Chapter 9
Cell Communication
By Boundless

Cellular communication ensures regulation of biological processes within various environments from single-celled to multicellular organisms.
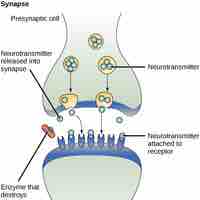
The major types of signaling mechanisms that occur in multicellular organisms are paracrine, endocrine, autocrine, and direct signaling.
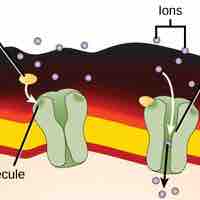
Receptors, either intracellular or cell-surface, bind to specific ligands, which activate numerous cellular processes.
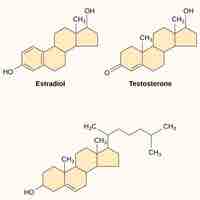
Signaling molecules are necessary for the coordination of cellular responses by serving as ligands and binding to cell receptors.
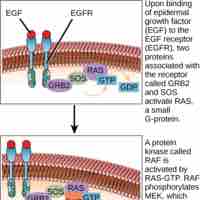
Ligand binding to cell-surface receptors activates the receptor's intracellular components setting off a signaling pathway or cascade.
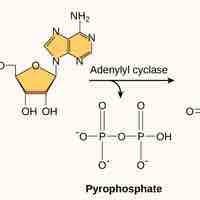
Signaling pathway induction activates a sequence of enzymatic modifications that are recognized in turn by the next component downstream.
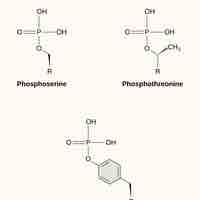
Signal cascades convey signals to the cell through the phosphorylation of molecules by kinases.
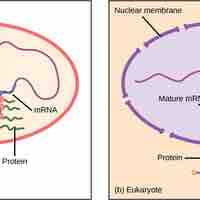
Gene expression, vital for cells to function properly, is the process of turning on a gene to produce RNA and protein.
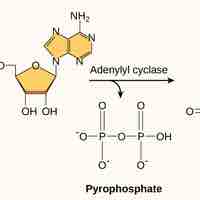
The rush of adrenaline that leads to greater glucose availability is an example of an increase in metabolism.
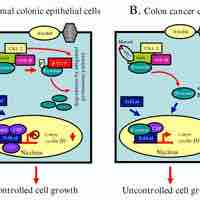
Cell growth is promoted by ligands known as growth factors.
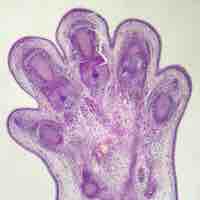
When a cell is damaged, unnecessary, or dangerous to an organism, a cell can initiate the mechanism for cell death known as apoptosis.