This article was co-authored by Jonas Jackel. Jonas Jackel is the Owner of Huckleberry Bicycles, a bicycle retail store based in San Francisco, California. Jonas has over 20 years of experience managing bicycle retail stores and has operated Huckleberry Bicycles since 2011. Huckleberry Bicycles specializes in servicing, repairing, and custom building road, cross, gravel, touring, folding, and e-bikes. Jonas was also previously sat on the Board of Directors for Bike East Bay, a bicycle-advocacy non-profit organization based in Oakland, California.
There are 22 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 38,250 times.
Wheel bearings on a bike help reduce friction and keep the wheels spinning smoothly. If your bike feels rough or shaky, then you may need to replace the bearings. This job requires some time and special tools, so pay close attention to the process. There are 2 types of bearings, ball and cartridge, and each has a different replacement process. If your bike has an unscrewable skewer, it uses ball bearings, and if it has removable axle caps, then it uses cartridge bearings. Follow the appropriate steps for the type of bearings your bike uses.
Steps
Exposing Ball Bearings
-
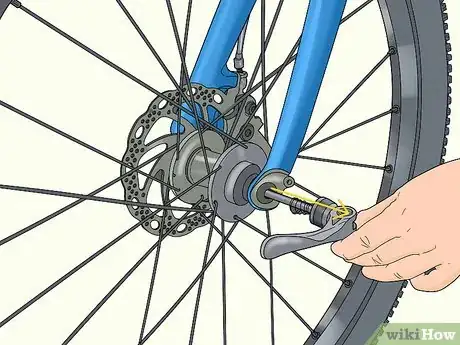
1Take the wheel off the bike. Most modern bikes have a quick-release lever on each wheel. Find that lever on the side of the axle and lift it up to free the wheel. Then slide the wheel out of its socket. If your bike doesn’t have a quick-release, use a wrench and unscrew the nut holding the axle in place. Then slide the wheel out of position.[1]
- If you have to unscrew the wheel, put the nut you remove in a safe place so you don’t lose it.
- If you’re removing a rear wheel, slide the chain off of the freewheel before removing the wheel. The freewheel is the geared part on the rear wheel that the chain loops around.
-
2Remove the skewer through the middle of the axle. Lay the wheel on a table with either side facing up. Hold the bottom end of the skewer in place and turn the nut on the top side counterclockwise to loosen it. Pull off the nut and the spring underneath it, then slide the skewer out of the axle.[2]
- To keep track of all your pieces, put the spring and nut back onto the skewer in the order you removed them. Then put the whole piece in a safe place.
Advertisement -
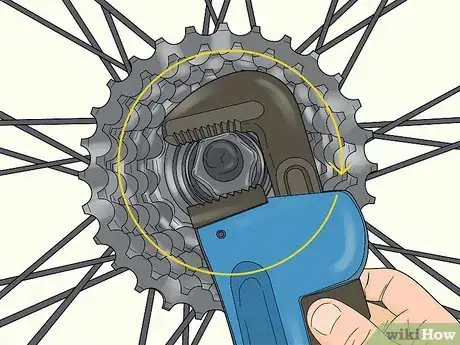
3Unscrew the freewheel if you’re working on a rear tire. Slide a freewheel remover over the nut through the middle of the piece. Turn it counterclockwise with a wrench to loosen the nut, then lift the freewheel off the axle.[3]
- You can get a freewheel remover tool at a bike shop, a department store that has a bike section, or online. They're usually around $10.
- There are also other methods to remove the freewheel. For instance, you could also lock it in place with a chain whip and use a socket wrench to unscrew it. A chain whip is a bicycle tool that wraps around the freewheel to hold it steady. You can buy them at bike shops or online for $15-20.
- In some areas, the freewheel is called a cassette. Remember that so if you use other instructions besides this article you won’t get confused.
