Chapter 6
Public Opinion
By Boundless

Public opinion or political opinion is the aggregate of individual attitudes or beliefs held by the adult population.
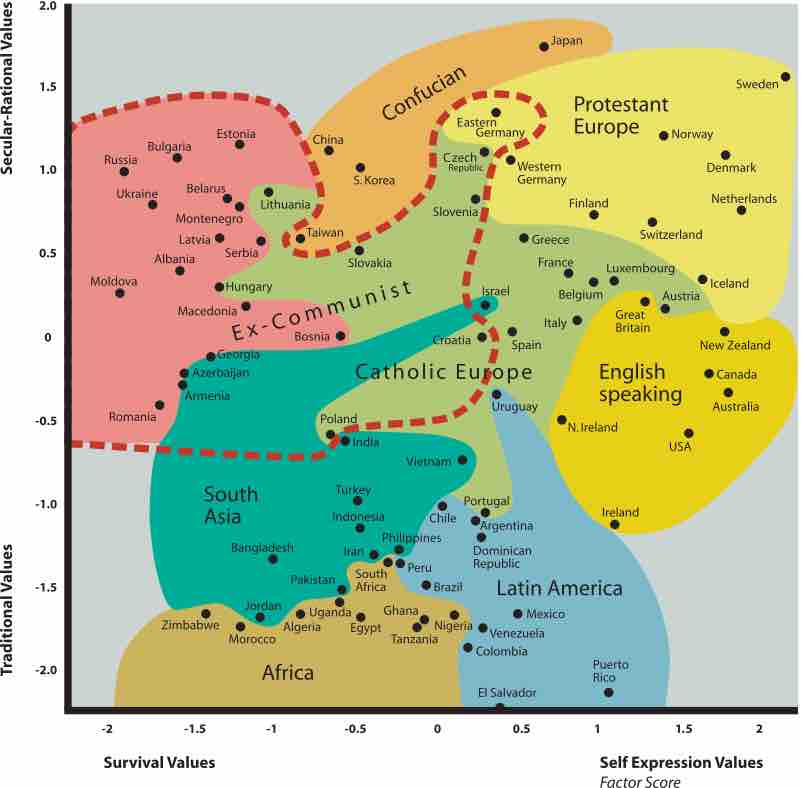
Political cultures have values that are largely shared by their members; these are called political values.

Political dissent refers to any expression designed to convey dissatisfaction with or opposition to the policies of a governing body.

People form political values throughout their life cycle through different agents of political socialization, including family, media, and education.

People learn political values and identities by interacting with other people and the media in a process called political socialization.
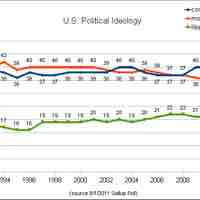
Core American political values general fall in line with one of three political ideologies: liberalism, conservatism, or moderate.
Political socialization experiences differ depending on group membership, such as socioeconomic status, gender, or geography.

People that surround a child during his or her childhood are crucial to the child's development of political values and voting behaviors.

Media can have an important affect on public opinion in several ways.

An opinion leader is an active media user who interprets the meaning of media messages for those less informed about political events.

Political socialization takes place throughout the life cycle, but major life or political events can also impact political values.

Political knowledge, in addition to political socialization and major events, impact the formation of people's political values and opinions.

An opinion poll is a survey of public opinion from a particular sample, and is designed to represent the opinions of a population.

The first known example of an opinion poll was an 1824 local straw poll by The Harrisburg Pennsylvanian for the Jackson Adams race.

Gallup Inc. was founded in 1958, when George Gallup grouped all of his polling operations into one organization.

The American National Election Studies (ANES) is the leading academically run national survey of voters in the United States.

The main types of polls are: opinion, benchmark, bushfire, entrance, exit, deliberative opinion, tracking, and the straw poll.

Steps to conduct a poll effectively including identifying a sample, evaluating poll questions, and selecting a question and response mode.

A very important tool in data analysis is the margin of error because it indicates how closely the results of the survey reflect reality.

Sampling is concerned with choosing a subset of individuals from a statistical population to estimate characteristics of a whole population.
Polling organization will lose credibility if they publish inaccurate results.
Problems with polls typically stem either from issues with the methodology that bias the sample or the responses that cause the bias.
Internet and telephone polls are very useful as they are much cheaper than most other polls and are able to reach a wide population.