Chapter 1
American Politics
By Boundless
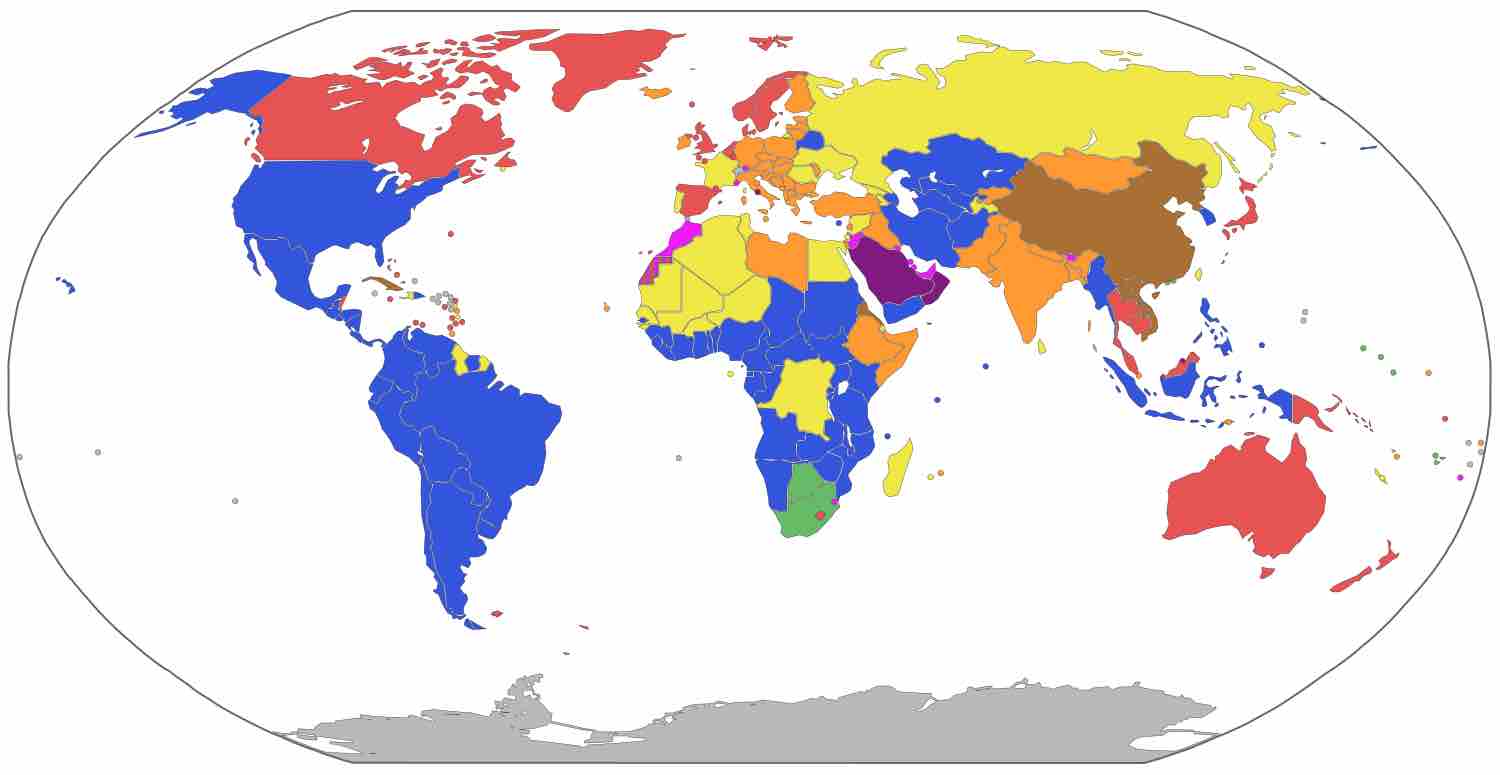
Forms of government are categorized by the power source and power structure of any given state.

Democracy is a form of government in which all eligible citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives.

Unlike democracy, authoritarianism and totalitarianism are forms of government where an individual or a single-party concentrates all power.

Some nondemocratic governments can be classified into categories such as monarchies, oligarchies, theocracies and technocracies.

From the political economy to political philosophy, politics determines "who gets what, when, and how" for all citizens.
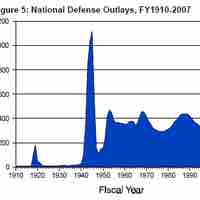
One of the most important functions of the U.S. government is to provide common defense and security for its citizens.

As the third branch of government, the judiciary is the system of courts that interprets and applies the law in order to mete out justice.
In many constitutions, the general welfare clause has been used as a basis for promoting the well-being of the governed people.
The legal system provides a structure for the resolution of many disputes, including litigation, arbitration, mediation, and conciliation.

A public service is a service that is provided by government to people living within its territory and considered essential to modern life.
The United States is a diverse country, racially and ethnically, with over six races officially recognized by the U.S. Census Bureau.
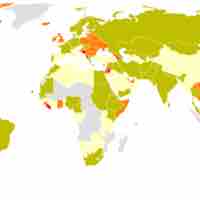
Immigration has been a pivotal source for change in the social, economic and political makeup of the U.S.

Liberty, the ability of individuals to have control over their lives, is a central aspect of modern political philosophy.

Equality refers to a state of affairs in which all people within a specific society or group have the same status.
Democracy is a form of government in which all eligible citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives.

Popular consent, majority rule, and popular sovereignty are related concepts that form the basis of democratic government.

Individualism is a philosophy that stresses the value and rights of the individual vis-a-vis society and government.
Freedom of religion is a principle that allows an individual or community to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship, and observance.

Conservatism is a social and political philosophy that supports retaining traditional social institutions and has many modern variations.

Liberalism is a broad political ideology or worldview founded on the ideas of liberty and equality.
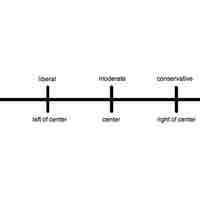
The traditional political spectrum models different political positions by placing them upon a left-right geometric axis.
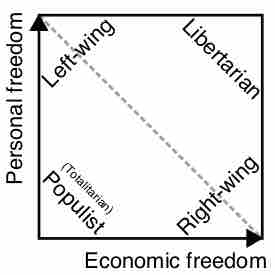
Researchers have frequently noted that a single left-right axis is insufficient to describe the existing variation in political beliefs.