-
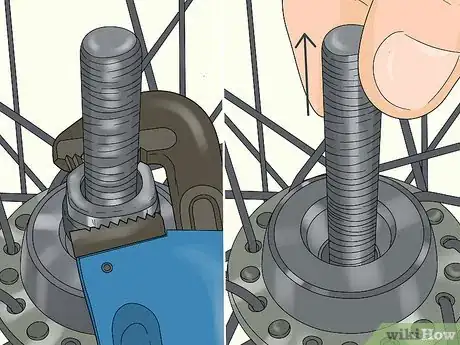
4Pull the axle out by unscrewing the locknut and cone. Lock a wrench around the cone at the base of the axle. Then lock another wrench around the nut at the end of the axle. Turn the nut counterclockwise to loosen and remove it. Then pull out the spacer tube between the nut and cone. Unscrew the cone nut turning it counterclockwise, then slide the axle out from the bottom.[4]
- Not all bikes have a spacer between the nut and cone. In this case, just unscrew the nut and cone.
- The other side of the axle has the same pieces, but you only have to remove the pieces on one side to take the axle out.
-
5Remove all of the old ball bearings with a magnet. Lifting the cone off exposes the bearings on each side, which are small metal balls arranged around the hub opening. Take a magnet and run it around the hub to pull out all the bearings. Then do the same on the other side.[5]
- You don't need a very strong magnet to get the bearings out, but you'll need something stronger than a kitchen magnet. Any workshop-type magnet that can pick up screws and nails will work.
- Count how many bearings you remove from each side so you know how many to replace. The number is the same on each side, so if you get 2 different numbers, a few bearings probably fell out. The larger number is the correct count.
-
6Clean the wheel hub with paint thinner. Pour some paint thinner onto a clean rag and wipe the inside and outside of the hub, which is the tunnel that the axle slides through. Make sure to clean out the threads on the end of the hub as well, since grease is usually trapped in there.[6]
- You could also use a similar solvent like mineral spirits or rubbing alcohol to clean out the hub.
- If the pieces you removed are greasy as well, then soak them in a can of paint thinner or another solvent for 5 minutes and wipe the excess grease off afterward.
- These solvents usually don’t cause irritation, so you don’t have to wear gloves unless you have sensitive skin. Wash your hands normally with soap and water when you’re done.
Adding New Ball Bearings
-
1Apply grease to both sides of the hub. Take a grease injector and squeeze dabs of grease around the hub rim. Make sure the grease doesn’t overflow over the hub border. Then flip the wheel over and apply the same amount to the other side.[7]
- There are many types of bike grease available, but lithium-based products are best to prevent water intrusion. You can buy these at a bike shop or online.[8]
-
2Press the new bearings into the grease. Grab the new bearings with a pair of tweezers and place them in a ring around the hub opening. Press down so they stick to the grease. Replace each bearing that you removed on each side.[9]
- You can buy new bearings at any bike shop or online. On most bikes, the rear wheel uses 1/4" bearings and the front wheel uses 3/16". If you aren't sure what type your bike uses, check the user manual and get the appropriate size.
- Be careful flipping the tire over so you don’t knock any bearings out.
-
3Reinstall the axle to cover the new bearings. Take the axle and slide it back through the hub until the cone covers the bearings on one side. Screw the cone back onto the other side to secure the axle. Slide the spacer back on and screw the nut to the end. Tighten up all the pieces with a wrench to make sure they're snug.[10]
- Make sure the axle is loose enough for the wheel to spin smoothly. If the motion seems tight or jerky, loosen up the nut a bit.
-
4Replace the freewheel if you were working on a rear tire. Take the freewheel and slide it back onto the axle. Put the nut back on and place the freewheel remover over it. Turn it clockwise with a wrench to tighten it up.[11]
-
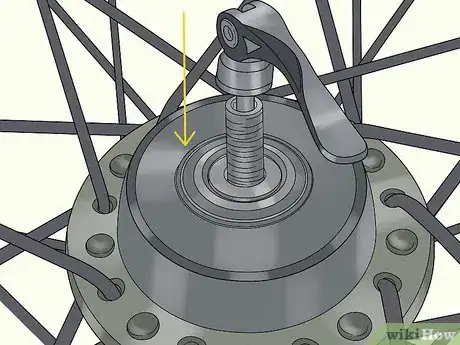
5Slide the skewer back through the axle. Remove the nut on one side of the skewer and slide it through either side of the axle. Replace the nut on the other side to lock it in place.[12]
-
6Put the wheel back onto the bike. Lift the wheel back into the bike socket. If it has a quick-release lever, press the lever down to lock the wheel in place. If not, tighten the nut around the axle to reattach the wheel.[13]
- If you were working on a rear wheel, loop the chain back around the freewheel as well.
