Identifying with the listeners
Step in to the minds of your listeners and see if you can identify with them. A successful speaker engages in perspective-taking. While preparing her speech, the speaker steps outside her own perceptual framework to understand the world as it is perceived by members of the audience. When the speaker takes an audience-centered approach to speech preparation, she focuses on the audience and how it will respond to what is being said. In essence, the speaker wants to mentally adopt the perspective of members of the audience in order to see the world as the audience members see it.
Encoding and Decoding
The speaker engages a process of encoding his or her ideas from thoughts into words, and of forming a message which is then delivered to an audience. The audience members then attempt to decode what the speaker is saying so that they can understand it. To better imagine this process, consider the example of encoding and decoding as it applies to the idea of a tree. I know that my audience is in New England and that they are familiar with oak trees . I use the word tree to encode my idea, and because my audience has experienced similar trees, they decode the word tree in the way that I intended . However, I may be thinking about a tree (a palm tree) that is in Hawaii, where I used to live, when I use the word tree to encode my idea. Unfortunately, when my audience decodes my word now, they are still thinking about the oak tree and will not see my palm tree. The audience no longer shares my perspective of the world or my experience with trees.
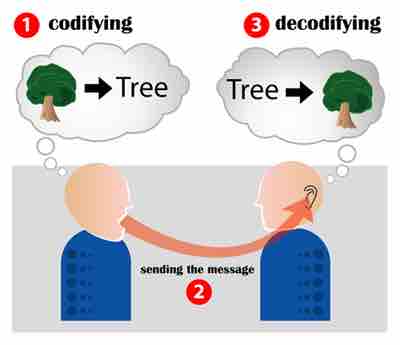
Encoding communication
Encoding and decoding a simple word picture
Finding Common Ground
The more you find out about your audience, the more you can adapt your message to the interests, values, beliefs, and language level of the audience. Once you collect data about your audience, you are ready to summarize your findings and select the language and structure that is best suited to your particular audience. You are on a journey to find common ground in order to identify with your audience. One of the most useful strategies for adapting your topic and message to your audience is to use the process of identification . What do you and your audience have in common? And, conversely, how are you different? What ideas or examples in your speech can your audience identify with?
Creating a Theoretical, Imagined Audience
Create a theoretical, imagined situation to test your view of an audience for practice. You can use your analysis to create what is called a "theoretical, universal audience. " The universal audience is an imagined audience that serves as a test for the speaker. Imagine in your mind a composite audience that contains individuals from the diverse backgrounds you have discovered in your audience analysis. Next, decide whether or not the content of your speech would appeal to individuals within that audience. What words or examples will the audience understand and what will they not understand? What terms about your subject will you need to define or explain for this audience? How different are the values and opinions you want your audience to accept from the present attitudes and beliefs they may hold?
Tips for the Speaker
In summary, use your knowledge of the audience to adapt your speech accordingly. Adopt the perspective of the audience in order to identify with them, and test out your ideas with an imagined audience composed of people with the background you have discovered through your research.