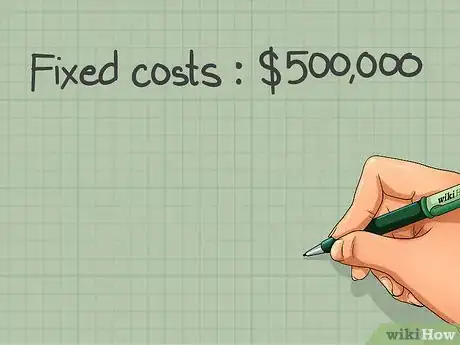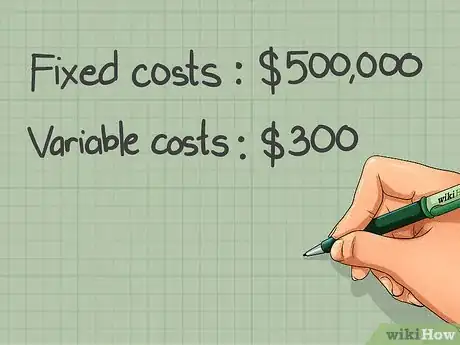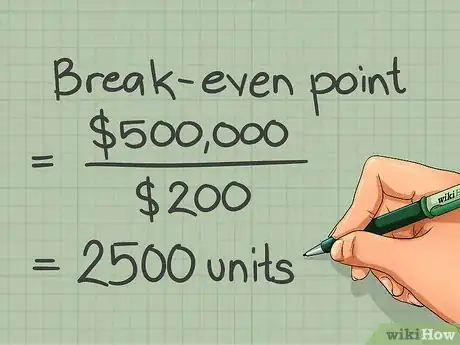X
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 9 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 79,265 times.
Learn more...
The break-even point (BEP) in economics, business, and specifically cost accounting, is the point at which total cost and total revenue are equal: there is no net loss or gain, and one has "broken even." A profit or a loss has not been made, although opportunity costs have been "paid", and capital has received the risk-adjusted, expected return. In short, all costs that needs to be paid are paid by the firm but the profit is equal to 0.[1]
Steps
-
1Determine your company's fixed costs. Fixed costs are any costs that don't depend on the volume of production. Rent and utilities would be examples of fixed costs, because you will pay the same amount for them no matter how many units you produce or sell. Categorize all your firm's fixed costs for a given period and add them together.[2]
-
2Determine your company's variable costs. Variable costs are those that will fluctuate along with production volume. For example, a business that sells shirts will have to purchase more shirts if they want to sell more shirts, so the cost of buying shirts is a variable cost.[3]Advertisement
-
3Determine the price at which you will sell your product. Pricing strategies are part of the much more comprehensive marketing strategy, and can be fairly complex. However, you know that your price will be at least as high as your production costs.[4]
-
4Calculate your unit contribution margin. The unit contribution margin represents how much money each unit sold brings in after recovering its own variable costs. It is calculated by subtracting a unit's variable costs from its sales price.[5]
- Contribution Margin= (Selling price / unit - Variable cost / unit)
-
5Calculate your company's break-even point. The break-even point tells you the volume of sales you will have to achieve to cover all of your costs. It is calculated by dividing all your fixed costs by your product's contribution margin.[6]
- Break Even Point= Total Fixed Cost / Contribution Margin
-
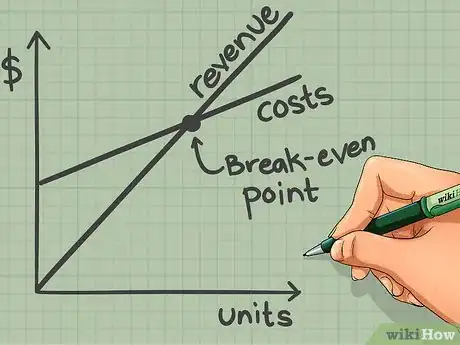
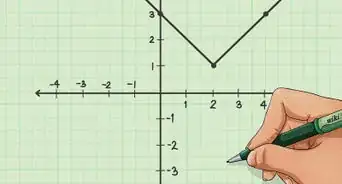
6Plot it on a graph.[7]
- X-axis is 'number of units' and Y-axis is 'revenue'.
- The plot of Fixed cost will be a line parallel to X axis and above the X axis.
- The line of Total cost would start from the point where line of fixed cost meets the Y axis. It would have a positive slope.
- The line of sales revenues would start from origin (0,0) and move upward with a slope greater than that of the total cost line.
- The point where these two lines intersect will be the 'Break Even Point'.
Advertisement
Community Q&A
-
QuestionHow do I calculate total costs and total revenue?
 Ashenoy15Community AnswerTotal cost is fixed cost plus variable cost, while total revenue is the sum of the marginal revenues for each unit.
Ashenoy15Community AnswerTotal cost is fixed cost plus variable cost, while total revenue is the sum of the marginal revenues for each unit. -
QuestionHow can I pick a scale to plot $2024 on 27 units?
 DonaganTop AnswererIf you have 27 units in which to display $2,024, divide 2,024 by 27. That's 74.96. Round up to 75. That means that each unit must represent at least $75.
DonaganTop AnswererIf you have 27 units in which to display $2,024, divide 2,024 by 27. That's 74.96. Round up to 75. That means that each unit must represent at least $75. -
QuestionHow is the profit calculated?
 Community AnswerSubtract total costs from total revenue to get the profit.
Community AnswerSubtract total costs from total revenue to get the profit.
Advertisement
References
- ↑ https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zt2xn39/revision/1
- ↑ https://www.accountingtools.com/articles/what-are-examples-of-fixed-costs.html
- ↑ https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zb2shbk/revision/2
- ↑ https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zb2shbk/revision/2
- ↑ https://openstax.org/books/principles-managerial-accounting/pages/3-1-explain-contribution-margin-and-calculate-contribution-margin-per-unit-contribution-margin-ratio-and-total-contribution-margin
- ↑ https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zb2shbk/revision/2
- ↑ https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zb2shbk/revision/2
About This Article
Advertisement