Chapter 1
Introduction to Management
By Boundless

Management is the act of engaging with an organization's human talent and its resources to accomplish desired goals and objectives.
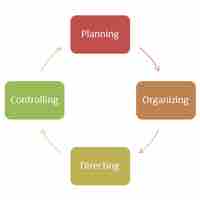
Management organizes by creating patterns of relationships among workers, optimizing use of resources to accomplish business objectives.
Management control can be defined as a systematic effort to compare performance to predetermined standards and address deficiencies.

Managers lead their organizations and can vary their style and approach to achieve the desired outcome.

Planning is the process of thinking about and organizing the activities required to achieve strategic objectives.
Top-level managers determine broad strategic strokes for the organization in general, and focus on the big picture.
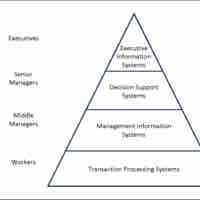
Middle management is the intermediate management level accountable to top management and responsible for leading lower level managers.
Frontline management balances functional expertise with strong interpersonal skills to optimize specific operational processes.
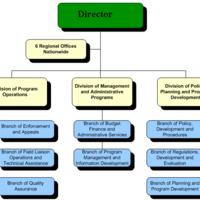
General managers focus on the entire business, while functional managers specialize in a particular unit or department.

Managers must adjust their management style to fit the type of organization.

Being accountable simply means being responsible for decisions made, actions taken, and assignments completed.

Management roles are defined by the capacity to motivate and leverage human capital in the organization to achieve efficiency in operations.
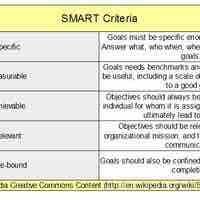
Performance standards motivate employees and management to use their time efficiently by setting achievable objectives.
Career success and fulfillment hinge on effective human-resource management and empowering employees with the necessary tools and skills.
Mintzberg defined ten management roles within three categories: interpersonal, informational, and decisional.
Agendas help to organize, prioritize, and facilitate discussion about a given set of points in an organizational pursuit.
Successful managers must possess certain technical skills that assist them in optimizing managerial performance.
Conceptual skills revolve around generating ideas through creative intuitions and a comprehensive understanding of a given context.

A manager must be both analytical and personable when it comes to managing time, resources, and personnel.

Experiential learning is the process of making meaning from direct experience.
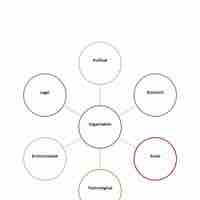
The PESTEL framework highlights six critical factors for management to consider when approaching the general business environment.
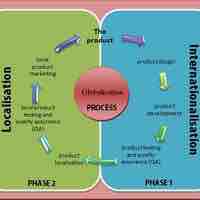
Globalization is the international integration of intercultural ideas, perspectives, products/services, culture, and technology.
Ethics is at the core of corporate governance, and management must reflect accountability for their actions on a global community scale.
Globalization demands a diverse workforce, and assimilating varying cultures, genders, ages, and dispositions is of high value.
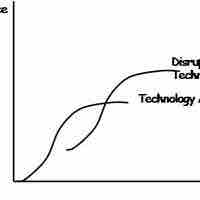
Technology management is crucial in offsetting the risks of new technology while acquiring the operational benefits it provides.

Managers must understand a company's competitive advantage and build a strategy that takes into account the competitive landscape.