Section 4
Muscle Contraction and Locomotion
By Boundless
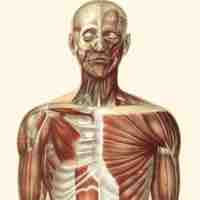
The muscular system controls numerous functions, which is possible with the significant differentiation of muscle tissue morphology and ability.
Skeletal muscles are composed of striated subunits called sarcomeres, which are composed of the myofilaments actin and myosin.

In the sliding filament model, the thick and thin filaments pass each other, shortening the sarcomere.
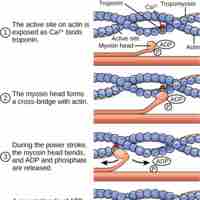
ATP is critical for muscle contractions because it breaks the myosin-actin cross-bridge, freeing the myosin for the next contraction.
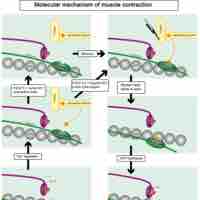
Tropomyosin and troponin prevent myosin from binding to actin while the muscle is in a resting state.
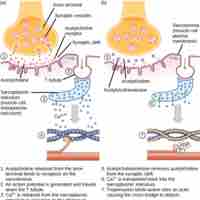
Excitation–contraction coupling is the connection between the electrical action potential and the mechanical muscle contraction.
Muscle tension is influenced by the number of cross-bridges that can be formed.