wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, volunteer authors worked to edit and improve it over time.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 15,622 times.
Learn more...
Fragile X syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that causes developmental delays and behavioral problems. The level of intellectual disability varies from mild to severe for people with this condition. This condition affects both males and females. Females often have milder symptoms than males if they have Fragile X syndrome. Around 1 in 7,000 males have the condition, and around 1 in 11,000 females have it. People with Fragile X syndrome usually live an average life expectancy, and can expect to live a good life. It is not a deadly condition. You can take steps to recognize the symptoms of Fragile X syndrome.
Steps
Symptoms of Fragile X Syndrome
-
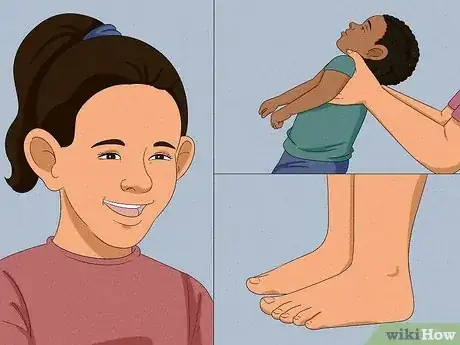
1Examine your child for the physical features of Fragile X syndrome. [1] Many kids with this condition have noticeable physical features that are a symptom of Fragile X syndrome. This includes:
- A long, narrow face
- A large forehead
- A large jaw
- Softer skin
- Larger ears
- Crossed eyes
- Flat feet (with no arches)
- Being overly flexible
- Low muscle tone
-
2Check if your child is fulfilling the same developmental milestones as other children. Each child is different, and some may accomplish milestones such as talking, walking, and reading slower or faster than other children, but kids with Fragile X Syndrome learn these skills at a very late age. Check if they have accomplished the following milestones at age 2:
- Sitting
- Walking
- Talking
Advertisement -
3See if your child is having trouble learning new skills. Many kids are slow in eating solid foods, reading, or doing academic work at first, but kids with Fragile X Syndrome might take longer than the average kid. They may have problems reading, writing, or doing math work at school.
-
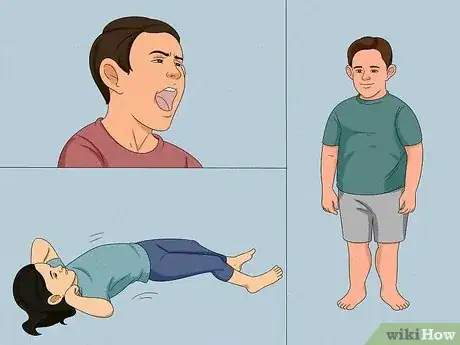
4Check if your child has sensory and communication difficulties.[2] Kids with Fragile X Syndrome have some degree of social and sensory problems. This varies for each Fragile X child, but some symptoms include:
- Not making eye contact with others
- Social anxiety
- Trouble paying attention
- Trouble understanding what someone is saying
- Acting and speaking on impulse
- Being hyperactive
- Flapping or biting their hands
- Sensory issues (e.g. having trouble processing certain sounds, tastes, touches, etc.)
- Difficulty in picking up social cues
-
5Check for other conditions and symptoms that may appear with Fragile X syndrome. [3] In one survey, parents said that their kids with Fragile X syndrome also had other conditions such as:
- Epilepsy
- Sleep disorders (insomnia, night terrors, etc.)
- Self-injury behaviors
- Being overly aggressive
- Obesity
Genetic Factors of Fragile X Syndrome
-
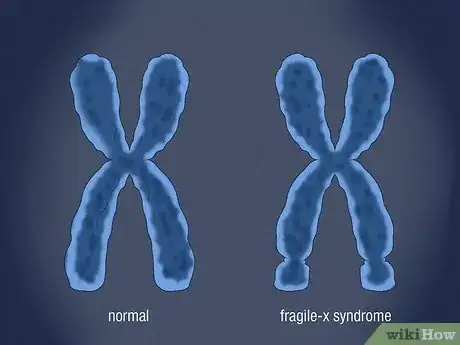
1Know what causes Fragile X syndrome. Fragile X syndrome is a genetic disorder, meaning that it is passed on by genes. A change to a gene on the X-chromosome called the FMR1 gene causes Fragile X syndrome. [4] When the gene is changed or altered, the gene cannot produce a certain protein that makes the brain work normally. This causes Fragile X syndrome.
-
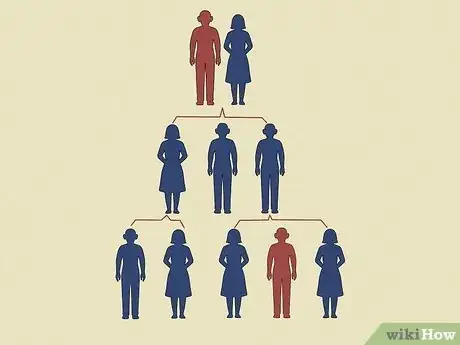
2Know factors that make this condition more likely. Your child is more likely to get Fragile X syndrome if: [5]
- You have a family history of Fragile X syndrome
- You have a family history of autism or other neurodevelopmental disorders
- You have infertility problems
- You have a family history of tremors/ataxia
Differentiating Between Other Conditions
-
1Know the difference between autism and Fragile X syndrome. [6] There are shared characteristics between the two conditions (mainly learning problems and late developmental milestones). But they have many differences too, such as how they are caused and other symptoms that differentiate between them.
- Autism is not caused by one single genetic mutation, whereas Fragile X syndrome is caused by a mutation in the FMR1 gene.
- Autistic people do not have seizures (unless they have epilepsy), whereas some people with this syndrome have seizures.
- Autistic people do not have a specific appearance, whereas most kids with Fragile X syndrome have low muscle tone, large foreheads, large ears, and other physical traits that indicate the condition.
-
2Know the difference between Down syndrome and Fragile X syndrome. [7] There are shared characteristics between the two conditions (mainly learning problems). But they have many differences too, such as how they are caused and other symptoms that differentiate between them.
- Down syndrome is caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 (all or part of it), whereas Fragile X syndrome is caused by a mutation in the FMR1 gene. [8]
- People with Down syndrome do not have seizures (unless they have epilepsy), whereas some people with this syndrome have seizures.
- People with Down syndrome usually have slanted eyes, flat noses, wide necks, and underdeveloped parts of their body. Kids with Fragile X syndrome have low muscle tone, large foreheads, large ears, and other physical traits that indicate the condition.
-
3Tell the difference between personality traits and Fragile X syndrome.
- Introversion is not caused by one gene, whereas Fragile X syndrome is caused by a mutation in the FMR1 gene. Introversion is not a condition- it is just someone's personality.
- Social anxiety is not caused by one gene- it can be environmental or genetic. Fragile X syndrome is caused by a mutation in the FMR1 gene. People with Fragile X syndrome are more likely to have social anxiety, whereas people with social anxiety are not more likely to have Fragile X syndrome.
References
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/5476-fragile-x-syndrome
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/fxs/facts.html
- ↑ https://www.healthline.com/health/fragile-x-syndrome#causes
- ↑ https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/fragile-x-syndrome
- ↑ https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/carrier-testing-for-fragile-x-syndrome
- ↑ https://fragilex.org/research/fxs-and-asd-similar-but-different/
- ↑ https://fragilex.org/research/fxs-and-asd-similar-but-different/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3532435/




























































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...