This article was medically reviewed by Janice Litza, MD. Dr. Litza is a board certified Family Medicine Physician in Wisconsin. She is a practicing Physician and taught as a Clinical Professor for 13 years, after receiving her MD from the University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health in 1998.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 88% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 306,315 times.
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by a microscopic parasite, usually found in the vagina and urethral tissues. Although it affects both men and women, the symptoms are more frequent in women. It is the most widespread curable STD among young sexually active men and women.
Steps
Learning the Symptoms
-
1Watch for unusual discharge. One of the most common symptoms of trichomoniasis in men is unusual discharge from the penis. Take stock of any unusual discharge you notice.
- You may notice some yellowish discharge coming from the penis, although it may also be grayish. Any unusual or unexplained discharge may be a sign of an STD.[1]
-
2Notice any burning or swelling. The other symptoms of trichomoniasis in men include burning, pain, or swelling in the genitals. If you have any such symptoms, you may be infected.
- You may notice burning after urination or ejaculation. Some men with trichomoniasis may also have difficulty urinating or ejaculating.[2]
- There may be some mild swelling of the scrotum as well. If anything looks or feels unusual, you should seek medical care.[3]
- Keep in mind that these symptoms can indicate problems other than an STD as well, which may require a full medical evaluation in addition to STD testing.
Advertisement -
3Pay attention to itching. Another symptom of trichomoniasis is mild to severe itching around or on the penis. If you notice any unusual itching, seek medical evaluation. Itching can be a symptom of a number of STDs in addition to trichomoniasis, so it's important to get unusual itching evaluated.[4]
-
4Be aware that the majority of men infected with trichomoniasis have no symptoms. The vast majority of anyone infected with trichomoniasis will have no symptoms. However, men are far less likely than women to experience symptoms. About 70% of infected people experience no symptoms at all, so you should get tested for STDs regularly even if things seem fine.[5]
Assessing Your Risk
-
1Ask sexual partners about their status, if possible. If you have regular contact with past sexual partners, ask them about their status. This may be awkward, but the best way to know if you're at risk is knowing whether previous partners have experienced symptoms of or tested positive for trichomoniasis. It is a highly contagious STD.[6]
-
2Review your sexual history. Certain behaviors put you at increased risk for trichomoniasis. You may be at increased risk if any of the following are true for you:
- You've had multiple sexual partners.
- You have a history of having other sexually transmitted infections.
- You have had unprotected sex with a partner whose STD status you do not know.[7]
-
3Consider whether you've previously had trichomoniasis. If you've previously had an outbreak of trichomoniasis, even if it was successfully treated, you're at increased risk of developing the disease again. Review any medical documents you've saved and look over your test results to see if you've ever tested positive for trichomoniasis.[8]
Seeing a Doctor
-
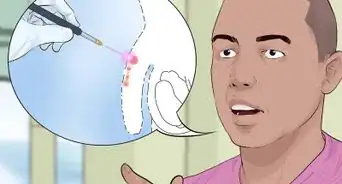
1Get an STD test. You should see a doctor if you believe you're at risk for trichomoniasis. He or she can perform a routine STD test to check for the condition.[9]
- Your health care provider will take a swab of your urethra and send it to a lab for testing. It may be painful to urinate after a swab is taken. It may take a few days before results are ready and may even take up to a week if the lab is busy.[10]
- Many labs can perform a urine test for multiple common STDs, such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis.
- As the symptoms of many other common STDs are similar to those of trichomoniasis, it's a good idea to get a full panel test. Also, if you're worried you're at risk because you've had unprotected sex you'll be at risk for other infections as well. You should wait two to three weeks after a sexual encounter before getting tested, however, as it will take a while for viruses to be detectable.[11]
-
2Seek treatment. Medical treatment for trichomoniasis is necessary. It can be cured with a single dose of prescription antibiotics that are taken orally. Ask your doctor about medication. Do not drink alcohol for 24 hours after receiving treatment.[12]
-
3Prevent outbreaks in the future. About 1 in 5 people get infected with trichomoniasis again within three months of treatment. Make sure you know how to prevent outbreaks in the future.
- Use a latex condom if you have sex with a new partner. While condoms do not completely eliminate the risk of STDs they do dramatically reduce it.[13]
- Make sure you wait until all symptoms of a previous infection pass before having sex again.[14]
- Talk to your partner about STDs. It's a good idea for both of you to get tested together before engaging in sexual activity.[15]
Warnings
- If you have trichomoniasis, it can increase your risk of becoming infected with HIV.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/stdfact-trichomoniasis.htm
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/stdfact-trichomoniasis.htm
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/stdfact-trichomoniasis.htm
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/stdfact-trichomoniasis.htm
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/stdfact-trichomoniasis.htm
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/trichomoniasis/basics/risk-factors/con-20034596
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/trichomoniasis/basics/risk-factors/con-20034596
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/trichomoniasis/basics/risk-factors/con-20034596
- ↑ http://www.emedicinehealth.com/trichomoniasis/page4_em.htm#when_to_seek_medical_care
- ↑ https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/stds-hiv-safer-sex/trichomoniasis
- ↑ http://www.emedicinehealth.com/trichomoniasis/page4_em.htm#when_to_seek_medical_care
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/stdfact-trichomoniasis.htm
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/stdfact-trichomoniasis.htm
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/stdfact-trichomoniasis.htm
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/stdfact-trichomoniasis.htm
About This Article
To recognize trichomoniasis symptoms in men, keep in mind that this is a sexually transmitted disease caused by a microscopic parasite. Make sure to watch for unusual yellowish or grayish discharge from your penis. Additionally, note any burning or swelling in your genitals, especially after urination or ejaculation. You should also take any mild to severe itching around or on the penis seriously, as this could be a symptom of a number of STDs. If you notice any of these symptoms, see your doctor as soon as possible, since trichomoniasis is curable with proper treatment. For more information from our Medical co-author, including how to assess your risk of having trichomoniasis, keep reading!
-Step-1-Version-2.webp)
-Step-2-Version-2.webp)
-Step-3-Version-2.webp)
-Step-4.webp)
-Step-5.webp)
-Step-6.webp)
-Step-7.webp)
-Step-8.webp)
-Step-9.webp)
-Step-10.webp)



-Step-17.webp)

-Step-11-Version-2.webp)




-Step-13.webp)
-Step-9.webp)














































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...