This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Nicole Levine, MFA. Nicole Levine is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. She has more than 20 years of experience creating technical documentation and leading support teams at major web hosting and software companies. Nicole also holds an MFA in Creative Writing from Portland State University and teaches composition, fiction-writing, and zine-making at various institutions.
This article has been viewed 17,459 times.
Learn more...
The clrscr() function was used to clear the MS-DOS console screen in older C compilers like Turbo C and Turbo C++. clrscr() is not a standard C function—if you try to compile a program that includes clrscr() in a modern compiler like GCC or Clang, you’ll get an error that says “function not declared” or “not declared in this scope." So what if you need to clear the console in your program? This wikiHow article will teach you how to replace clrscr() with the system() function to clear the screen in C.
Steps
-
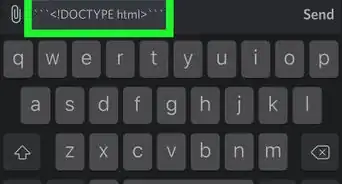
1Add the stdlib.h header file to your code. The system() function is used to pass commands to the terminal or console, and it’s declared in the stdlib.h header file.[1]
- clrscr() is defined in the conio.h header file. Since we'll be removing clrscr() and replacing it with system(), you can remove the conio.h header file.
-
2Replace clrscr() with system("cls") on Windows. The cls command, when run at the Windows command prompt, clears the console screen. Passing cls through the system() function effectively clears the screen.Advertisement
-
3Replace clrscr() with system("clear") on Linux or macOS. The system() function will pass the clear command to the console. The Linux command (and thus the macOS command) to clear the console is clear, so system("clear") will clear the console window. [2]
References
About This Article
clrscr() is not a standard C function. It was only used to clear MS DOS consoles in Borland compilers like Turbo C. If you want to clear the console screen in C, you'll want to use system("clear") for Linux and macOS, or system("cls") for Windows.
-in-C-Step-1.webp)
-in-C-Step-2.webp)
-in-C-Step-3.webp)