This article was co-authored by Andrew Carberry, MPH. Andrew Carberry is a Food Systems Expert and the Senior Program Associate at the Wallace Centere at Winrock International in Little Rock, Arkansas. He has worked in food systems since 2008 and has experience working on farm-to-school projects, food safety programs, and working with local and state coalitions in Arkansas. He is a graduate of the College of William and Mary and holds a Masters degree in public health and nutrition from the University of Tennessee.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 30 testimonials and 90% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 442,583 times.
Beetroot (also known by its colloquial name, "beet," or beta vulgaris) is a sweet, healthy vegetable loaded with antioxidants. It's actually these antioxidants, packed inside beetroot's red pigments, that contain cancer-preventing and heart-protecting properties. Beetroot is generally easy to grow and is consistently ranked as one of the top 10 vegetables grown in home gardens.
Steps
Planting
-
1Select either seeds or seedlings. These should be readily available from your local nursery or garden center. Don't shy away from seeds – beetroot is notoriously easy to take care of.
- The "Boltardy" variety of beetroot is best if you're sowing early. White and golden varieties take about half as long to grow and don't bleed in salads (the downside being they don't have that beautiful carmine color). Apart from these things, the variety you choose will depend on the look and flavor that appeals to you most.[1]
-
2Select a suitable space for growing. Beetroot likes neutral, moist, fertile soil without too much lime or acidity (pH 6.5-7.0). The soil should be soft and not have too much clay or too much sand; however, since the root develops at the surface, a clay soil can be tolerated if the top has been loosened by the addition of lots of well-rotted organic matter (don't add this unless the soil has much clay). The position needs to be sunny and open but it will tolerate part shade.
- If you have the foresight in late autumn or early spring, it's a good idea to use a general granular fertiliser a few weeks before sowing and rake it into the soil to let the nutrients absorb.
Advertisement -
3Know that you can also grow beetroot in pots. If you're dealing with the round variety (which you probably are – the long, cylindrical varieties are rarely grown), a pot can work just as well, so long as it's at least 20cm (8in) in diameter and at least 20cm (8in) deep.
- Fill the pot up to the top with loose, multi-purpose compost. The seeds should then be sown thinly across the surface and covered with 2cm (0.75in) of compost. Then, when the seedlings reach 2 cm (about an inch) in height, remove the weaker of the seedlings to give the vigorous plants room to grow – aim for about 12cm (5 inches) between seeds.
-
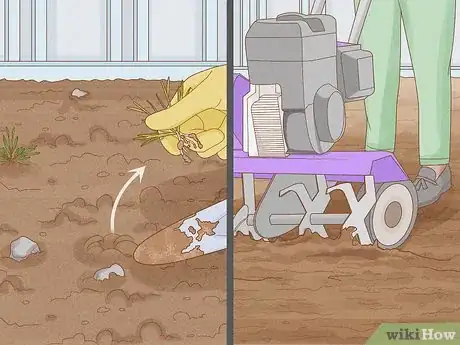
4Till the soil to prepare it. Remove weeds and any other debris, as well as any stones that might impede root growth. The soil only needs tilling to one spade blade of depth. Roughly level the area and rake over the top to loosen.
- If you have heavy soil, it's best prepared in late autumn. If it's lighter, aim for early spring.[2] If you're planting in autumn, leave the top of the soil rough so the winter weather can break it down.
- In the northern hemisphere, sow seeds after the last frost. In the southern hemisphere, sow seeds from September through February.
-
5Sow the seeds or plant the seedlings. Sow your beetroot seeds 2cm (3/4"-1") deep. Keep seeds or seedlings apart at a distance of at least 10 to 15cm (4-6"). It'll be easiest to plant them in rows.
- If you're succession planting, sow beetroot every 14 days for a continuous harvest. This is an easy alternative to succession harvesting.
Nurturing
-
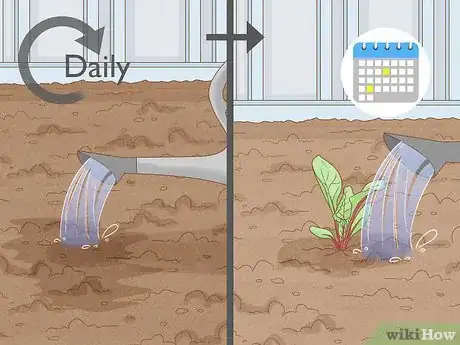
1Water daily until the leaves begin to sprout. At the beginning, your seeds need plenty of water to start the germination process. The roots will take moisture from the soil once they're established.
