Is the Pay Fair?
Imagine that see a job posted on the internet. It reads, "Office Assistant wanted, starting at $8.00 an hour." How did the manager decide to pay $8.00 per hour? Why did he or she decide that was fair? In this subchapter, we will cover the two types of "fairness" important in designing a base pay system.
Internal Equity
The first consideration is that the base pay system needs to be internally equitable: the amount of base pay assigned to jobs needs to reflect the relative contribution of each job to the company's business objectives . In determining this, the manager should ask, "How does the work of the office assistant described above compare with the work of the office manager?" Another question to be asked is, "Does this worker contribute to solutions for customers more than another?"
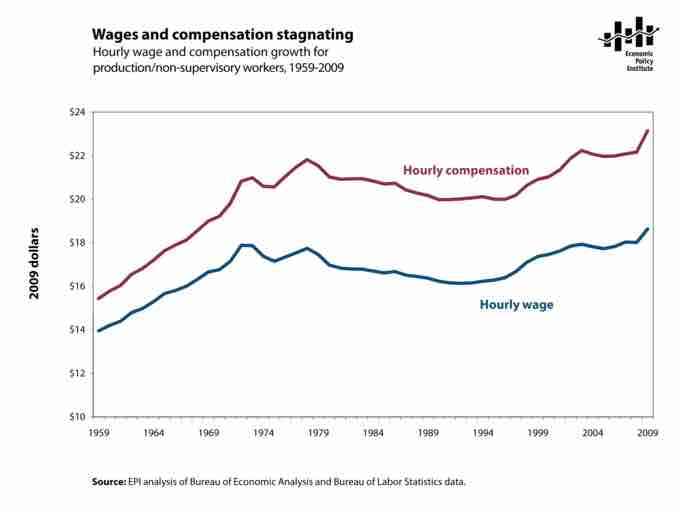
Hourly wage and compensation growth for production/non-supervisory workers, 1959-2009
This graph shows that compensation and wages have been more or less stagnant since the 1970's.
Internal equity implies that pay rates should be the same for jobs where the work is similar and different for jobs where the work is dissimilar. Compensation specialists use two tools to help make these decisions: job analysis and job evaluation.
What is Job Analysis?
A job analysis is a systematic method to discover and describe the differences and similarities among jobs. A good job analysis collects sufficient information to adequately identify, define, and describe the content of a job. Since job titles may be misleading (for example, "systems analyst" does not reveal much about the job) the content of the job is more important to the analysis than the title.
In general, a typical job analysis attempts to describe the following:
- skill (the experience, training, education, and ability required by the job);
- effort (the degree of effort actually expended in performing the job);
- responsibility (the degree of accountability required in the performance of a job); and
- working conditions of each job (the physical surroundings and hazards of a job, including dimensions such as inside versus outside work, heat, cold, and poor ventilation).
What is a Job Evaluation?
A job evaluation is a process that takes the information gathered by the job analysis and places a value on the job. It is the process of systematically determining the relative worth of jobs based on a judgment of each job's value to the organization. The most commonly used method of job evaluation in the United States and Europe is the "point method." The point method consists of three steps:
- defining a set of compensable factors;
- creating a numerical scale for each compensable factor; and
- weighting each compensable factor.
Each job's relative value is determined by the total points assigned to it . The result of the job analysis and job evaluation processes will be a pay structure or queue in which jobs are ordered by their value to the organization.
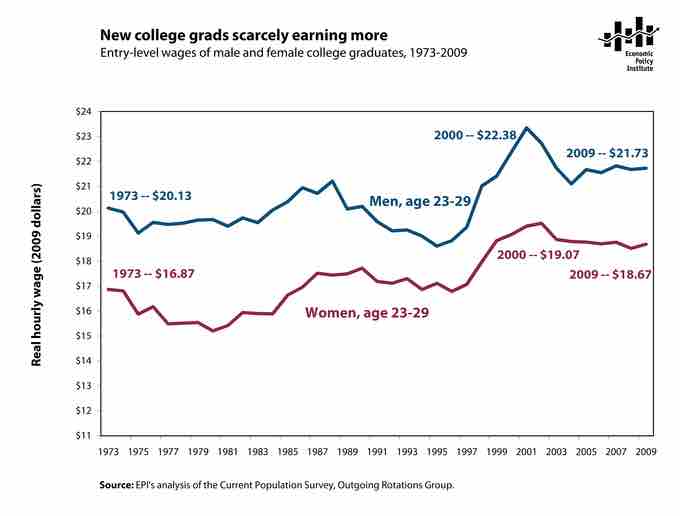
Entry Level Wages for College Graduates, 1973-2009
New college graduates are scarely earning more than they did a few decades ago.
External Equity
"External equity" refers to the relationship between one company's pay levels in comparison to what other employers pay. Some employers set their pay levels higher than their competition, hoping to attract the best applicants. This is called "leading the market."
Other employers set their pay levels lower than their competition, hoping to save labor costs. This is called "lagging the market." The risk in lagging the market is that the company will be unable to attract the best applicants.
Most employers set their pay levels the same as their competition. This is called "matching the market." Matching the market maximizes the quality of talent while minimizing labor costs. An important question in external equity is how you define your market. Traditionally, markets can be defined in one of three ways:
- By identifying companies who hire employees with the same occupations or skills
- By identifying companies who operate in the same geographic area
- By identifying direct competitors, that is, those companies who produce the same products and services.
Once you have defined your market, the next step is to survey the compensation paid by employers in your market.
Combining Internal and External Equity
How do companies combine internal and external equity to decide the pay associated with each job?
- First, they analyze the content of each job.
- Second, they assess the value each job contributes to the company.
- Third, they price each job in the market.
- Finally, they look at the relationship between what they value internally and what the market values externally.
By following each of these steps, a company will have a fair base pay system, which will lead to attracting and retaining the best employees.