This article was medically reviewed by Erik Kramer, DO, MPH. Dr. Erik Kramer is a Board-Certified Primary Care Physician at the University of Colorado. With over 15 years of experience, his clinical interests include obesity and weight management, diabetes care, and preventive care, as well as embracing a holistic approach to primary care. He received his Doctorate in Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) from the Touro University Nevada College of Osteopathic Medicine and completed his residency at Central Maine Medical Center. Dr. Kramer is a Diplomate of the American Board of Obesity Medicine.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 6,480 times.
Penicillin is used to treat infections by killing off harmful bacteria. It comes in the form of a tablet as well as a liquid, and it's taken by mouth. It's especially important to read the instructions that come on your bottle of penicillin so you know how much of it to take each day, decided by your doctor. Take penicillin on an empty stomach so it works its best, and finish your entire prescription to ensure you're feeling better.[1]
Steps
Using Penicillin Safely
-
1Take penicillin to fight off bacterial infections. Penicillin helps treat ear, skin, and respiratory infections, including strep throat. Its brand names include Bactocill, Cloxapen, Geocillin, and Pfizerpen, among many others. If you have something like strep throat, your doctor may prescribe penicillin to help treat it.[2]
- Penicillin also treats gum and mouth infections, as well as prevents rheumatic fever.
-
2Tell your doctor if you're taking any other medications. This is important because the medications you're currently taking may not work well with the penicillin, or might cause negative reactions when they're mixed. Tell your doctor which medications you're taking, as well as any supplements or vitamins.[3]
- If you're taking several different medications, make a list of each one, how much you're taking, and how often you're taking them to show to your doctor.
- Let your doctor know if you shouldn't be taking penicillin due to an allergy or other reason.
Advertisement -
3Seek medical help if you think you're having an allergic reaction. If you're allergic to penicillin, you may develop hives, fever, rash, or itching. Feeling out of breath, wheezing, or being unable to breathe properly are also signs that you need medical help. If you experience any allergy symptoms, call your doctor or visit an emergency room to be treated right away.[4]
- If you have a runny nose or itchy eyes, you may be allergic to penicillin.
- Visit an allergy or immunology provider to confirm whether or not you have a penicillin allergy. It's possible for an allergy to get mislabeled or for an early allergy to go away. Allergy testing can confirm that you do or don't have an allergy to the drug.
-
4Be aware of side effects such as a headache or diarrhea. These are common side effects, as are a sore mouth and tongue. Less common side effects include nausea, vomiting, or fever. If you experience any side effects while taking penicillin, call your doctor to let them know and ask for advice as to how you should continue your treatment.[5]
- Find a more complete list of side effects online by typing "side effects of penicillin" into the search bar if desired.
-
5Keep penicillin out of reach of children and pets. Stash your penicillin in a cupboard or other spot where kids can't get to it. Make sure the cap is securely fastened when you store it for an extra layer of precaution.[6]
Following Your Dosage Instructions
-
1Follow the instructions on the bottle for the proper dosage. Your doctor will decide how many times a day you should take the penicillin, as well as how much will be in each dose. All of this information is on the instructions label on your bottle of penicillin. Refer to the directions carefully to make sure you’re taking the penicillin safely.[7]
- Don’t take any more or less of the penicillin than what’s instructed.
- Your dosage amount will depend on your type of illness as well as your age and body weight.
- Ask your pharmacist or doctor questions if you don’t understand the directions on your prescription.
-
2Take the doses at the same time each day. Whether you’re instructed to take the medicine twice a day, 3 times a day, or even 4 times a day, try to take it at the same times. For example, if you’re supposed to take it twice a day, you might take the first dose before breakfast at 7 in the morning and the second dose before bedtime at 8 at night.[8]
- If you’re taking it 4 times a day, try taking it before breakfast, before lunch, in the late afternoon, and before bedtime.
- Spreading your doses out will ensure that the medicine is working most effectively.
- Make a chart to help you remember when to take the penicillin, if needed.
-
3Continue taking penicillin until the prescription runs out. It’s important to finish the penicillin completely, even if you start feeling better. If you stop taking the penicillin while you still have doses left, the infection might not completely go away.[9]
- The average length of time for a penicillin prescription is 10 days, but this may vary depending on your illness.
-
