Chapter 16
Taxes and Public Finance
By Boundless
On a general level, tax collections provide a revenue source to support the outlays or primary activities of a government.
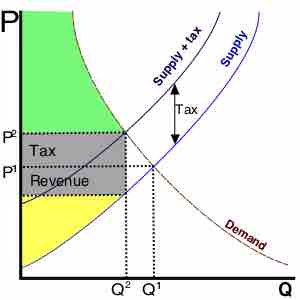
In economics, deadweight loss is a loss of economic efficiency that can occur when equilibrium for a good or service is not Pareto optimal.
Taxes can be evaluated based on an average impact or a marginal impact and can be categorized as progressive, regressive, or proportional.

Tax incidence is the analysis of the effect of a particular tax on the distribution of economic welfare.
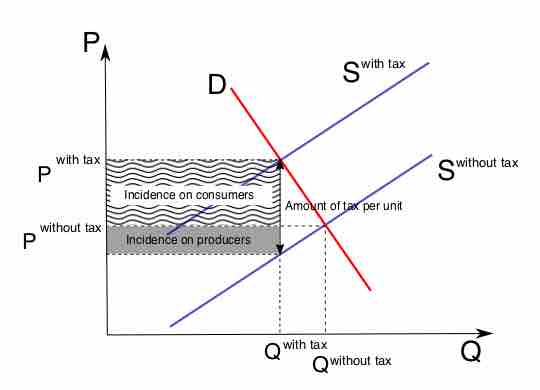
Tax incidence or tax burden does not depend on where the revenue is collected, but on the price elasticity of demand and price elasticity of supply.
Taxes may be considered equitable if they are administered in accordance with the definition of either horizontal or vertical equity.
- Sources of Inefficiency
