Section 5
Cranial Nerves
By Boundless
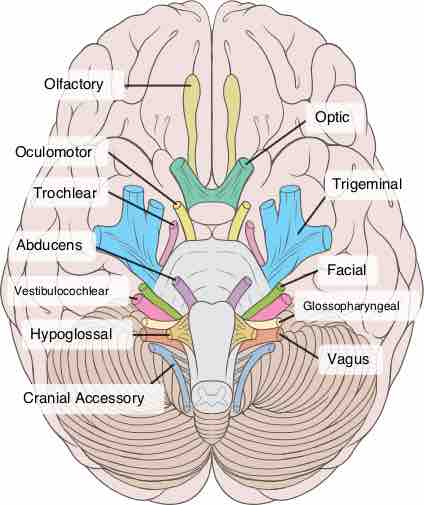
The peripheral nervous system has 12 pairs of cranial nerves that control much of the motor and sensory functions of the head and neck.
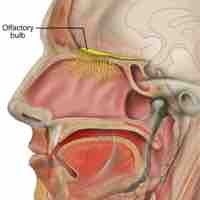
The olfactory nerve, or cranial nerve I, is the first of 12 cranial nerves and is responsible for the sense of smell.
The optic nerve (cranial nerve II) receives visual information from photoreceptors in the retina and transmits it to the brain.
The oculomoter nerve (cranial nerve III) controls eye movement, such as constriction of the pupil and open eyelids.
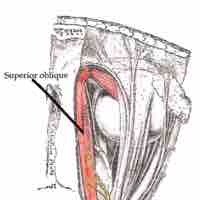
The trochlear nerve (cranial nerve IV) is a motor nerve that innervates a single muscle: the superior oblique muscle of the eye.
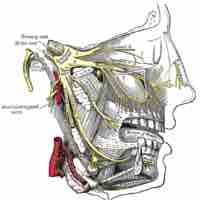
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve and it is responsible for sensation and motor function in the face and mouth.
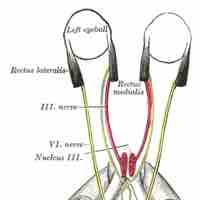
The abducens nerve (cranial nerve VI) controls the lateral movement of the eye through innervation of the lateral rectus muscle.
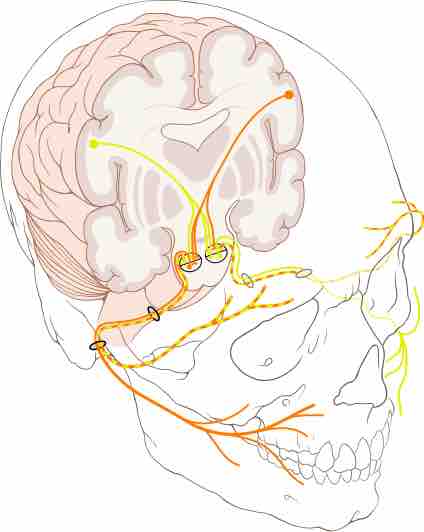
The facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) determines facial expressions and the taste sensations of the tongue.
The vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII) carries information about hearing and balance.
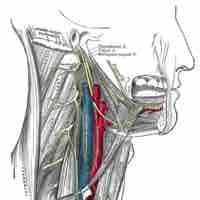
The glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve IX) serves many distinct functions, including providing sensory innervation to various head and neck structures.
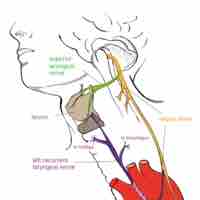
The vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) is responsible for parasympathetic output to the heart and visceral organs.
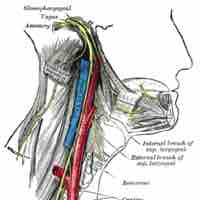
The accessory nerve (cranial nerve XI) controls the muscles of the shoulder and neck.
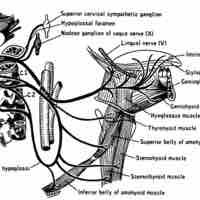
The hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII) controls the muscles of the tongue.