Chapter 3
Biological Macromolecules
By Boundless
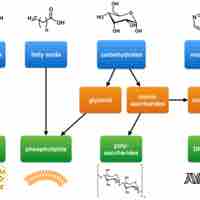
Biological macromolecules, the large molecules necessary for life, include carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.

In dehydration synthesis, monomers combine with each other via covalent bonds to form polymers.
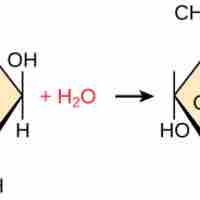
Hydrolysis reactions result in the breakdown of polymers into monomers by using a water molecule and an enzymatic catalyst.
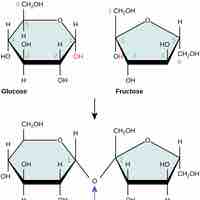
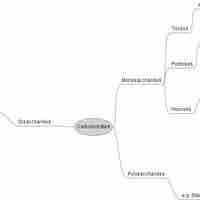
Carbohydrates are essential macromolecules that are classified into three subtypes: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Carbohydrates are a major class of biological macromolecules that are an essential part of our diet and provide energy to the body.
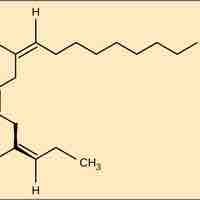
Fats and oils, which may be saturated or unsaturated, can be unhealthy but also serve important functions for plants and animals.
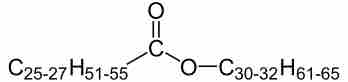
Waxes are nonpolar lipids that plants and animals use for protection and have many functions in society.
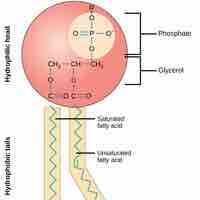
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules that make up the bilayer of the plasma membrane and keep the membrane fluid.
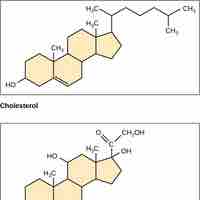
Steroids, like cholesterol, play roles in reproduction, absorption, metabolism regulation, and brain activity.
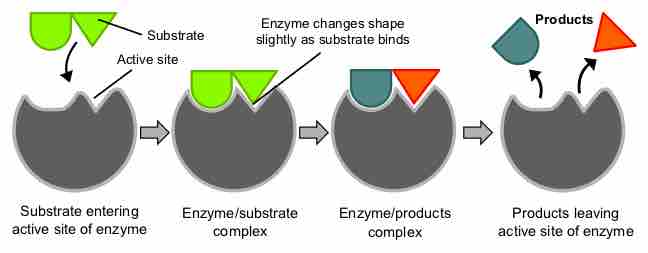
Proteins perform many essential physiological functions, including catalyzing biochemical reactions.
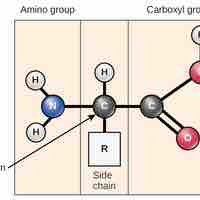
An amino acid contains an amino group, a carboxyl group, and an R group, and it combines with other amino acids to form polypeptide chains.
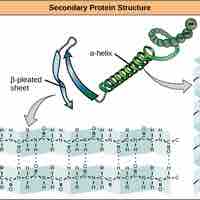
Each successive level of protein folding ultimately contributes to its shape and therefore its function.

Denaturation is a process in which proteins lose their shape and, therefore, their function because of changes in pH or temperature.
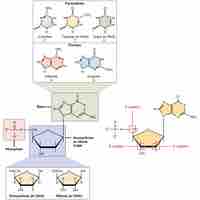
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that carry out cellular processes, especially the regulation and expression of genes.
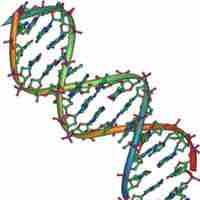
The DNA double helix looks like a twisted staircase, with the sugar and phosphate backbone surrounding complementary nitrogen bases.
DNA packaging is an important process in living cells. Without it, a cell is not able to accommodate the large amount of DNA that is stored inside.
RNA is the nucleic acid that makes proteins from the code provided by DNA through the processes of transcription and translation.