Concept
Version 6
Created by Boundless
The Evolution of Plastids
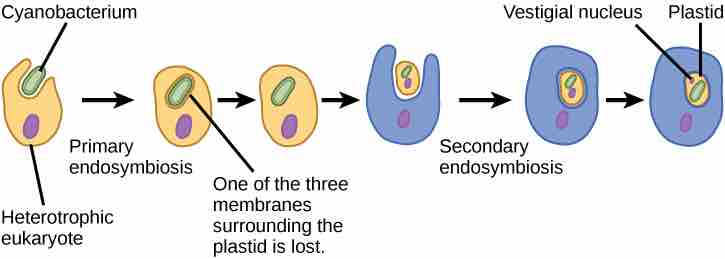
Primary and secondary endosymbiosis
The hypothesized process of endosymbiotic events leading to the evolution of chlorarachniophytes is shown. In a primary endosymbiotic event, a heterotrophic eukaryote consumed a cyanobacterium. In a secondary endosymbiotic event, the cell resulting from primary endosymbiosis was consumed by a second cell. The resulting organelle became a plastid in modern chlorarachniophytes.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"OpenStax College, Eukaryotic Origins. October 16, 2013."
http://cnx.org/content/m44614/latest/Figure_23_01_05.jpg
OpenStax CNX
CC BY 3.0.