In economics, competition is the rivalry among sellers trying to achieve such goals as increasing profits, market share, and sales volume by varying the elements of the marketing mix: price, product, distribution, and promotion. Merriam-Webster defines competition in business as "the effort of two or more parties acting independently to secure the business of a third party by offering the most favorable terms. " It was described by Adam Smith in The Wealth of Nations (1776) and later economists as allocating productive resources to their most highly-valued uses and encouraging efficiency. Smith and other classical economists before Cournot were referring to price and non-price rivalry among producers to sell their goods on best terms by the bidding of buyers, and not necessarily to a large number of sellers or to a market in final equilibrium.
Competitive-based pricing, or market-oriented pricing, involves setting a price based upon analysis and research compiled from the target market . With competition pricing, a firm will base what they charge on what other firms are charging. This means that marketers will set prices depending on the results from their research. For instance, if the competitors are pricing their products at a lower price, then it's up to them to either price their goods at a higher or lower price, all depending on what the company wants to achieve.
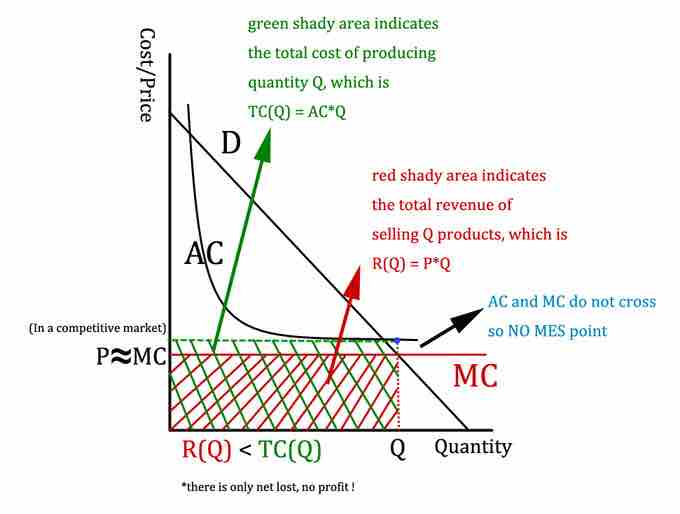
Competitive Market Pricing
Status-quo pricing, also known as competition pricing, involves maintaining existing prices or basing prices on what other firms are charging.
One advantage of competitive-based pricing is that it avoids price competition that can damage the company. Disadvantages include that businesses have to attract customers in other ways, since the price will not grab the customer's interest. The price may also barely cover production costs, resulting in low profits.