Production of Vaccines, Antibiotics, and Hormones
Vaccines
Traditional vaccination strategies use weakened or inactive forms of microorganisms to mount the initial immune response. Modern techniques use the genes of microorganisms cloned into vectors to mass produce the desired antigen. The antigen is then introduced into the body to stimulate the primary immune response and trigger immune memory. Genes cloned from the influenza virus have been used to combat the constantly-changing strains of this virus.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are biotechnological products that inhibit bacterial growth or kill bacteria. They are naturally produced by microorganisms, such as fungi, to attain an advantage over bacterial populations. Antibiotics are produced on a large scale by cultivating and manipulating fungal cells. Many antibacterial compounds are classified on the basis of their chemical or biosynthetic origin into natural, semisynthetic, and synthetic. Another classification system is based on biological activity. In this classification, antibiotics are divided into two broad groups according to their biological effect on microorganisms: bactericidal agents kill bacteria, and bacteriostatic agents slow down or stall bacterial growth .
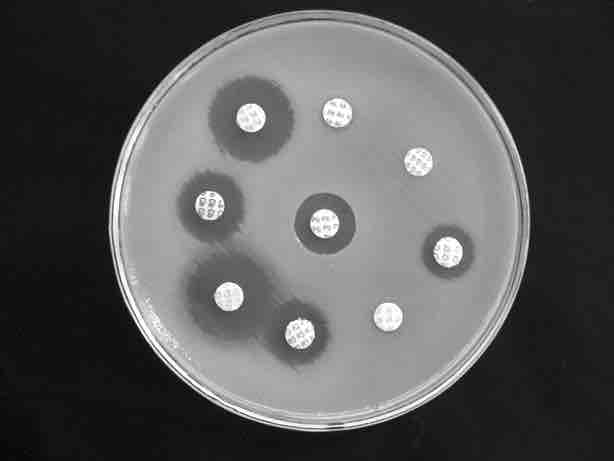
Antibiotic Treatment
Assays such as the one shown help scientists understand the effects of antibiotics on bacterial species. Clear rings around the round inserts, which contain antibiotic, mean that bacteria on the plate are inhibited or killed by the compound.
Hormones
Recombinant DNA technology was used to produce large-scale quantities of human insulin (a hormone) in E. coli as early as 1978. Previously, it was only possible to treat diabetes with pig insulin, which caused allergic reactions in humans because of differences in the gene product. In recent times, human growth hormone (HGH) has been used to treat growth disorders in children. The HGH gene was cloned from a cDNA library and inserted into E. coli cells by cloning it into a bacterial vector. The bacteria was then grown and the hormone isolated, enabling large scale commercial production.