A tradeoff always exists between material economic development and the welfare of society and the environment. Social responsibility is the idea that an organization or individual is obligated to act to benefit society at large—i.e., to maintain equilibrium between the economy and the ecosystem.
Social responsibility in business is also known as corporate social responsibility (CSR), corporate responsibility, corporate citizenship, responsible business, sustainable responsible business, or corporate social performance. This term refers to a form of self-regulation that is integrated into different disciplines, such as business, politics, economy, media, and communications studies.
The Conference Board of Canada, a not-for-profit organization that specializes in economic trends, organizational performance, and public policy, wrote a National Corporate Social Responsibility Report. In it they explain that corporate social responsibility is a way of conducting business through balancing the long-term objectives, decision making, and behavior of a company with the values, norms, and expectations of society.
Companies can demonstrate social responsibility in a myriad of ways. They can donate funds to education, arts and culture, underprivileged children, or animal welfare, or they can make commitments to reduce their environmental footprint, implement fair hiring practices, sponsor events, and work only with suppliers with similar values. CSR can be practiced passively, through refraining from committing socially harmful acts, or actively, through performing activities that directly advance social goals. The below diagram shows the various ways that a company can invest in being socially responsible and the value those actions can bring to the company.
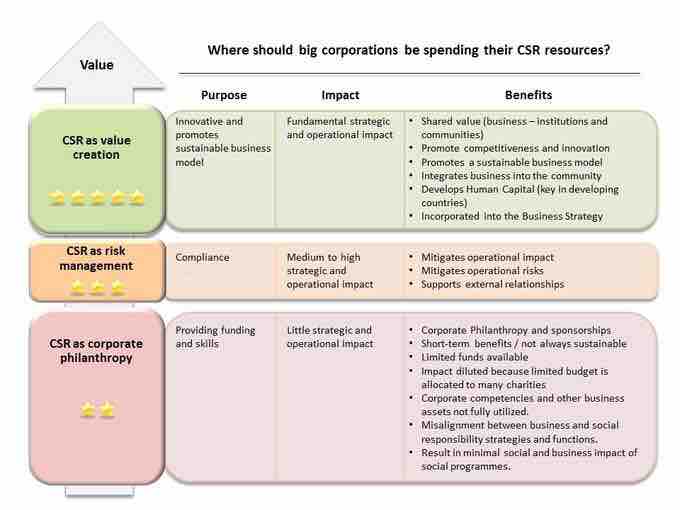
The Value of CSR
This diagram shows the various ways that a company can invest in being socially responsible and the value those actions can bring to the company.
The Conference Board of Canada, a not-for-profit organization that specializes in economic trends, suggests that social responsibility is a way of conducting business through balancing the long-term objectives, decision-making, and behavior of a company with the values, norms, and expectations of society. Social responsibility can be a normative principle and a soft law principle engaged in promoting universal ethical standards in relationship to private and public corporations.
Companies can demonstrate social responsibility in a myriad of ways. They can donate funds to education, arts and culture, underprivileged children, animal welfare, or they can make commitments to reduce their environmental footprint, implement fair hiring practices, sponsor events, and work only with suppliers with similar values.
Social responsibility in business is also known as corporate social responsibility, corporate responsibility, corporate citizenship, responsible business, sustainable responsible business, or corporate social performance. This term refers to a form of self-regulation that is integrated into different disciplines, including business, politics, economy, media, and communications studies.