Chapter 7
Cellular Respiration
By Boundless

Cellular respiration is the process of transforming chemical energy into forms usable by the cell or organism.
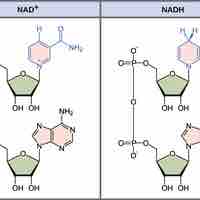
The transfer of electrons between molecules via oxidation and reduction allows the cell to transfer and use energy for cellular functions.
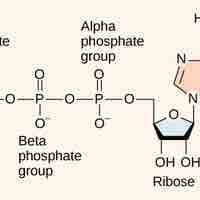
ATP, produced by glucose catabolized during cellular respiration, serves as the universal energy currency for all living organisms.
Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism.
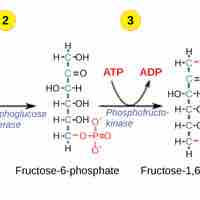
In the first half of glycolysis, energy in the form of two ATP molecules is required to transform glucose into two three-carbon molecules.
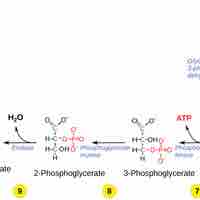
In the second half of glycolysis, energy is released in the form of 4 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules.
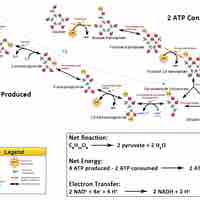
One glucose molecule produces four ATP, two NADH, and two pyruvate molecules during glycolysis.
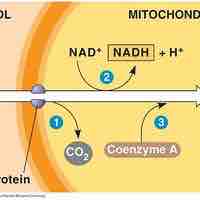
After glycolysis, pyruvate is converted into acetyl CoA in order to enter the citric acid cycle.
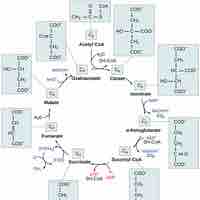
The acetyl carbons of acetyl CoA are released as carbon dioxide in the citric acid cycle.
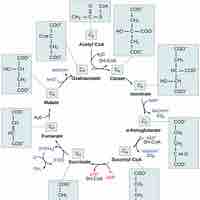
The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions that produces two carbon dioxide molecules, one GTP/ATP, and reduced forms of NADH and FADH2.
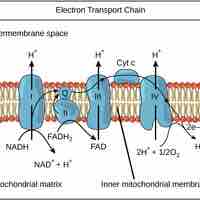
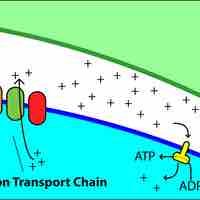
The electron transport chain uses the electrons from electron carriers to create a chemical gradient that can be used to power oxidative phosphorylation.

Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions across a selectively permeable membrane, down their electrochemical gradient.

The amount of energy (as ATP) gained from glucose catabolism varies across species and depends on other related cellular processes.
Sugars, such as galactose, fructose, and glycogen, are catabolized into new products in order to enter the glycolytic pathway.
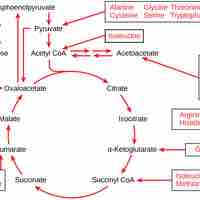
Excess amino acids are converted into molecules that can enter the pathways of glucose catabolism.
Lipids can be both made and broken down through parts of the glucose catabolism pathways.
Cellular respiration can be controlled at each stage of glucose metabolism through various regulatory mechanisms.
Catabolic pathways are controlled by enzymes, proteins, electron carriers, and pumps that ensure that the remaining reactions can proceed.