Removing Cartridge Bearings
-
1Pull off the axle end caps. If your bike has cartridge bearings, the end caps just pull off. Grab the ends with your hand or pliers and pull back until they pop off.[14]
- You could also close each end in a vise and pull the whole wheel up if you have trouble getting the ends off. Remember that the ends are plastic, so don't tighten the vise enough to crack them.
- Keep all of the parts you remove in a safe place so you don’t lose them.
-
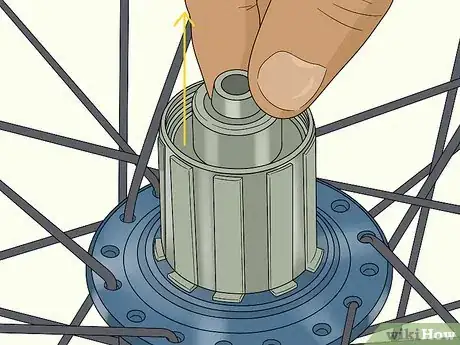
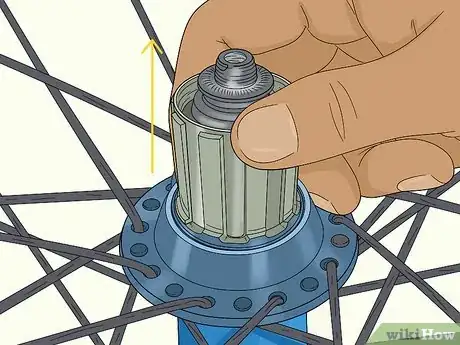
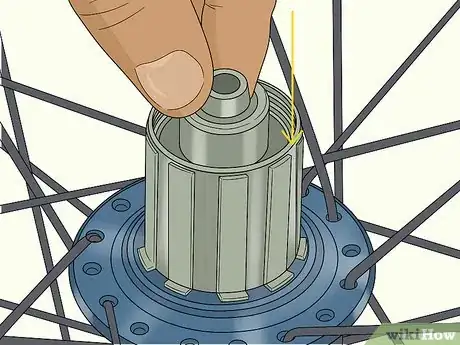
2Remove the freehub body covering the bearings. On the drive side of the bike, almost always the right side, there is a freehub underneath the end caps. The freehub houses the axle and other internal wheel components. Pull this off the same way that you pulled off the axle caps. Be careful when you remove it because there is a spring and 2 caps underneath it. Put the pieces together and leave them in a safe place.[15]
- In some cases, you’ll have to unscrew the freehub instead of pulling it off. This is specific to different bike manufacturers. If there is a nut or screw on the freehub, then unscrew it instead.
- You can tell the drive side of the bike because that's the side where the freewheel is. The freewheel, also called a cassette, is the gear section that the chain loops over. On almost all bikes, this is on the right.
-
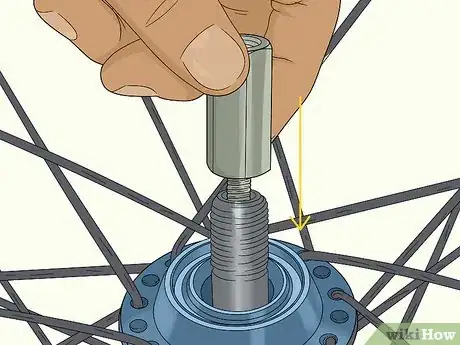
3Insert an axle protector into the axle on the non-drive side. Flip the tire so the non-drive side, or the left side, is pointing up. Then slide an axle protector into the hub so it sits snuggly around the axle.[16]
- You can buy an axle protector from any bike store or online.
