This article was medically reviewed by Sarah Gehrke, RN, MS and by wikiHow staff writer, Sophia Latorre. Sarah Gehrke is a Registered Nurse and Licensed Massage Therapist in Texas. Sarah has over 10 years of experience teaching and practicing phlebotomy and intravenous (IV) therapy using physical, psychological, and emotional support. She received her Massage Therapist License from the Amarillo Massage Therapy Institute in 2008 and a M.S. in Nursing from the University of Phoenix in 2013.
There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 40,141 times.
Dimethyl sulfoxide, or DMSO, is a colorless liquid byproduct of the wood industry that has typically been used as a commercial solvent.[1] More recently, however, people have begun to use DMSO for symptomatic relief of a number of medical maladies, from pain and swelling to arthritis and sciatica. Consult your doctor before using DMSO, as it has only been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating interstitial cystitis.
Steps
Treating Interstitial Cystitis with DMSO
-
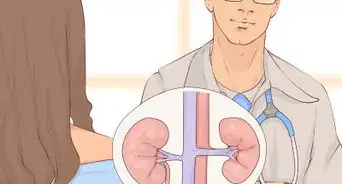
1Find out if you are a good candidate for DMSO treatment. Talk to your doctor to find out if DMSO can help relieve the symptoms of your interstitial cystitis. If so, schedule an appointment to receive the treatment from your doctor.[2]
-
2Allow your doctor to insert a catheter. Over the course of several weeks, your doctor will flush liquid DMSO through a catheter into your bladder. The liquid is absorbed into the bladder lining and can reduce pain. Another benefit of DMSO is that it can increase the absorption of other medications, including steroids.[3]
- Some people experience pain or discomfort when the catheter is inserted. If you are concerned about this pain, speak to your doctor about receiving pain medication or the possibility of inserting DMSO through a syringe, rather than a catheter.[4]
Advertisement -
3Expect some relief from your symptoms. DMSO can reduce inflammation and pain and help relax the bladder and pelvis muscles. It may even break down scar tissue, which can increase your bladder capacity. Relief may be immediate, or it may take several treatments until you begin to feel relief from your symptoms.[5]
Applying DMSO Topically to Reduce Pain and Inflammation
-
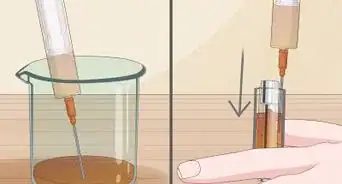
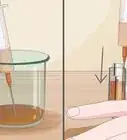
1Choose a low concentration of pharmaceutical-grade DMSO. Because topical use of DMSO is not regulated by the FDA, it's available in a wide range of concentrations. Choose a low concentration, like 25%, to be safe. Always choose pharmaceutical-grade, rather than industrial-grade, DMSO.[6]
- Speak to your doctor before beginning topical DMSO treatments.
-
2Wash your hands. It's crucial that you thoroughly scrub your hands before using them to apply DMSO in order to remove any skin products or lotions that could negatively interact with DMSO. Use soap and warm water, and be sure to clean under your nails as well. Dry your hands when finished.[7]
-
3Clean the area to be treated. The skin that you intend to put DMSO on needs to be thoroughly cleaned as well. Wash the area with warm water and soap, then pat it dry. This removes other substances from your skin that could react poorly with DMSO.[8]
-
4Test your sensitivity to DMSO. Before applying DMSO for the first time, you should test your sensitivity to it by applying a small amount of a low-concentration DMSO solution to a small area of skin. If your skin becomes itchy, red, or irritated, or if you develop a rash, stop using the product immediately. If you do have a reaction, it should appear within the first few minutes after applying DMSO.[9]
-
5Apply DMSO directly to the skin two to three times per day. You can use your hands, a cotton ball, or a clean paintbrush to apply DMSO to your skin. For pain relief, dab the DMSO onto an area larger than the pained area, such as several inches above and below your knee to treat knee pain. You can rub it in or allow it to soak in on its own.
