Chapter 10
Cell Reproduction
Book
Version 32
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Biology
Biology
by Boundless
Section 1
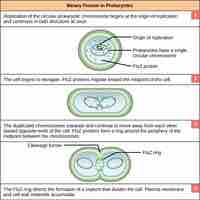
Cell Division
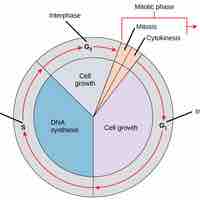
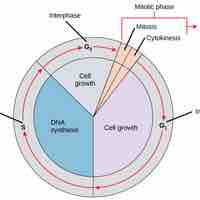
The Role of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle allows multiicellular organisms to grow and divide and single-celled organisms to reproduce.
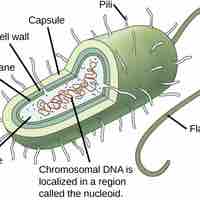
Genomic DNA and Chromosomes
The genome of an organism consists of its entire complement of DNA, which encodes the genes that control the organism's characteristics.
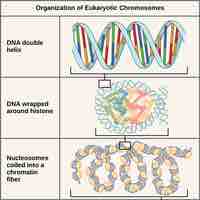
Eukaryotic Chromosomal Structure and Compaction
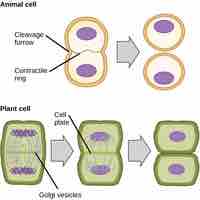
Chromosomes must coil to pack DNA into the cell during cell division, a process involving 3 levels of compaction.
Section 3
Control of the Cell Cycle

Regulation of the Cell Cycle by External Events
External factors can influence the cell cycle by inhibiting or initiating cell division.
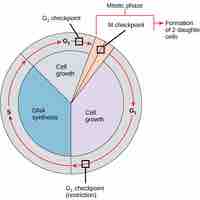
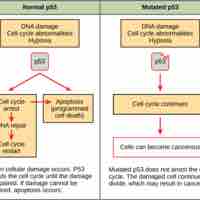
Regulation of the Cell Cycle at Internal Checkpoints
The cell cycle is controlled by three internal checkpoints that evaluate the condition of the genetic information.
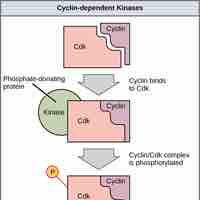
Regulator Molecules of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is controlled by regulator molecules that either promote the process or stop it from progressing.
You are in this book
Boundless Biology
by Boundless