Chapter 45
Population and Community Ecology
By Boundless
Demography is the study of population dynamics, using statistical and mathematical tools.
Scientists study population size and density using a variety of field sampling methods, including quadrats and mark-recapture.
Scientists gain insight into a species' biology and ecology from studying spatial distribution of individuals.
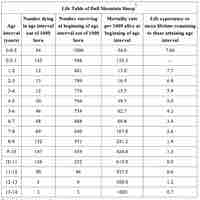
Demography, or the study of population dynamics, is studied using tools such as life tables and survivorship curves.
When resources are unlimited, a population can experience exponential growth, where its size increases at a greater and greater rate.
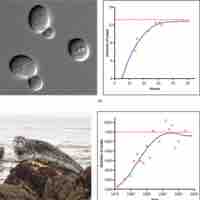
Logistic growth of a population size occurs when resources are limited, thereby setting a maximum number an environment can support.
Population regulation is a density-dependent process, meaning that population growth rates are regulated by the density of a population.
Energy budgets and life history strategies determine the type of reproductive capacity displayed by a population.
Modern theories of life history incorporate life and survivorship factors with ecological concepts associated with r- and K-selection theories.

The exponential growth of the human population could lead to food shortages, global warming, and other issues of resource scarcity.

Humans have exceeded density-dependent limits on population by enacting various environmental changes to accommodate our needs for hygiene, shelter, and food.
A population's growth is strongly influenced by the proportions of individuals in different age brackets, which in turn is influenced by economic development.
Communities are shaped by foundation species and keystone species, while invasive species disrupt the natural balance of an area.
Predation and herbivory are two methods animals use to obtain energy; many species have developed defenses against them.
Commensalism, mutualism, and parasitism are three symbiotic ways organisms interact with each other with differing degrees of benefit.
When disturbances occur, succession allows for communities to become re-established over periods of time.
Behavior is the change in activity of an organism in response to a stimulus and can be grouped as innate or learned.
Innate behaviors, such as kinesis, taxis, and migration, are instinctual responses to external stimuli.
Animals communicate using signals, which can be chemical (pheromones), aural (sound), visual (courtship displays), or tactile (touch).
Altruistic behaviors may be explained by the natural instinct to improve the chances of passing on one's genes.
In mating, there are two types of selection (intersexual, intrasexual) and three mating systems (monogamous, polygynous, polyandrous).
Simple learned behaviors include habituation and imprinting, both of which are important to the maturation process of young animals.
In classical conditioning, a behavior is paired with an unrelated stimulus; in operant conditioning, behaviors are modified by consequences.
Cognitive learning relies on cognitive processes such as reasoning and abstract thinking; it is much more efficient than conditioning.