TORCH complex is a medical acronym for a set of perinatal infections (which are infections passed from a pregnant woman to her fetus). TORCH infections can lead to severe fetal anomalies or even fetal loss. They are a group of viral, bacterial, and protozoan infections that gain access to the fetal bloodstream through the placenta via the chorionic villi. Haematogenous transmission may occur at any time during gestation or occasionally at the time of delivery via maternal-to-fetal transfusion . The TORCH panel is used to screen for certain infectious diseases that can cause birth defects in a baby if the mother contracts them during the pregnancy. The TORCH panel of tests acronym spells out as follows:
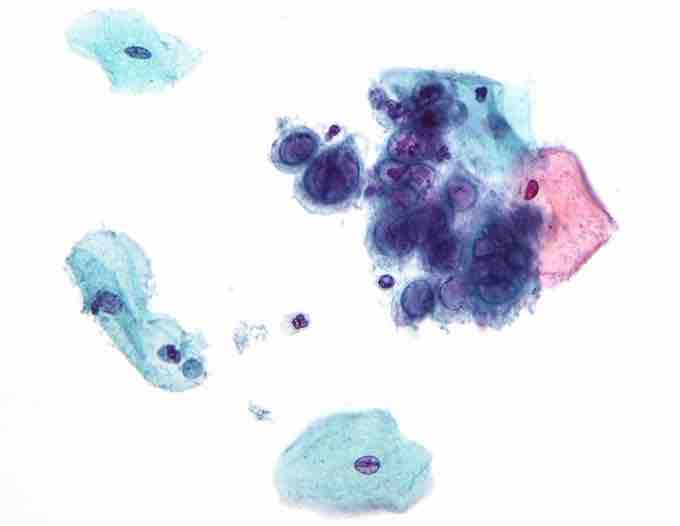
Herpes Simplex Virus
Micrograph of a pap test showing changes (upper-right of image) associated with Herpes Simplex Virus, a TORCH infection.
- T – Toxoplasmosis / Toxoplasma gondii
- O – Other infections
- R – Rubella
- C – Cytomegalovirus
- H – Herpes simplex virus
The "other infections" included under the letter O include Coxsackievirus, Syphilis, Varicella-Zoster Virus, HIV, and Parvovirus B19. Hepatitis B is also sometimes included among "other infections," but Hepatitis B is a large virus and does not cross the placenta, hence it cannot infect the fetus unless there have been breaks in the maternal-fetal barrier, such as can occur due to bleeding during childbirth or during amniocentesis.
TORCH infections cause a syndrome characterized by microcephaly, sensorineural deafness, chorioretinitis, hepatosplenomegaly, and thrombocytopenia. Symptoms of a TORCH infection may include fever and difficultly feeding. The newborn is often small for their gestational age. A petechial rash on the skin may be present, with small reddish or purplish spots due to bleeding from capillaries under the skin. An enlarged liver and spleen (hepatosplenomegaly) is common, as is jaundice. However, jaundice is less common in Hepatitis B because a newborn's immune system is not developed well enough to mount a response against liver cells, as would normally be the cause of jaundice in an older child or adult. Hearing impairment, eye problems, mental retardation, autism, and death can be caused by TORCH infections. The TORCH panel is valuable for checking for infections because the mother often has a mild infection with few or no symptoms. It is also possible for genetic conditions (such as Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome) to present in a similar manner.
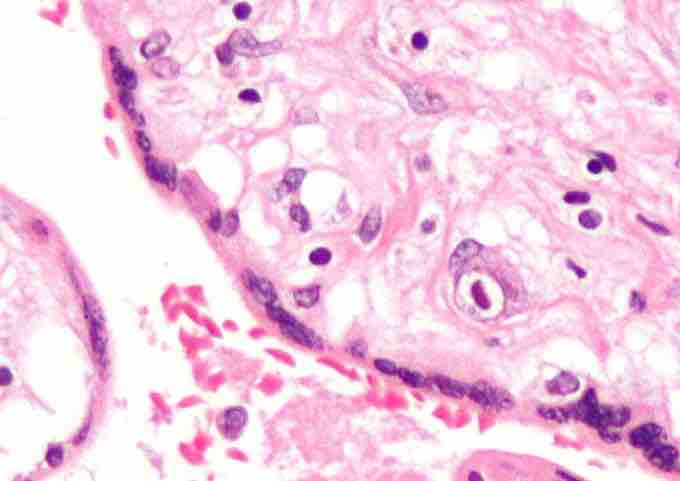
Cytomegalovirus infection
Hematoxylin and Eosin stain showing cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection of the placenta (CMV placentitis), a TORCH infection. The characteristic large nucleus of a CMV infected cell is seen off-center at the bottom-right of the image.