4Avoid double dosing if you accidentally miss a dose. If you forget to take your penicillin, take it as soon as you remember it unless it’s almost time for the next dose. If this is the case, skip your missed dose and take the next one as you normally would. This will get you back on a regular schedule.[10]
- If you miss a dose and have to skip it, it’s still important to finish the entire prescription to cure your illness.
-
5Take penicillin on an empty stomach if possible. The medicine works best if you haven’t just eaten so that the food doesn’t absorb all of the penicillin. Try to take your dose 30 minutes before a meal. If you’re taking it after a meal, wait at least 3 hours to ensure your food has digested.[11]
- If your stomach tends to get upset, it’s okay to take penicillin with a small amount of food.
Swallowing a Penicillin Tablet
-
1Pay attention to how many tablets you’re supposed to take each day. Read the instructions on your bottle telling you how many tablets to swallow. The instructions should be very clear, such as "Take 1 capsule 2 times a day."[12]
- Penicillin tablets are often in 250-mg doses.
-
2Swallow the penicillin tablet with a glass of water. Penicillin capsules are made to be swallowed whole. Place the tablet on the back of your tongue and take a big sip of water, swallowing the tablet.[13]
- Avoid chewing the tablets.
- You can also take the tablet with a glass of juice or milk.
-
3Store the tablets at room temperature away from direct sunlight. Keep the tablets in the prescription container that they come in. Place them in a cupboard out of the heat and sun.[14]
- Avoid keeping the penicillin tablets in the bathroom to prevent them from being around too much moisture.
Drinking Penicillin in Liquid Form
-
1Shake the bottle well before using it. This will ensure the penicillin is mixed evenly before you measure it out. Shake the bottle for roughly 3-5 seconds before opening it.[15]
- Make sure the bottle’s top is securely fastened before shaking it.
-
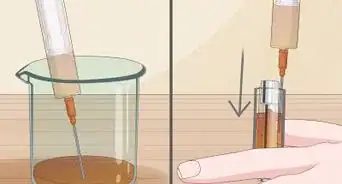
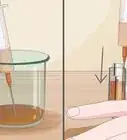
2Measure out the proper dosage using a medicine spoon. Follow the dosage instructions that are on your bottle of penicillin. Use a medicine spoon or oral syringe to measure out the medicine.[16]
- For example, if your doctor tells you to take 250 mg of penicillin, pour the liquid up to the 250-mg mark.
- Avoid using a regular kitchen spoon to measure the medicine, as this won’t be accurate.
-
3Store liquid penicillin in the refrigerator. Read the instructions that are on your bottle’s label to see how they tell you to store the penicillin. If there aren’t any storage instructions, place it in the refrigerator in its original bottle with the top tightly closed.[17]
- Avoid freezing penicillin.
Warnings
- Tell your doctor of any allergies you have, especially if you're allergic to certain medications.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Let your doctor know if you're taking other medications, as well as any supplements or vitamins.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Keep penicillin out of reach of children.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Tell your doctor if you have side effects like nausea, vomiting, or severe diarrhea.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Get emergency help if you develop signs of an allergic reaction like wheezing, hives, or swelling lips and throat.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Never let someone else take your medication.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Don't take penicillin that's past its expiration date.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/penicillin-oral-route-injection-route-intravenous-route-intramuscular-route/proper-use/drg-20062334
- ↑ https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/files/pil.6952.pdf
- ↑ https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/files/pil.6952.pdf
- ↑ https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/penicillin-allergy/symptoms-causes/syc-20376222
- ↑ https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/penicillin-oral-route-injection-route-intravenous-route-intramuscular-route/side-effects/drg-20062334
- ↑ https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/penicillin-oral-route-injection-route-intravenous-route-intramuscular-route/proper-use/drg-20062334
- ↑ https://www.medicinesforchildren.org.uk/penicillin-v-bacterial-infections
- ↑ https://www.healthnavigator.org.nz/medicines/p/phenoxymethylpenicillin/
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a685015.html
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a685015.html
- ↑ https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/files/pil.6952.pdf
- ↑ https://www.medicinesforchildren.org.uk/penicillin-v-bacterial-infections
- ↑ https://www.healthnavigator.org.nz/medicines/p/phenoxymethylpenicillin/
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a685015.html
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a685015.html
- ↑ https://www.healthnavigator.org.nz/medicines/p/phenoxymethylpenicillin/
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a685015.html


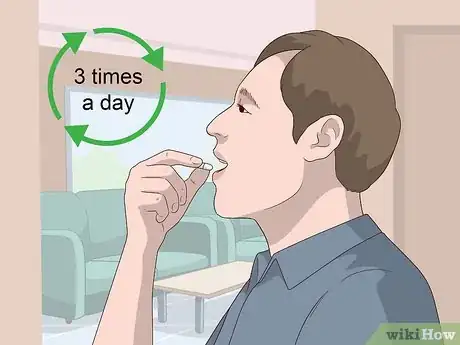


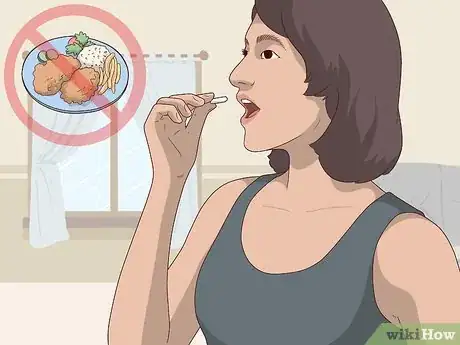



























































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...