Chapter 37
The Endocrine System
By Boundless
Hormones are chemical messengers that relay messages to cells that display specific receptors for each hormone and respond to the signal.
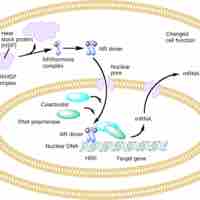
Lipid-soluble hormones diffuse across the plasma membrane of cells, binding to receptors inside the cells where they alter gene expression.
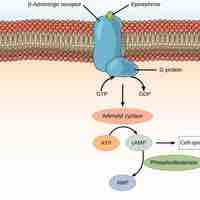
Hormones that cannot diffuse through the plasma membrane instead bind to receptors on the cell surface, triggering intracellular events.
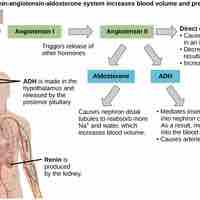
The contrasting actions of antidiruetic hormone and aldosterone work to regulate the level of water in the body.
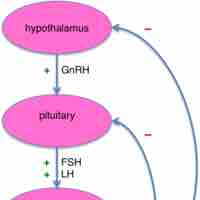
Male and female gonads are regulated by FSH and LH from the pituitary; their production is stimulated by GnRH, secreted by the hypothalamus.
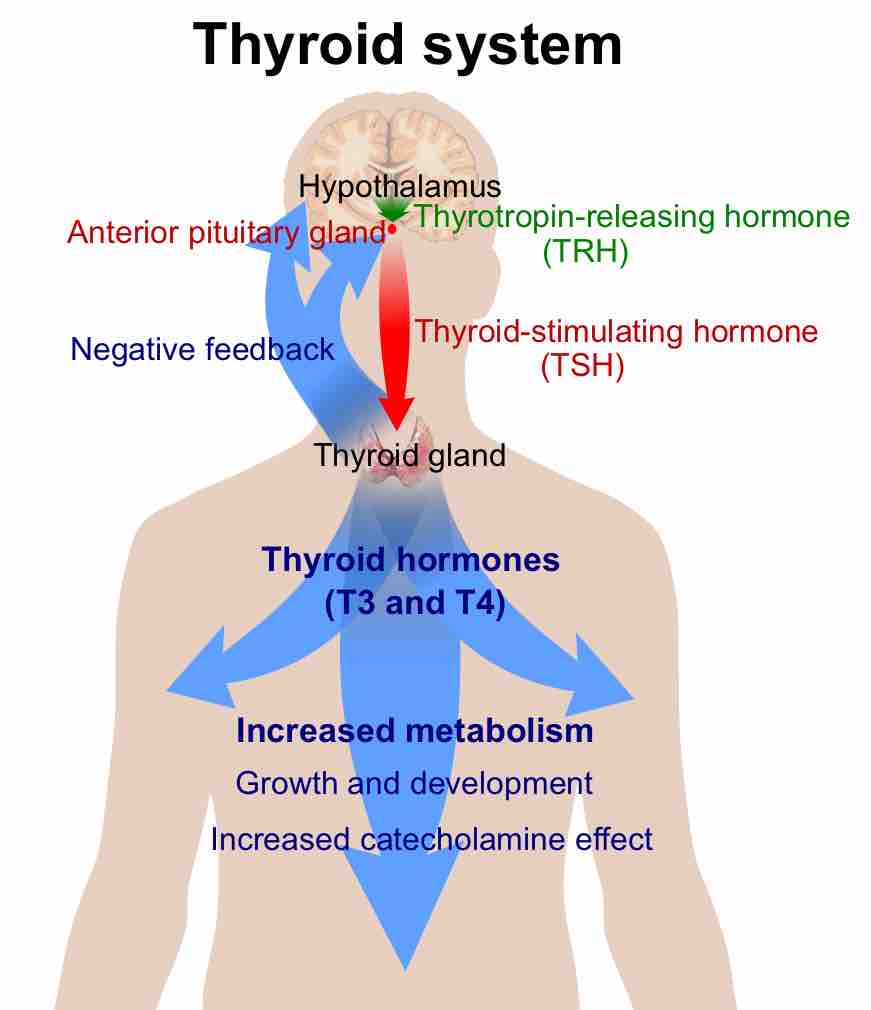
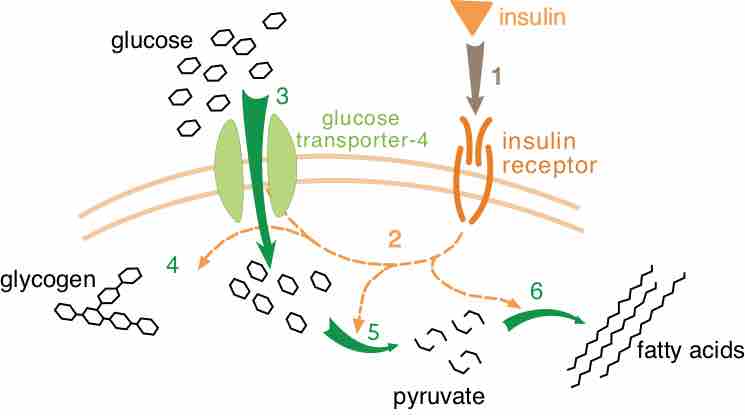
The levels of glucose in the blood are regulated by the hormones insulin and glucagon from the pancreas, and T3 and T4 from the thyroid.
Blood levels of calcium are regulated by the parathyroid hormone, which acts on the bones, kidneys, and intestines to keep levels constant.
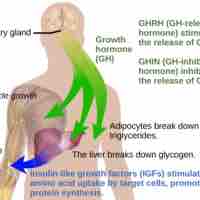
Body growth is controlled by growth hormone (GH), produced by the anterior pituitary, and IGF-1, whose production is stimulated by GH.
The adrenal glands respond to either short-term or long-term stressors by releasing different hormones that act differently on the body.
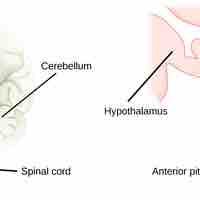
The hypothalamus, an endocrine organ, regulates the anterior pituitary gland and transports hormones along the posterior pituitary gland.
The thyroid gland, the largest endocrine gland, is responsible for the production of the hormones T3, T4, and calcitonin.
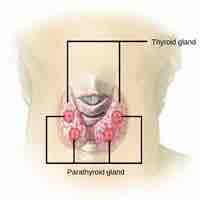
Parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone, which is responsible for specific physiological responses in the body related to calcium.
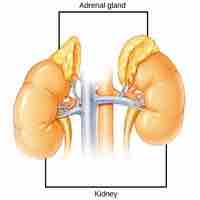
Adrenal glands are composed of the adrenal cortex and medulla; both produce hormones that control essential body functions and responses.
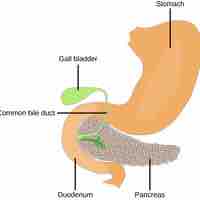
The pancreas produces digestive enzymes and hormones, which are important in blood sugar regulation and other body functions.

The pineal gland is responsible for melatonin production, while the gonads secrete hormones relating to sexual characteristic development.
Several organs with specialized non-endocrine functions possess endocrine roles, such as hormone production and release.