Chapter 24
Polymers
Book
Version 33
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Chemistry
Chemistry
by Boundless
Section 2
Lipids
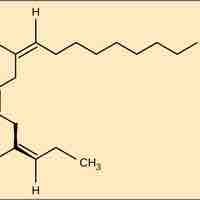
Lipid Molecules
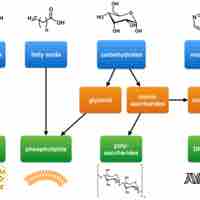
Fats and oils, which may be saturated or unsaturated, can be unhealthy but also serve important functions for plants and animals.
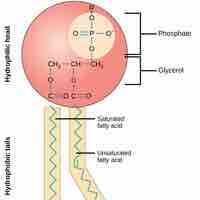
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules that make up the bilayer of the plasma membrane and keep the membrane fluid.
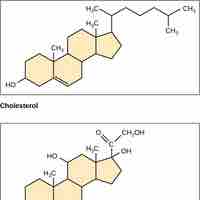
Steroids
Steroids, like cholesterol, play roles in reproduction, absorption, metabolism regulation, and brain activity.
Section 7
Synthetic Organic Polymers

Types of Synthetic Organic Polymers
Synthetic organic polymers are human-made polymers with various main chain and side chain compositions.
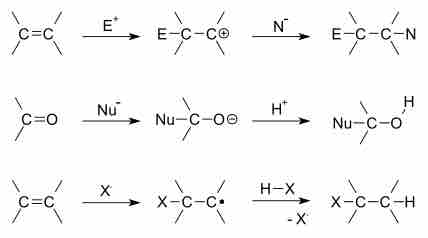
Addition Reactions
In addition reaction, two molecules combine to create one bigger molecule.
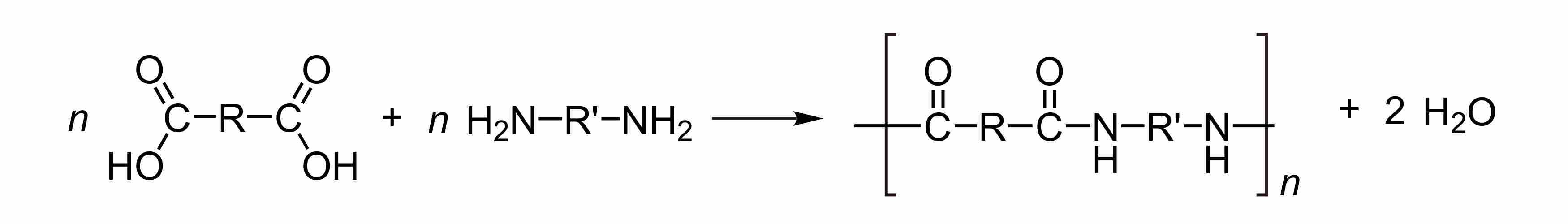
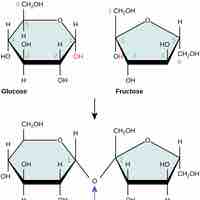
Condensation Reactions
Condensation is a chemical reaction in which one molecule is formed and one small molecule (often water) is lost.
You are in this book
Boundless Chemistry
by Boundless