-
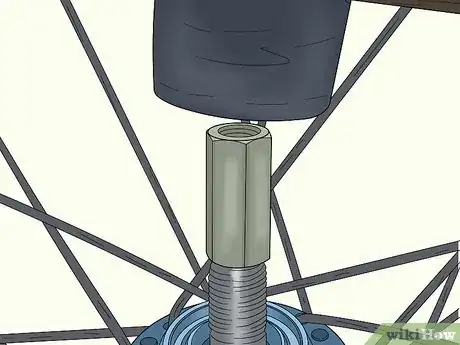
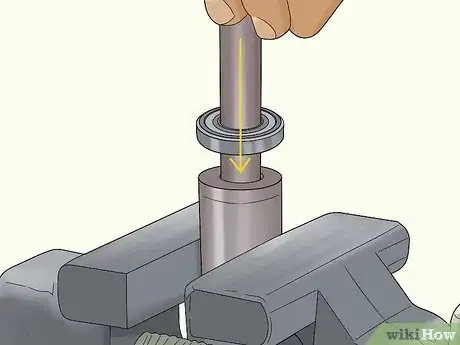
4Tap the axle out with a hammer to remove the bearing. Use a rubber mallet or hammer with a rubber protector on the bottom. Tap the top of the axle protector gently until the bearing pops out from the other side.[17]
- Don’t hit the hub directly with a hammer without using an axle protector. You could damage the hub and have to replace the whole wheel.
-
5Flip the wheel around and tap it to remove the second bearing. Flip the wheel so the drive side is facing up. Slide the axle protector into this side and tap the other bearing out.[18]
-
6Clean the bike hub and pieces you removed with paint thinner. Pour some paint thinner onto a clean rag and wipe it around the hub to remove any grease buildup. Also soak the axle, caps, and other piece you removed in a jar of the solvent you use for 5 minutes to clean them. Wipe them dry afterward.[19]
- You can also use mineral spirits or rubbing alcohol to clean the hubs.
- Wash your hands normally with soap and water after using these solvents. Don’t touch your face until you’ve washed it all off. If you have sensitive skin, you should wear gloves to avoid irritation.
Inserting New Cartridge Bearings
-
1Grease the hub so the bearings insert easier. Apply a thin layer of bicycle grease to the inner and outer parts of the hub. This protects the pieces from rust and helps the bike move more smoothly. You can either use a grease gun or rub the grease on with your hands.[20]
- Use a lithium-based grease for the best protection against water damage.
-
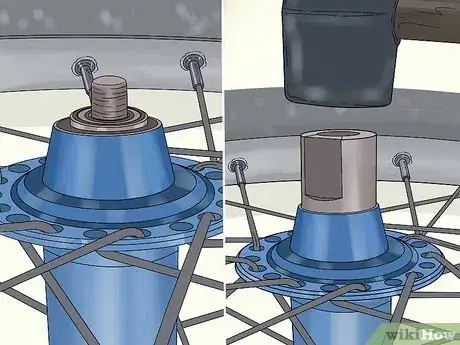
2Place an axle drift into a vise. Take the drift and angle it straight up. Then close the vise around it tightly to lock it in place.[21]
- An axle drift is a tool that helps push the bearing into place. You can buy one at a bike shop.
-
3Slide a new bearing onto either side of the axle. Grease both the axle and the bearing to make sure they slide together easily. Then place the bearing onto either side of the axle. Press it down so some of the axle pokes out, but don’t worry about tightening it yet.[22]
- If you’re replacing a rear wheel, the drive side of the axle is longer than the other. Start with the longer side in this case.
-
4Insert the axle into the drift. Flip the axle so the side with the bearing points down. Insert that side into the drift so it sits upright.[23]
-
5Lift the wheel onto the axle. Take the wheel and line up the hub with the axle. Slide the axle through the hub until the bearing enters it. Let the wheel sit on top of the vise.[24]
- If you’re working on a rear wheel, make sure you match the drive side of the wheel with the drive side of the axle. The hub on the wheel is thicker on the drive side.
-
6Insert the other drift through the other side of the hub. Line up the drift with the axle and hub on the wheel side facing up. Slide it over the axle and into the hub.[25]
- Don’t worry about pressing the drift into the hub tightly. It just needs to sit on top of the hub opening.
