The cross-price elasticity of demand shows the relationship between two goods or services. More specifically, it captures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of one good to a change in price of another good. Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand (EA,B) is calculated with the following formula:
The cross-price elasticity may be a positive or negative value, depending on whether the goods are complements or substitutes. If two products are complements, an increase in demand for one is accompanied by an increase in the quantity demanded of the other. For example, an increase in demand for cars will lead to an increase in demand for fuel. If the price of the complement falls, the quantity demanded of the other good will increase. The value of the cross-price elasticity for complementary goods will thus be negative .
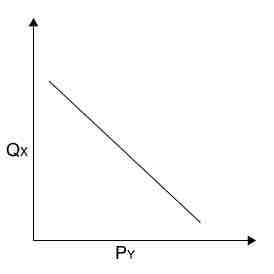
Complements
Two goods that complement each other have a negative cross elasticity of demand: as the price of good Y rises, the demand for good X falls.
A positive cross-price elasticity value indicates that the two goods are substitutes. For substitute goods, as the price of one good rises, the demand for the substitute good increases. For example, if the price of coffee increases, consumers may purchase less coffee and more tea. Conversely, the demand for a substitute good falls when the price of another good is decreased. In the case of perfect substitutes, the cross elasticity of demand will be equal to positive infinity .
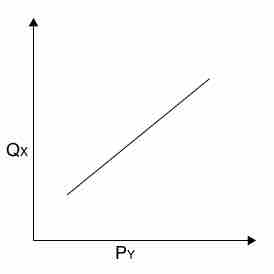
Substitutes
Two goods that are substitutes have a positive cross elasticity of demand: as the price of good Y rises, the demand for good X rises.
Two goods may also be independent of each other. In this instance, if the price of one good changes, demand for the other good will stay constant. For independent goods, the cross-price elasticity of demand is zero : the change in the price of one good with not be reflected in the quantity demanded of the other.
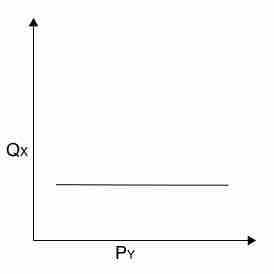
Independent
Two goods that are independent have a zero cross elasticity of demand: as the price of good Y rises, the demand for good X stays constant.