- That being said, avoid over-watering. This causes beetroot to produce more leaves and less root, risking them "bolting" (flowering and not producing a vegetable). What's more, under-watering creates woody roots.
- Once you have sprouts, only water them every 10-14 days in dry spells.[3] Other than when the weather is unnaturally dry, normal rainfall should be fine.
-
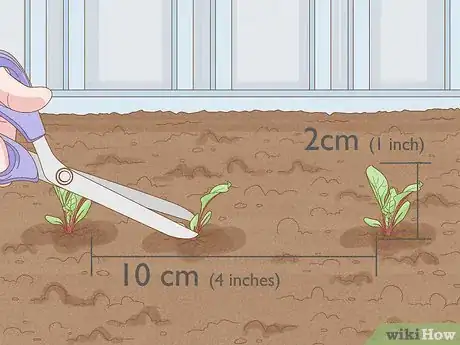
2Thin them out. Once your beetroots have about 2cm (1 inch) of leaves sprouting, cut the weakest seedlings until the remaining plants are at least 10 cm (4 inches) apart.[4] Do not pull them by hand, since this could disturb the roots of neighbouring plants.
-
3Fertilise your plants. Add 4–6 liters (1.1–1.6 US gal) of complete organic fertiliser per 10 square metres of bed. Add a thin layer of compost or well-rotted manure. You may also want to use 30g of high nitrogen fertiliser per square metre if your plants aren't growing well.
- Applying too much nitrogen can cause lots of leafy growth and little root development. If you notice large leaves and smaller roots, reduce fertiliser applications or switch to a fertiliser with lower nitrogen levels.
-
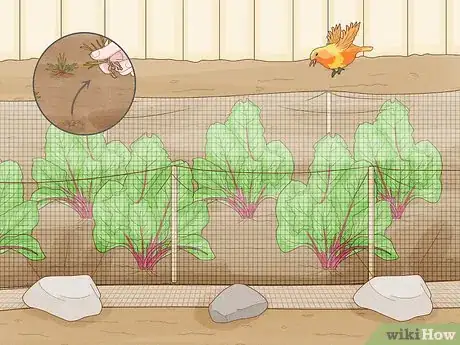
4Watch out for birds and weeds. Depending on your area, you may need to devise some sort of cover for your plants to keep them away from animals. As for weeds, you'll have to take care of those by hand. As soon as you see one cropping up, get rid of it. However, be careful weeding. Avoid using hoes or other sharp objects near the roots or you might cut them. Hand weeding is best.
Harvesting and Storing
-
1Harvest (some of) your plants. When you can start seeing the root, you will have a good idea of its size. The beetroots are ready to harvest when they are approximately the size of a small orange; too large and they won't be as tasty. Do this by holding the top and leveraging the root up with a fork-like tool or spade.
- Generally they're ready around 8 weeks after sowing, or when the veggie reaches 2.5cm (1 inch) in diameter. Many people harvest alternately, picking out some of the beetroots now and leaving others to develop to full maturity. This allows the others to grow bigger more quickly. The ones with a diameter of about 7.5cm (3 inches) usually have the best flavor.
-
2Leave some in the soil for the season. If desired, you can leave some beetroot in the soil until next spring, but you will need to protect it. Cover it in a heavy mulch of hay or straw. Provided the winter cold doesn't go below -18ºC/0ºF, this should allow you to remove the protective layer of straw and dig up more roots through winter.[7]
- Be aware that this can cause the beetroots to develop a woody texture.
-
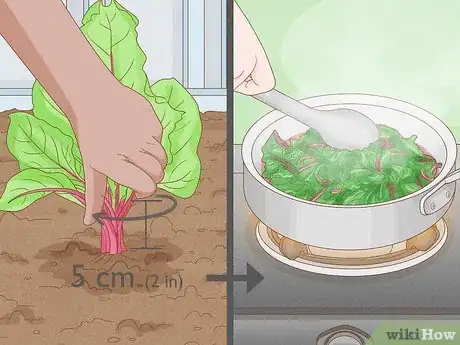
3Be careful with the tops. Do not cut off the leaves; instead, remove them by twisting about 5cm (2") above the crown. This will help prevent bleeding, which takes away from the flavour and colour of the beet.