-
7Tap the drift with a hammer to set the hub in place. Take a hammer and lightly tap the drift. Continue tapping until the bearing enters the hub.[26]
- You can tell if the bearing inserts by looking below the wheel where the vise is. When you can’t see the bearing anymore, it’s in the hub.
- Use either a rubber mallet or a hammer with a rubber covering on the bottom to avoid damaging the wheel.
-
8Slide the other bearing over the top side of the axle. Let the bearing sit on top of the hub opening. Then place the drift over the bearing and tap it until the bearing enters the hub.[27]
- You may need to push the axle up from the bottom to give the bearing enough space to slide over.
-
9Grease the new bearings to protect the hub from damage. Take some more grease on your fingers and rub it on each side of the hub to cover the new bearings. This prevents rusting and water damage.[28]
- Only apply a thin layer of grease. If you glob it on, it could lock up the axle.
-
10Reassemble the bike freewheel body. Take the 2 caps that were underneath the freewheel and grease them lightly. Slide them onto the axle. Then slide the spring into place. Finally, pop the freewheel body back over the axle.[29]
- If you’re worried you might forget the correct order of piece while you’re reassembling the hub, try taking pictures as you work to see what everything should look like.
-
11Replace the axle end caps. Take the end caps and press them onto each side of the axle. When they make a “pop” sound, they’re in place.[30]
Things You’ll Need
Exposing Ball Bearings
- Wrenches
- Freewheel remover
- Rags
- Paint thinner
Adding New Ball Bearings
- New ball bearings
- Grease
- Wrenches
- Freewheel remover
Removing Cartridge Bearings
- Pliers
- Wrench
- Paint thinner
- Axle protector
- Hammer
- Rags
Inserting New Cartridge Bearings
- New cartridge bearings
- Grease
- Vise
- Hammer
- Axle drift
Warnings
- Your bike may not work properly if you don’t replace the bearings correctly, which is dangerous for you. If you’re not confident in your ability to work on the bike, take it to a bike shop for a professional repair.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://www.bikeride.com/overhaul-wheel-bearings/
- ↑ https://youtu.be/_axwV6sfaAs?t=20
- ↑ https://www.bikeride.com/overhaul-wheel-bearings/
- ↑ https://youtu.be/_axwV6sfaAs?t=233
- ↑ https://youtu.be/_axwV6sfaAs?t=261
- ↑ https://www.bikeride.com/overhaul-wheel-bearings/
- ↑ https://youtu.be/_axwV6sfaAs?t=556
- ↑ https://www.bicycling.com/repair/a20017188/bike-repair-17/
- ↑ https://youtu.be/_axwV6sfaAs?t=585
- ↑ https://www.bikeride.com/overhaul-wheel-bearings/
- ↑ https://youtu.be/_axwV6sfaAs?t=852
- ↑ https://youtu.be/_axwV6sfaAs?t=20
- ↑ https://www.bikeride.com/overhaul-wheel-bearings/
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=90
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=135
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=223
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=239
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=259
- ↑ https://www.singletracks.com/mtb-repair/winter-wear-swapping-cartridge-bearings-in-your-front-wheel/
- ↑ https://www.singletracks.com/mtb-repair/winter-wear-swapping-cartridge-bearings-in-your-front-wheel/
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=374
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=377
- ↑ https://www.singletracks.com/mtb-repair/winter-wear-swapping-cartridge-bearings-in-your-front-wheel/
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=393
- ↑ https://www.singletracks.com/mtb-repair/winter-wear-swapping-cartridge-bearings-in-your-front-wheel/
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=410
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=533
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=583
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=600
- ↑ https://youtu.be/XXZlM5ibl5s?t=600
- ↑ https://www.centurycycles.com/tips/5-tips-buying-a-new-bicycle-pg1483.htm
- ↑ https://www.centurycycles.com/tips/5-tips-buying-a-new-bicycle-pg1483.htm
- ↑ https://www.centurycycles.com/tips/5-tips-buying-a-new-bicycle-pg1483.htm