Collective Bargaining Defined
Collective bargaining is a process of negotiation between employers and a group of employees aimed at reaching an agreement that regulates working conditions .
Collective Bargaining
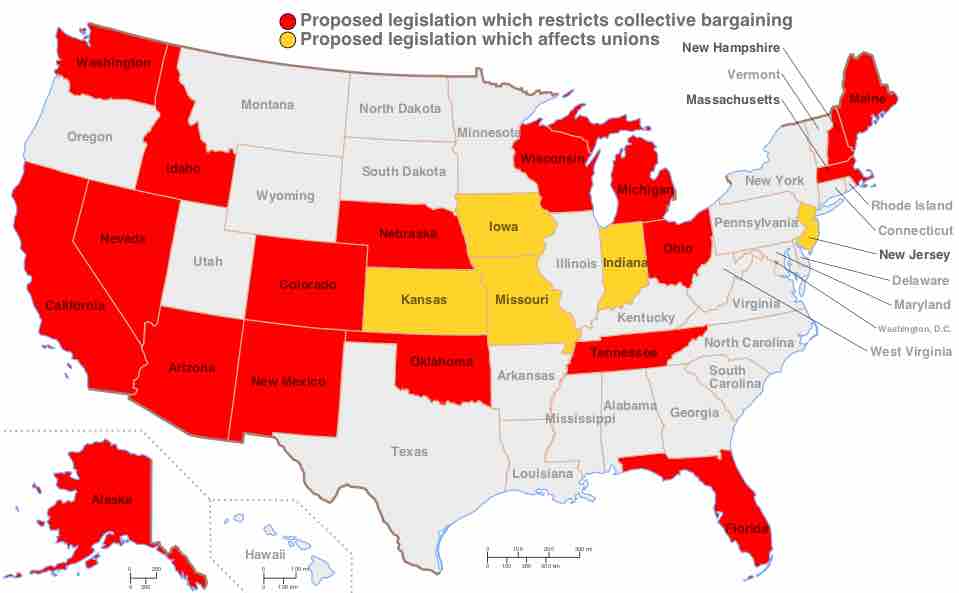
Map of proposed collective bargaining legislation
The right to collectively bargain is recognized through international human rights conventions. Article 23 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights identifies the ability to organize trade unions as a fundamental human right. Item 2(a) of the International Labour Organization's Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work defines the "freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining" as an essential right of workers.
The Participants
The interests of the employees are commonly presented by representatives of a trade union to which the employees belong. The union may negotiate with a single employer (who is typically representing a company's shareholders) or may negotiate with a group of businesses, depending on the country, to reach an industry-wide agreement.
The Result
The parties often refer to the result of the negotiation as a collective bargaining agreement (CBA) or as a collective employment agreement (CEA). A collective agreement functions as a labor contract between an employer and one or more unions.
The collective agreements reached by these negotiations usually set out wage scales, working hours, training, health and safety, overtime, grievance mechanisms, and rights to participate in workplace or company affairs.
Collective Bargaining Models
Different economic theories provide a number of models intended to explain some aspects of collective bargaining:
- The so-called monopoly union model (Dunlop, 1944) states that the monopoly union has the power to maximize the wage rate; the firm then chooses the level of employment.
- The right-to-manage model, developed by the British school during the 1980s (Nickell), views the labor union and the firm bargaining over the wage rate according to a typical Nash Bargaining Maximin.
- The efficient bargaining model (McDonald and Solow, 1981) sees the union and the firm bargaining over both wages and employment (or, more realistically, hours of work).