This article was medically reviewed by Sarah Gehrke, RN, MS. Sarah Gehrke is a Registered Nurse and Licensed Massage Therapist in Texas. Sarah has over 10 years of experience teaching and practicing phlebotomy and intravenous (IV) therapy using physical, psychological, and emotional support. She received her Massage Therapist License from the Amarillo Massage Therapy Institute in 2008 and a M.S. in Nursing from the University of Phoenix in 2013.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 78,436 times.
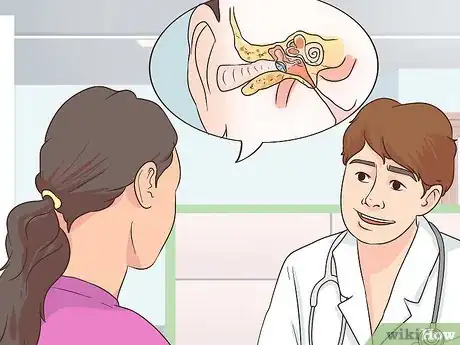
If you’ve ever been on an airplane with a nasal problem and felt your ears need to pop during takeoff or landing, you know how obnoxious (and sometimes even painful) a Eustachian tube blockage can be. Eustachian tubes are tiny passageways in your inner ears that can be blocked by a variety of causes – allergies, sinuses, colds, or even chronic dysfunction. It is quite common in children under 6 years of age. If you (or your child) have painful pressure in your ears, try releasing the pressure by yawning, chewing gum, or gently blowing air through your plugged nose. If your symptoms persist, you may need to try nasal decongestants, nasal washes, or talk to your doctor about surgical possibilities.
Steps
Treating the Blockage on Your Own
-
1Recognize the symptoms of a blockage. Check your symptoms if you think you might have a Eustachian tube blockage in your ears. Some common symptoms of this type of ear problem include:[1]
- Ear popping
- Ringing in the ears
- Feeling of ear fullness
- Mild hearing loss
- Occasional poor balance
-
2Try yawning. This simple exercise is often quite effective at removing Eustachian tube blockage because the muscles used in the movement are quite strong. Yawning can help to equalize the pressure in the middle ear by temporarily opening your Eustachian tubes, which allows the air to flow out of the middle ear.[2]
- You may need to attempt several yawns before you feel the popping motion that indicates a pressure release.
Advertisement -
3Chew gum. Try popping a piece of gum in your mouth and chewing it for a while if you’re having trouble with your Eustachian tubes hurting or feeling clogged. The chewing motion, combined with the swallowing motion, is a great way to naturally get your ears to pop.[3]
- You can also try eating, drinking, or any other activity that promotes a swallowing reflex.
-
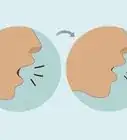
4Blow air through your nose while you hold it shut. Try keeping your mouth shut while you plug your nose with your fingers. Gently blow out through your nose like you would if you were blowing your nose. This will redirect the air to help your ears pop as you hold your nose shut.
- You should hear a small popping sound in your ears that means the blockage of your Eustachian tubes is lessening.
-
1
- Be sure not to blow too hard, as this could cause your eardrum to perforate.
-
2Apply a hot compress. Take a warm face cloth or heating pad (on the low setting) and place it on your face so that it is overlapping your sinus cavities and draping down the side of your face over the clogged ear. You should cover your cheek and eye socket on the side of your face with the blockage. [4]
- Make sure the cloth is not too hot, as this could potentially burn your skin. You might want to consider placing a dry cloth between your skin and the heating pad to protect the skin from burning.
Getting Over-the-Counter Assistance
-
1Use nasal decongestant spray. One of the quickest ways to help your Eustachian tube blockage is to use a spray that is meant to help decongest your nasal cavity. Just remember that this relief will only be temporary, so you will need to continue treating the symptoms until the blockage is gone.[5]
- Try an over-the-counter nasal decongestant spray like Afrin, or a stronger prescription type recommended by your doctor.
- This is a great option if you are trying to clear your Eustachian tubes in a hurry, such as before a flight.
