Chapter 38
The Musculoskeletal System
By Boundless

The musculoskeletal system provides form, support, stability, and movement to the body.
The hydrostatic skeleton, exoskeleton, and endoskeleton support, protect, and provide movement to the bodies of different types of animals.
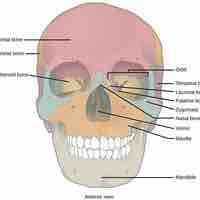
The axial skeleton forms the central axis of the human body and consists of the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage.
The appendicular skeleton supports the attachment and functions of the upper and lower limbs of the human body.
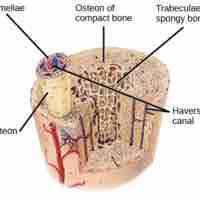
Bones are made of a combination of compact bone tissue for strength and spongy bone tissue for compression in response to stresses.
The osteoblast, osteoclast, osteocyte, and osteoprogenitor bone cells are responsible for the growing, shaping, and maintenance of bones.
Intramembranous ossification stems from fibrous membranes in flat bones, while endochondral ossification stems from long bone cartilage.
Long bones lengthen at the epiphyseal plate with the addition of bone tissue and increase in width by a process called appositional growth.
Bone is remodeled through the continual replacement of old bone tissue, as well as repaired when fractured.
Joints, responsible for movement and stability of the skeleton, can be classified based on structure or function.
Synovial joints allow for many types of movement including gliding, angular, rotational, and special movements.
Synovial joints include planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket joints, which allow varying types of movement.
The most common bone and joint disorder are types of arthritis.
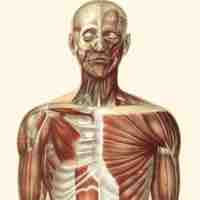
The muscular system controls numerous functions, which is possible with the significant differentiation of muscle tissue morphology and ability.
Skeletal muscles are composed of striated subunits called sarcomeres, which are composed of the myofilaments actin and myosin.

In the sliding filament model, the thick and thin filaments pass each other, shortening the sarcomere.
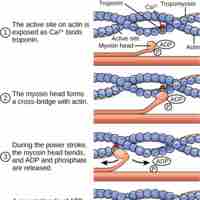
ATP is critical for muscle contractions because it breaks the myosin-actin cross-bridge, freeing the myosin for the next contraction.
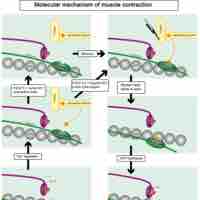
Tropomyosin and troponin prevent myosin from binding to actin while the muscle is in a resting state.
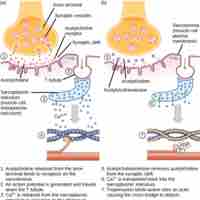
Excitation–contraction coupling is the connection between the electrical action potential and the mechanical muscle contraction.
Muscle tension is influenced by the number of cross-bridges that can be formed.
- Types of Hormones
- How Hormones Work
- Regulation of Body Processes
- Regulation of Hormone Production
- Endocrine Glands