Section 4
Hearing and Vestibular Sensation
Book
Version 32
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Biology
Biology
by Boundless
5 concepts
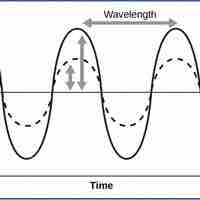
Sound
Sound waves, characterized by frequency and amplitude, are perceived uniquely by different organisms.
Reception of Sound
The outer, middle, and inner structures of the ear collect sound energy, converting it to audible sound.

Transduction of Sound
When sound waves reach the ear, the ear transduces this mechanical stimulus (pressure) into a nerve impulse (electrical signal) that the brain perceives as sound.
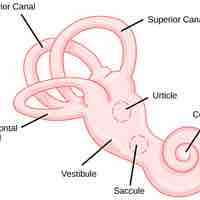
The Vestibular System
Gravity, acceleration, and deceleration are detected by evaluating the inertia on receptive cells in the vestibular system.
Balance and Determining Equilibrium
With hair cells in the inner ear that sense linear and rotational motion, the vestibular system determines equilibrium and balance states.