Aggregate Supply
In economics, aggregate supply is defined as the total supply of goods and services that firms in a national economy produce during a specific period of time. It is the total amount of goods and services that firms are willing to sell at a specific price level in the economy.
Shift in Aggregate Supply
The aggregate supply curve may shift labor market disequilibrium or labor market equilibrium. If labor or another input suddenly becomes cheaper, there would be a supply shock such that supply curve may shift outward, causing the equilibrium price in to drop and the equilibrium quantity to increase.
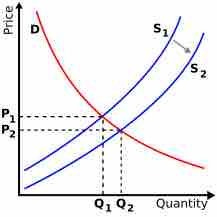
Supply Shift
A supply shock could be caused by changing regulations or a sudden change in the price of an input, among other reasons.
During the short-run, there is one fixed factor of production, usually capital. However, the fixed factor does not stop the curve's ability to shift outward. When the curve shifts to the right, it causes an increase in the output and a decrease in the GDP at a given price. Examples of events that cause the curve to shift to the right in the short-run include a decrease in the wage rate, an increase in physical capital stock, and technological progress.
In the long-run only capital, labor, and technology affect the aggregate supply curve because at this point everything in the economy is assumed to be used optimally. The long run curve is often seen as static because it shift the slowest. The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical which shows economist's belief that changes in aggregate demand only have a temporary change on the economy's total output. Examples of events that shift the long-run curve to the right include an increase in population, an increase in physical capital stock, and technological progress.
Reasons for Shifts
The short-run aggregate supply curve is affected by production costs including taxes, subsidies, price of labor (wages), and the price of raw materials. All of these factors will cause the short-run curve to shift. When there are changes in the quality and quantity of labor and capital the changes affect both the short-run and long-run supply curves. The long-run aggregate supply curve is affected by events that change the potential output of the economy.
Changes in short-run aggregate supply cause the price level of the good or service to drop while the real GDP increases. In the long-run the prices stabilize and the price level of the good or service increase in response to the changes.