The human eye is the gateway to one of our five senses. The human eye is an organ that reacts with light. It allows light perception, color vision, and depth perception, but not all eyes are perfect. A normal human eye can see about 10 million different colors!
Properties
Contrary to what you might think, the human eye is not a perfect sphere, but is made up of two differently shaped pieces, the cornea and the sclera. These two parts are connected by a ring called the limbus. The part of the eye that is seen is the iris, which is the colorful part of the eye. In the middle of the iris is the pupil, which is the black dot that changes size. The cornea covers these elements, but it is transparent. The fundus is on the opposite of the pupil, but inside the eye and cannot be seen without special instruments. The optic nerve is what conveys the signals of the eye to the brain. shows a diagram of the eye.
Vision
The different parts of the eye have different refractive indexes, and this is what bends the rays to form an image. The cornea provides two-thirds of the power to the eye. The lens provides the remaining power. The image passes through several layers of the eye, but this happens in a way very similar to that of a convex lens. When the image finally reaches the retena, it is inverted, but the brain will correct this . For the vision to be clear, the image has to be formed directly on the retina. The focus needs to be changed, much like a camera, depending on the distance and size of the object. The eye's lens is flexible, and changes shape. This changes the focal length. The eye's ciliary muscles control the shape of the lens. When you focus on something, you squeeze or relax these muscles.
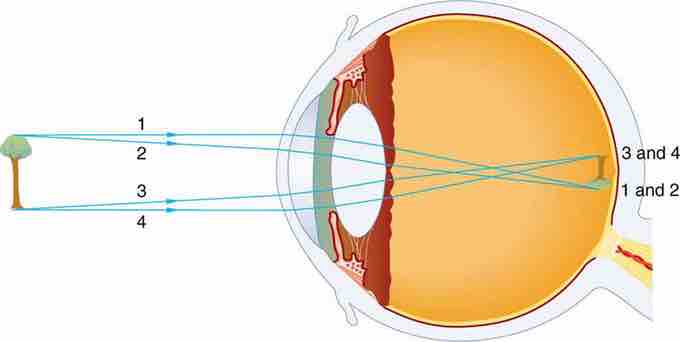
Vision Diagram
An image is formed on the retina with light rays converging most at the cornea and upon entering and exiting the lens. Rays from the top and bottom of the object are traced and produce an inverted real image on the retina. The distance to the object is drawn smaller than scale.
Near Sighted Vision
Nearsightedness, or myopia is a vision defect that occurs when the focus of the image is in front of the retina. This is shown in . Close objects are seen fine, but distant objects are blurry. This can be corrected by placing diverging lenses in front of the eye. This will cause the light rays to spread out before they enter the eye.
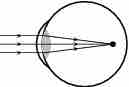
Near Sighted Vision
This occurs when the image is formed before the retina
Far Sighted Vision
Farsightedness, or hyperopia, is a vision defect that occurs when the focus of the image is behind the retina. This is shown in . Distant objects are seen fine, but closer objects are blurry. This can be corrected by placing converging lenses in front of the eye. This will cause the light rays to slightly converge together before they enter the eye.

Far Sighted Vision
This occurs when the image is formed behind the retina