Internet polls
Online polls are becoming an essential research tool for a variety of research fields, including marketing and official statistics research.
Advantages of Internet Surveys
Web polls are faster, simpler, and cheaper than many other polling methods. However, lower costs are not so straightforward in practice, as they are strongly interconnected to errors. Because response rate comparisons to other survey modes are usually not favorable for online surveys, efforts to achieve a higher response rate may substantially increase costs. Additionally, the entire data collection period is significantly shortened, as all data can be collected and processed in typically little more than a month.
Interaction between the respondent and the questionnaire is also more dynamic compared to e-mail or paper surveys. Online surveys are also less intrusive, and they suffer less from social desirability effects. Questions with long lists of answer choices can be used to provide immediate coding of answers to certain questions that are usually asked in an open-ended fashion in paper questionnaires. Finally, online surveys can be tailored to the situation (the questionnaire may be preloaded with already available information).
Methodological Issues of Online Surveys
Sampling
The difference between probability samples (where the inclusion probabilities for all units of the target population is known in advance) and non-probability samples (which often require less time and effort but generally do not support statistical inference) is crucial. Probability samples are highly affected by problems of non-coverage (not all members of the general population have Internet access) and frame problems (online survey invitations are most conveniently distributed using e-mail, but there are no e-mail directories of the general population that might be used as a sampling frame). Because coverage and frame problems can significantly impact data quality, they should be adequately reported when disseminating the research results.
Invitations to Online Surveys
Due to the lack of sampling frames, many online survey invitations are published in the form of an URL link on web sites or in other media, which leads to sample selection bias that is out of research control and to non-probability samples. Traditional solicitation modes, such as telephone or mail invitations to web surveys, can help overcoming probability sampling issues in online surveys. However, such approaches are faced with problems of dramatically higher costs and questionable effectiveness.
Non-response
Online survey response rates are generally low and also vary extremely. In addition to refusing participation, terminating surveying during the process, or not answering certain questions, several other non-response patterns can be observed in online surveys, such as lurking respondents and a combination of partial and item non-response. Response rates can be increased by offering monetary or some other type of incentive to the respondents, by contacting respondents several times, and by keeping the questionnaire difficulty as low as possible.
Questionnaire Design
The use of design features should be limited to the extent necessary for respondents to understand questions or to stimulate the response. The features should not affect their response as that would mean lower validity and reliability of data.
It is important that uncontrolled variations in how a questionnaire appears are minimized. Web-based survey methods make the construction and delivery of questionnaire instruments relatively easy, but what is difficult to ensure is that everyone sees the questionnaire as its designer intended it to be. This problem can arise due to the variability of software and hardware used by respondents.
Telephone Polling
An important aspect of telephone polling is the use of interviewers. Interviewers encourage sample persons to respond, leading to higher response rates and interviewers may increase comprehension of questions by answering respondents' questions.
Telephone polling is also fairly cost efficient, depending on local call charge structure, which makes it good for large national (or international) sampling frames .
However, there are some disadvantages to telephone polling. For instance, there is some potential for interviewer bias (e.g. some people may be more willing to discuss a sensitive issue with a female interviewer than with a male one), telephone polling cannot be used for non-audio information (graphics, demonstrations, taste/smell samples), and it is unreliable for consumer surveys in rural areas where telephone density is low .
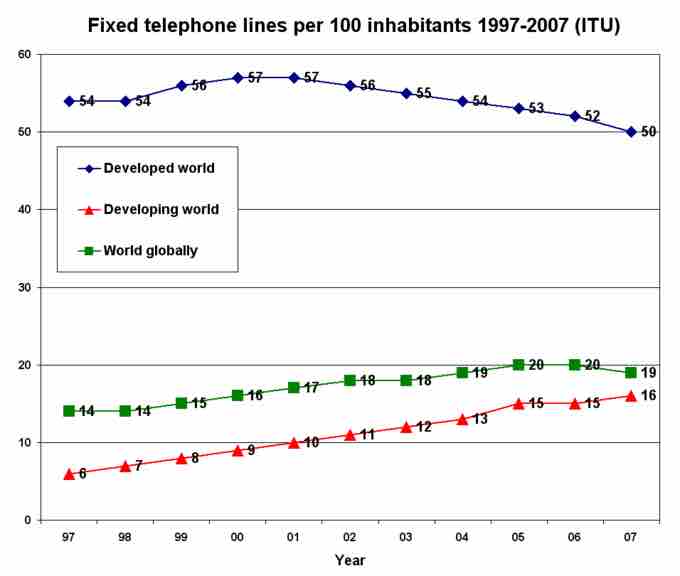
Number of fixed telephone lines globally
This chart shows the numbers of fixed telephone lines from 1997 to 2007.
There are three main types of telephone polling: traditional telephone interviews, computer assisted telephone dialing, and computer assisted telephone interviewing ( CATI ).