Chapter 2
Kinematics
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Physics
Physics
by Boundless
Section 1
Basics of Kinematics

Defining Kinematics
Kinematics is the study of the motion of points, objects, and groups of objects without considering the causes of its motion.
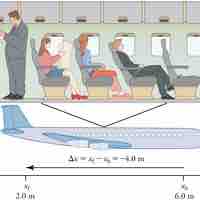
Reference Frames and Displacement
In order to describe an object's motion, you need to specify its position relative to a convenient reference frame.
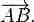
Introduction to Scalars and Vectors
A vector is any quantity that has both magnitude and direction, whereas a scalar has only magnitude.
Section 2
Speed and Velocity
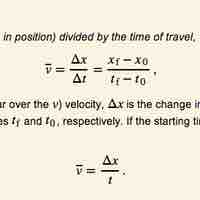
Average Velocity: A Graphical Interpretation
Average velocity is defined as the change in position (or displacement) over the time of travel.
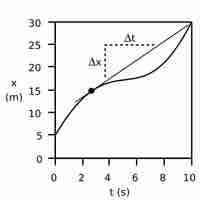
Instananeous Velocity: A Graphical Interpretation
Instantaneous velocity is the velocity of an object at a single point in time and space as calculated by the slope of the tangent line.
You are in this book
Boundless Physics
by Boundless