This article was medically reviewed by Lacy Windham, MD and by wikiHow staff writer, Madeleine Flamiano. Lacy Windham, MD, is a Board-Certified Obstetrician & Gynecologist in Cleveland, Tennessee. Dr. Windham attended medical school at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis. Her residency was completed at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, Virginia. She was the recipient of multiple awards during her residency training, including Most Outstanding Resident in Maternal Fetal Medicine, Most Outstanding Resident in Oncology, Most Outstanding Resident Overall, and Special Award in Minimally Invasive Surgery.
There are 22 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 100% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 521,409 times.
If you've noticed an uncomfortable itch in your genital region, you may have crabs (pubic lice). Crabs are usually sexually transmitted—in fact, there's over a 90% likelihood that you'll catch pubic lice from sexual contact with an infected person. However, pubic lice are also spread through sharing infested clothing, towels and bed linens. Here, we'll share how to deal with crabs, understand the types of medications available, and prevent future outbreaks. Read on to treat pubic lice and find relief.
Steps
How do you catch crabs?
-
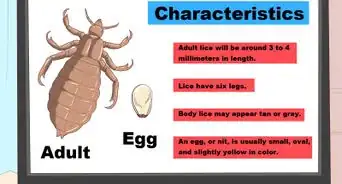
1People who are sexually active are most at risk of getting pubic lice. Since pubic lice prefer to live in pubic hair, these insects are spread whenever people's pubic regions come into close contact. Any sex act with an infected individual increases the likelihood of an infestation.[2]
- Once people's pubic regions are close to each other, lice can easily move from one person's hairs to another individual's hairs.
- Other forms of close contact can spread pubic lice. For example, if someone kisses you, pubic lice on their eyelashes can move onto the hair on your face.
- Quick forms of contact, like a handshake, won't spread pubic lice because they aren't close and prolonged enough to expose anyone to crabs.
-
2Anyone who shares items, like towels, can also contract pubic lice. If you use bedding, towels, or clothing that is infested with nits or pubic lice, then you'll come in contact with these parasites. As soon as you place the infested item against your body, the pubic lice may move to your pubic region, armpit region, eyelashes, or eyebrows.[3]
- This way of spreading pubic lice is less common than sexual activity.
- Pubic lice are highly unlikely to survive on smooth surfaces, like toilet seats. They usually slip off because they can't hang onto them.[4]
Using Over-the-Counter Treatments
-
1Purchase an OTC lice-killing product. Get a lotion with 1% permethrin, like one of Nix’s lice treatment products or a mousse with pyrethrins and piperonyl butoxide. Both of these OTC treatments are non-toxic to humans.
-
2Wash the infected area. Before you apply any treatment, make sure that your pubic region is clean and dry. Use soap and warm water to completely clean the area infested by crabs. Dry the area with a clean towel.[8]
- It will be easier to thoroughly apply the treatment over the infested region when the skin is cool, clean and dry.
- Do not shave during this step, as live lice can just crawl to another area with body hair.
- Once you've dried off, immediately throw the towel into the washing machine. Use hot 140 °F (60 °C) water to kill off any nits or lice.[9]
-
3Apply your lice-killing product according to the directions. Whether you've chosen a lotion with 1% permethrin, or a mousse with pyrethrins and piperonyl butoxide, check the label. Pay attention to the recommended method for applying the treatment—such as putting it on while wearing gloves—as well as the correct amount of time to leave it on.[10]
- When you follow the package instructions carefully, you'll get the most benefits out of the lice-killing product.
-
4Leave the product on for the recommended amount of time. Shampoos may only need to be left on for about 10 minutes, but lotions and creams may need to be left on for 8-14 hours. Note the time when you apply the product and set a timer or watch the time.[11]
-
5Rinse off the medication and dry your pubic area. After you have left the product on for the indicated amount of time, rinse it off with warm water. Rinsing away the product will help to remove dead nits and lice from your skin. It is important to rinse the dead parasites away because they may lead to hygiene problems, like an infection, if they're left on your skin.[12]
- Be sure to separate the towels you used from your other clothes and linens. Wash the towels separately to avoid cross-contamination.
- If you find nits at the base of the hair, you can just remove them using your fingernails or a fine toothed comb.
-
6Use a fine-toothed comb to remove any nits. Use a "nit comb" that's specially designed to catch the tiny nits and remove them from your hair. Carefully comb through your hair, section by section. Throughout this process, dip the comb in a solution of hot, soapy water to get rid of the nits.[13]
- When you're done, sterilize the comb by washing it with hot, soapy water. Rinse the pubic area to remove dead lice or nits.
- You can also use clean tweezers to carefully pluck away the nits. This will prevent them from hatching, causing another outbreak of pubic lice a few weeks later.
- After you've completed all nit-removing steps, you can shave in order to get rid of any remaining nits.[14]
-
7Treat lice in eyelids and eyelashes with petroleum jelly. Since you'll need a special grade of petroleum jelly that requires a prescription, consult your doctor. Let your physician know that you've seen signs of lice around your eyes. Once you receive medical-grade petroleum jelly, apply it to the edges of your eyelids 2-4 times a day over the course of 10 days.[15]
- Don't use the regular lice shampoos near your eyes. Instead, use any medication your doctor prescribes or you pluck the lice using tweezers.
-
8Put on clean underwear and clothing. To prevent further infestation from used clothes that may have nits or lice, put on clean clothes and underwear after your treatment. Throw the clothes you wore prior to your treatment in the washing machine. Make sure to use hot 140 °F (60 °C) water to kill any nits or lice.[16]