- DMSO may dissolve other substances, so don't allow it to touch your clothing or other materials in its liquid form.
- Avoid applying DMSO to irritated areas, open wounds, or broken skin.
-
6Avoid contact with toxic substances for three hours. Because DMSO opens up your pores, refrain from being around toxic substances, like lower velocity hydrocarbons and pesticides, for at least three hours after applying DMSO to ensure they are not absorbed into your skin.[10]
Taking Safety Precautions
-
1Consult your doctor before you begin using DMSO. Schedule a visit with your doctor to discuss the benefits and detriments of using this product. Discuss the effect DMSO may have on other supplements or medications you are taking, as it may increase the effectiveness of certain medications, including blood thinners, sedatives, and steroids. Ask your doctor for concentration and dosage recommendations as well.[11]
- Be sure to let your doctor know of any other medical conditions you have, including diabetes, asthma, and liver or kidney problems, as DMSO may worsen these conditions.
-
2Look for adverse reactions. Side effects of DMSO may include an odor of garlic, skin irritation, and upset stomach. More serious reactions include itching or burning at the application site, headache, and severe allergic reactions. If you have an adverse reaction, stop using DMSO and contact your doctor. In the case of a severe allergic reaction, obtain emergency medical attention.[12]
-
3Avoid taking DMSO by mouth or through injection. Taking DMSO orally can cause dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, drowsiness, and decreased appetite. Until the safety of taking DMSO by mouth or through injection has been established, only apply it topically or through a catheter with your doctor's approval and under their supervision.[13]
Warnings
- Pregnant women and women who are breastfeeding should not use DMSO, as its effect on fetuses and infants has not been studied.[14]⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Though DMSO has been promoted as an alternative cancer treatment, it has not been approved by the FDA as such.[15]⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Do not use DMSO to treat poison ivy, poison oak, or insect bites.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Do not apply DMSO to infected wounds.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- DMSO is used to treat symptoms of medical conditions and is not a cure.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3510103/
- ↑ http://www.healthline.com/health/what-is-dmso#research3
- ↑ http://www.healthline.com/health/what-is-dmso#research3
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/18021-dimethyl-sulfoxide-dmso-bladder-irrigation
- ↑ https://www.ichelp.org/diagnosis-treatment/treatments/bladder-instillations/dmso/
- ↑ http://www.arthritis.org/living-with-arthritis/treatments/natural/supplements-herbs/guide/dmso.php
- ↑ http://www.arthritis.org/living-with-arthritis/treatments/natural/supplements-herbs/guide/dmso.php
- ↑ http://www.arthritis.org/living-with-arthritis/treatments/natural/supplements-herbs/guide/dmso.php
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/dimethyl-sulfoxide-intravesical-route/before-using/drg-20063424
- ↑ http://www.healthline.com/health/what-is-dmso#risks4
- ↑ https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/d01431a1
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/dimethyl-sulfoxide-intravesical-route/side-effects/drg-20063424
- ↑ http://www.arthritis.org/living-with-arthritis/treatments/natural/supplements-herbs/guide/dmso.php
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/dimethyl-sulfoxide-intravesical-route/before-using/drg-20063424
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/dimethyl-sulfoxide-intravesical-route/before-using/drg-20063424



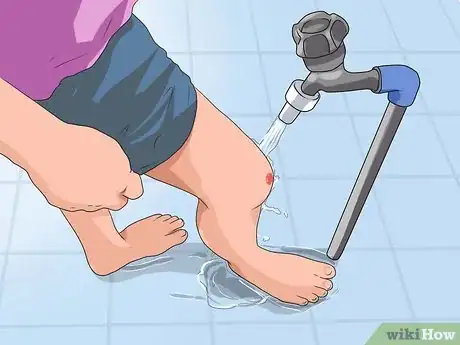

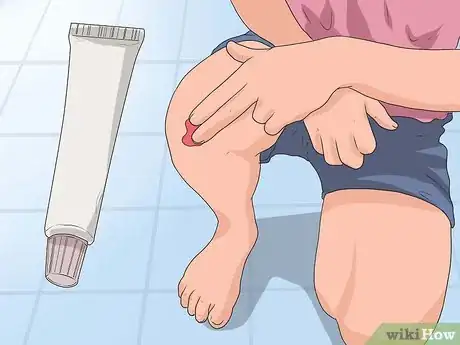


























































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...