Chapter 36
Sensory Systems
By Boundless
Reception is the first step in the processing of sensation and is dependent on the receptor type, stimulus, and receptive field.
Transduction is the process that converts a sensory signal to an electrical signal to be processed in a specialized area in the brain.
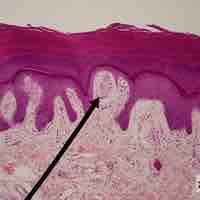
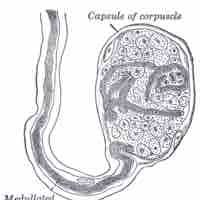
There are various types of tactile mechanoreceptors that work together to signal and process "touch."
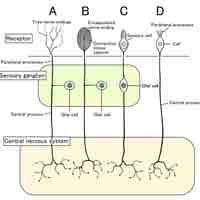
The many types of somatosensory receptors work together to ensure our ability to process the complexity of stimuli that are transmitted.
Thermoreception is the process of determining temperature by comparing the activation of different thermoreceptors in the brain.
The senses of taste and smell are related because they use the same types of receptors and are stimulated by molecules in solutions or air.
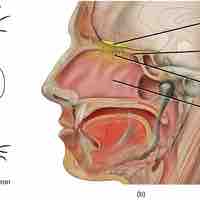
Odorants and tastants produce signal molecules received by receptors, which are then processed by the brain to identify smells and tastes.
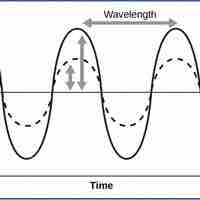
Sound waves, characterized by frequency and amplitude, are perceived uniquely by different organisms.
The outer, middle, and inner structures of the ear collect sound energy, converting it to audible sound.

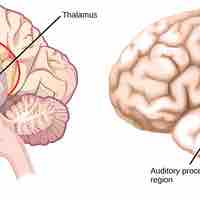
When sound waves reach the ear, the ear transduces this mechanical stimulus (pressure) into a nerve impulse (electrical signal) that the brain perceives as sound.
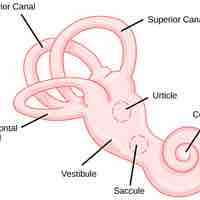
Gravity, acceleration, and deceleration are detected by evaluating the inertia on receptive cells in the vestibular system.
With hair cells in the inner ear that sense linear and rotational motion, the vestibular system determines equilibrium and balance states.
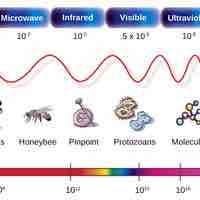
Light is composed of photons that make up electromagnetic waves, which are characterized by wavelength, frequency, and amplitude.

Many structures in the human eye, such as the cornea and fovea, process light so it can be deciphered by rods and cones in the retina.
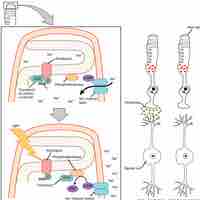
Light is tranduced in rods and cones; visual information is processed in the retina before entering the brain.
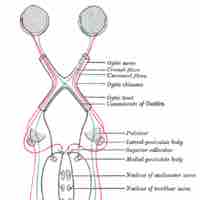
Visual signals are processed in the brain through several different pathways.