Follow-Up Care and Prevention
-
1Wash clothing, bedding, and towels in hot water to kill lice. Since all of the items you used since catching pubic lice may be infected, throw all of them in the washing machine. Make sure the temperature of the water is at least 140 °F (60 °C) so you can completely disinfect your load of laundry and get rid of nits or live lice.[17]
- After you've washed them, put them in the dryer and select the high heat drying cycle. This cautionary measure will prevent any nits or lice from surviving.
-
2Store items that can't be laundered in a sealed plastic bag for 2 weeks. If you have any garments that aren't machine-washable, like suits or delicates, put them in an airtight storage bag. Seal the bag, vacuum the air out, and place it somewhere away from any other clothes for 14 days.[18]
- Keep the bag on an empty shelf, in a storage shed, or in your garage.
- 14 days is enough time for nits to hatch into nymphs—when you wait 2 weeks, both recently hatched nymphs and adult lice will die in the storage bag since they didn't have access to blood.
-
3Get tested for other STIs (Sexually Transmitted Infections). Since it's common to contract other STIs when you come in contact with pubic lice, get an STI check-up at a public health clinic or with your doctor. Test for gonorrhea and chlamydia since these two STIs are commonly found in individuals infested with pubic lice.[19]
- As an extra precaution, test for all the STIs you can, including syphilis and HIV.
- After you get tested, follow up with a medical professional after 3 months to check in about your sexual health status. They can also examine you to see if you're still infested with pubic lice.
-
4Inform intimate partners about pubic lice and avoid sex. If you have any nits or lice remaining, you can pass pubic lice to someone else. Abstain from any sexual contact until you're certain you've eliminated all pubic lice. Inform sex partners from the last 3 months about your sexual health status and let them know you've come in contact with pubic lice. Then, encourage them to get tested.[20]
- Remember that it's responsible to share your sexual health status and is a normal part of being sexually active.
-
5Monitor the treated area. Watch the area over the next few weeks for signs of nits or lice. If you see more lice or experience itching and redness, follow the same process to retreat the area 9-10 days after the first treatment. Repeat all the steps for follow-up care: remove nits, launder your clothes to disinfect them, store any infested items that aren't machine-washable, and monitor the area.[21]
- A second treatment after 9-10 days allows you to kill any live lice that just hatched before they can lay eggs.
- Some products only kill live lice, not the nits, which means you'll need to retreat the area once the nits hatch.
-
6Consult your doctor if OTC treatments don't work. Ask your doctor to prescribe a stronger medication. They might recommend ivermectin as a topical therapy to combat pubic lice. If you're resistant to topical insecticides, your doctor may suggest an oral dose of ivermectin. In extremely rare cases, your doctor might direct you to use Lindane shampoo for severe infestations of pubic lice.[22] Also seek out medical attention if you experience:[23]
- Severe redness due to itching
- Pus formation from a secondary bacterial infection
- Red and itchy eyes
References
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/lice/pubic/biology.html
- ↑ https://dph.illinois.gov/topics-services/diseases-and-conditions/diseases-a-z-list/crabs.html
- ↑ https://www.cdph.ca.gov/Programs/CID/DCDC/Pages/BodyLice.aspx
- ↑ https://hshc.ca/pubic-lice/
- ↑ https://ufhealth.org/pubic-lice
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/lice/pubic/treatment.html
- ↑ http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/pyrethrins.html
- ↑ https://patient.info/sexual-health/pubic-and-body-lice-leaflet
- ↑ https://www.healthygallatin.org/blog/lice-dont-panic-read-on/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1070891/
- ↑ https://www.bop.gov/resources/pdfs/lice_protocol.pdf
- ↑ https://www.saginawpublichealth.org/media/hvtj1vgy/lice.pdf
- ↑ https://www.health.pa.gov/topics/Documents/Diseases%20and%20Conditions/Pubic%20Lice%20.pdf
- ↑ https://goshh.ie/sti-information-2/stis-2/crabs-pubic-lice-2/
- ↑ https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/485738
- ↑ https://myhealth.alberta.ca/sexual-reproductive-health/sexually-transmitted-infections/pubic-lice-(crabs)
- ↑ https://myhealth.alberta.ca/sexual-reproductive-health/sexually-transmitted-infections/pubic-lice-(crabs)
- ↑ https://sense.info/en/stis/types-stis/pubic-lice
- ↑ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12035022/
- ↑ https://www.dshs.texas.gov/region1/documents/Epi/Public-Lice-Fact-Sheet.pdf
- ↑ https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2004/0115/p341.html
- ↑ https://www.uptodate.com/contents/head-lice-beyond-the-basics
- ↑ https://wa.kaiserpermanente.org/kbase/topic.jhtml?docId=abr8715
About This Article
To treat pubic lice, also known as crabs, get an over-the-counter lotion or shampoo that contains 1 percent permethrin or pyrethrin. Then, wash your pubic region with soap and water and apply the medication according to the package instructions. Allow the medication to sit for the specified time and then rinse it off. When you're done, use a flea comb or tweezers to remove any eggs in your pubic hair and put them in a bowl of hot, soapy water. To learn how to prevent pubic lice from coming back or spreading, scroll down.
-Step-1-Version-3.webp)
-Step-2-Version-3.webp)
-Step-3-Version-3.webp)
-Step-4-Version-3.webp)
-Step-5-Version-3.webp)
-Step-6-Version-3.webp)
-Step-7-Version-3.webp)
-Step-8-Version-3.webp)
-Step-9-Version-3.webp)
-Step-10-Version-3.webp)
-Step-11-Version-3.webp)
-Step-12-Version-3.webp)
-Step-13-Version-3.webp)
-Step-14-Version-3.webp)
-Step-15.webp)
-Step-16.webp)
-Step-17.webp)
-Step-18.webp)


-Step-14.webp)
















-Step-14.webp)



































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...