- This doesn't mean you should throw them away, however. The tops can be saved, cooked, and eaten like spinach. Believe it or not, they usually have loads of flavour.[8]
-
4Store them for later consumption. Root vegetables store well, making them ideal for winter stocking up. Beetroots can be stored layered in sand in wooden boxes in a frost-free, dry environment.
- To do this, take a container and line the bottom with 5 cm (2 inches) of sand. Place in a layer of beets. Then, repeat until the container is full. The sand keeps them from sprouting and keeps their flavours fresh.
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article?
Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionShould I mound up soil around beets like you do with potatoes?
 Andrew Carberry, MPHAndrew Carberry is a Food Systems Expert and the Senior Program Associate at the Wallace Centere at Winrock International in Little Rock, Arkansas. He has worked in food systems since 2008 and has experience working on farm-to-school projects, food safety programs, and working with local and state coalitions in Arkansas. He is a graduate of the College of William and Mary and holds a Masters degree in public health and nutrition from the University of Tennessee.
Andrew Carberry, MPHAndrew Carberry is a Food Systems Expert and the Senior Program Associate at the Wallace Centere at Winrock International in Little Rock, Arkansas. He has worked in food systems since 2008 and has experience working on farm-to-school projects, food safety programs, and working with local and state coalitions in Arkansas. He is a graduate of the College of William and Mary and holds a Masters degree in public health and nutrition from the University of Tennessee.
Food Systems Expert
-
QuestionHow long does it take to grow beetroot?
 Andrew Carberry, MPHAndrew Carberry is a Food Systems Expert and the Senior Program Associate at the Wallace Centere at Winrock International in Little Rock, Arkansas. He has worked in food systems since 2008 and has experience working on farm-to-school projects, food safety programs, and working with local and state coalitions in Arkansas. He is a graduate of the College of William and Mary and holds a Masters degree in public health and nutrition from the University of Tennessee.
Andrew Carberry, MPHAndrew Carberry is a Food Systems Expert and the Senior Program Associate at the Wallace Centere at Winrock International in Little Rock, Arkansas. He has worked in food systems since 2008 and has experience working on farm-to-school projects, food safety programs, and working with local and state coalitions in Arkansas. He is a graduate of the College of William and Mary and holds a Masters degree in public health and nutrition from the University of Tennessee.
Food Systems Expert
-
QuestionCan beetroot survive in a tropical region like Nigeria?
 Community AnswerYes. It does well in and around Oyo state. I presently have beetroot growing on my farm in Ibadan.
Community AnswerYes. It does well in and around Oyo state. I presently have beetroot growing on my farm in Ibadan.
Warnings
- A spell of cold or heat can produce stress-induced white-coloured rings on beetroot ("zoning"). However, the flavour will be unaffected.⧼thumbs_response⧽
Things You'll Need
- Beetroot seeds or seedlings
- Fertilizer
- Neutral, fertile soil
- Gardening tools
References
- ↑ http://www.growingyourownveg.com/how-to-grow/beetroot.html
- ↑ http://www.growingyourownveg.com/how-to-grow/beetroot.html
- ↑ https://www.rhs.org.uk/advice/grow-your-own/vegetables/beetroot
- ↑ http://www.bbc.co.uk/gardening/basics/techniques/growfruitandveg_growingbeetroot1.shtml
- ↑ http://www.growingyourownveg.com/how-to-grow/beetroot.html
- ↑ http://www.growingyourownveg.com/how-to-grow/beetroot.html
- ↑ Carleen Madigan, The Essential Guide to Backyard Self-Sufficiency, p. 68, (2009), ISBN 978-1-60469-103-0
- ↑ http://www.bbc.co.uk/gardening/basics/techniques/growfruitandveg_growingbeetroot1.shtml
About This Article
If you want to grow beetroot, pick a spot with rich, fertile soil that receives plenty of sunlight, although a little shade is okay. Till the soil 3-4 inches deep and remove any weeds, stones, or other debris. Sow your seeds or plant your seedlings after the last frost of the year. Water your plants daily until the leaves begin to sprout, then water them every 10-14 days if the weather is dry, and not at all during periods of normal rainfall. To learn tips from our gardening reviewer on how to thin out your beetroot sprouts, read on!