Section 1
Derivatives
By Boundless
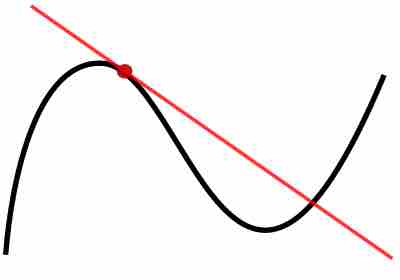
The use of differentiation makes it possible to solve the tangent line problem by finding the slope
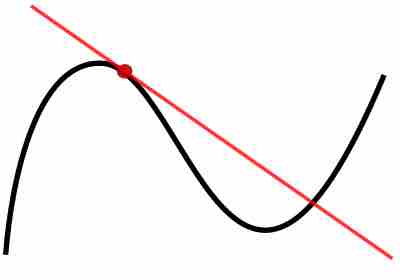
Differentiation is a way to calculate the rate of change of one variable with respect to another.
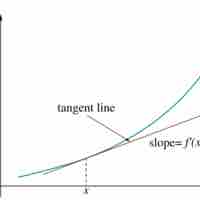
If every point of a function has a derivative, there is a derivative function sending the point

The rules of differentiation can simplify derivatives by eliminating the need for complicated limit calculations.
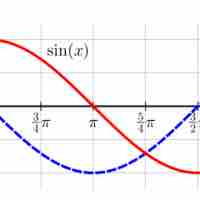
Derivatives of trigonometric functions can be found using the standard derivative formula.

The chain rule is a formula for computing the derivative of the composition of two or more functions.
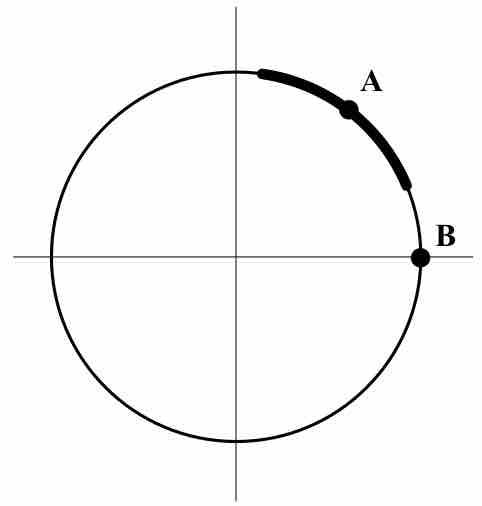
Implicit differentiation makes use of the chain rule to differentiate implicitly defined functions.
Differentiation, in essence calculating the rate of change, is important in all quantitative sciences.
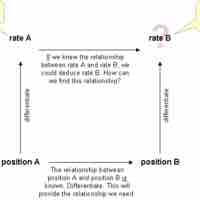
Related rates problems involve finding a rate by relating that quantity to other quantities whose rates of change are known.
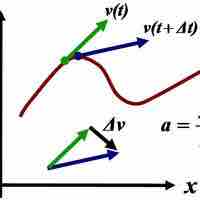
The derivative of an already-differentiated expression is called a higher-order derivative.