-
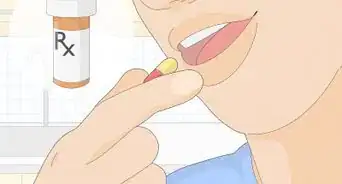
2Take an oral decongestant medication. These types of medications can be quite effective in treating blocked Eustachian tubes. You can find them at your local pharmacy, but they are often regulated. So you will probably have to ask for them specifically and provide the pharmacy with a copy of your identification card when you purchase them.[6]
- Look for ingredients like pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine.
- These kinds of oral decongestants can cause side effects like heart palpitations or a rise in blood pressure.
-
3Use a nasal wash. Nasal washes are intended to help clean out the nasal cavity and remove any possible irritants. As these irritants can often cause problems with the Eustachian tubes, this can be an effective source of treatment for Eustachian tube blockage. To use a nasal wash, tilt your head sideways over a sink and pour the nasal wash solution into the nostril that is closest to the ceiling. The solution will rinse out your nasal cavities and drain out the other nostril into the sink.[7]
- These types of treatments come in the forms of saline rinses, sprays, and neti pots.
Getting Professional Help
-
1Visit your doctor. If you are having trouble clearing a Eustachian tube blockage on your own, consider making an appointment with your doctor. You’ll need to describe your symptoms so your doctor can advise you on the best course of action.
- Be sure to schedule an appointment with your doctor right away if you have a headache that continues for more than a couple days, or if there is pain associated with your Eustachian tube blockage.
-
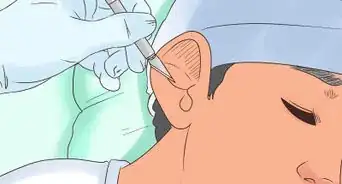
2Consider getting PET tubes. If you have chronic Eustachian tube blockage, you may want to talk to your doctor about the possibility of corrective tubal surgery. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend placing a pressure equalization tube (PET) in your eardrum in a fairly minor surgical procedure.[8]
- This surgery is quite common in young children who have recurrent ear infections because of poor-functioning Eustachian tubes.
-
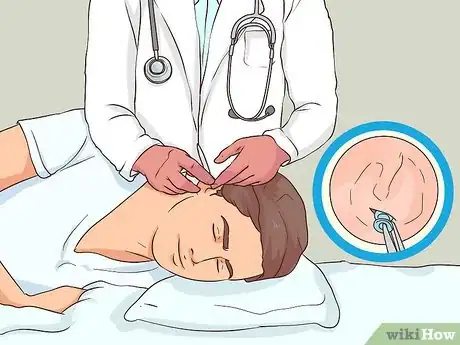
3Get myringotomy. In this minor surgery, your doctor will make a tiny incision in your eardrum that allow access to any fluid that has built up so it can be suctioned out. The incision may need to remain open for a little while to allow the swelling of the Eustachian tube lining to go down.
- Discuss this option with your doctor and decide if it is the right path for your treatment.
References
- ↑ https://www.medicinenet.com/eustachian_tube_problems/article.htm
- ↑ https://myhealth.alberta.ca/Health/Pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=uf9680
- ↑ http://edition.cnn.com/2010/HEALTH/expert.q.a/09/20/ear.drainage.shu/index.html
- ↑ https://myhealth.alberta.ca/Health/Pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=uf9680
- ↑ https://patient.info/health/eustachian-tube-dysfunction/treatment
- ↑ https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/tc/blocked-eustachian-tubes-topic-overview#2
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK262265/
- ↑ https://familydoctor.org/condition/eustachian-tube-dysfunction/








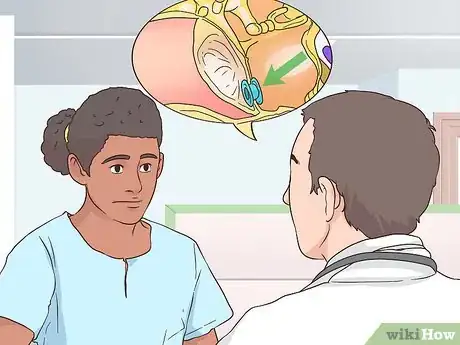





















































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...