keynesian economics states that in the short-run, economic output is substantially influenced by aggregate demand.

Aggregate demand (AD) is defined as the total demand for final goods and services in a given economy at a specific time.
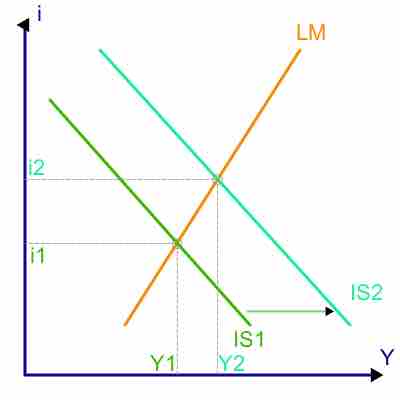
Due to Pigou's Wealth Effect, the Keynes' Interest Rate Effect, and the Mundell-Fleming Exchange Rate Effect, the AD curve slopes downward.

An increase in any of the four inputs into AD will result in higher real output or an increase in prices.
Aggregate supply is the total supply of goods and services that firms in a national economy plan to sell during a specific time period.
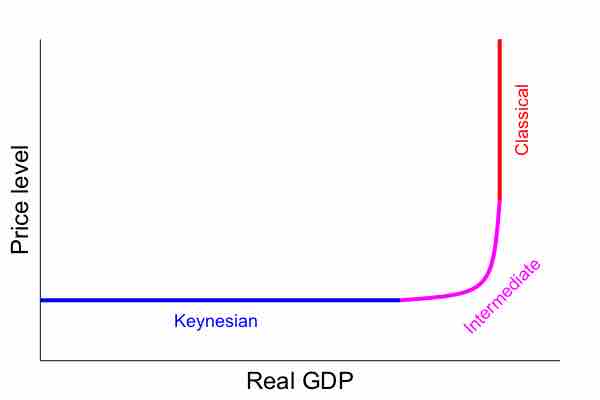
In the short-run, the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.
The long-run aggregate supply curve is perfectly vertical; changes in aggregate demand only cause a temporary change in total output.
In the short-run, the price level of the economy is sticky or fixed; in the long-run, the price level for the economy is completely flexible.

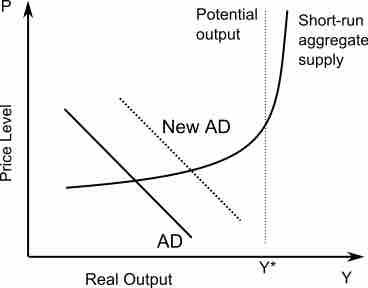
The short-run aggregate supply shifts in relation to changes in price level and production.
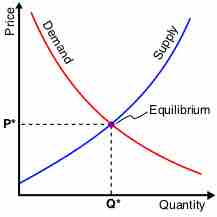
In economics, the macroeconomic equilibrium is a state where aggregate supply equals aggregate demand.
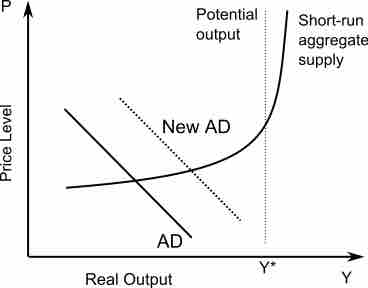
A short-run shift in aggregate demand can change the equilibrium price and output level.
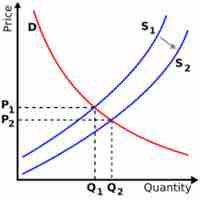
In economics, the aggregate supply shifts and shows how much output is supplied by firms at different price levels.