This article was medically reviewed by Troy A. Miles, MD and by wikiHow staff writer, Jessica Gibson. Dr. Miles is an Orthopedic Surgeon specializing in Adult Joint Reconstruction in California. He received his MD from the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in 2010, followed by a residency at the Oregon Health & Science University and fellowship at the University of California, Davis. He is a Diplomat of the American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery and is a member of the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons, American Orthopaedic Association, American Association of Orthopaedic Surgery, and the North Pacific Orthopaedic Society.
There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 89% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 272,121 times.
While there are several types of hernias, all hernias are an "out-pouching" of an organ, part of an organ or fatty tissue. This material squeezes through weak areas or gaps in the surrounding tissues of your abdomen. Because of this, hernias can't be prevented, although you can reduce your risk of developing one. Hernias develop when physical stress forces the tissue or organ through a weakened area. This might happen if you lift a heavy object incorrectly, are pregnant, have diarrhea or constipation, or you suddenly cough or sneeze. Other factors like obesity, smoking, and poor nutrition can weaken the tissue area, increasing your risk for a hernia.[1]
Should You Push a Hernia Back In?
Do Not Push the Hernia Back In If:
- The hernia is in an infant or a child.
- Pushing the hernia causes discomfort or pain.
Consider Pushing a Hernia Back In If:
- You've already seen your doctor about the hernia.
- You've been trained on how to use a truss, patch, or belt.
Steps
Pushing In a Hernia at Home
-
1Get your supplies. You can buy a hernia truss or belt at a medical supply store or pharmacy. Your doctor should recommend a specific type of support based on your hernia. In general, these supports are elastic bands or elastic underwear designed to keep the area around the hernia flat.
- Your doctor should also teach you how to put on the truss, patch or belt.
- A hernia belt will wrap around your waist, supporting the hernia. A hernia truss is an undergarment that helps keep the hernia in place.
-
2Lay down. Lay on your back so gravity helps push the hernia down. If you're using a belt, be sure to lay down on the belt so you can wrap it around your waist and the hernia. If you're putting on a tress, you can either pull it on while you lay down or stand up if it's easier for you.
- Wash your hands before you put on the hernia support and make sure the support is clean and dry.
Advertisement -
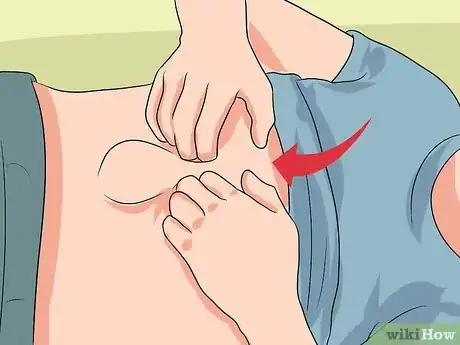
3Use your hands to reposition the hernia. Depending on your hernia, you should be able to use your hands and gently push the hernia into your stomach, groin, or belly button. This won't require much maneuvering and it shouldn't hurt.
- If it hurts when you apply pressure to the hernia, stop and contact your doctor. You don't want to force the hernia into place which could cause more damage to your abdominal muscles.
-
4Apply the support. If you're using a band, carefully bring one side of the wrap over your abdomen. Remember, you should be laying on top of it. Bring the other side of the wrap across your abdomen so that it gives snug pressure. This keeps your hernia in place.
- If you're using a hernia truss, simply pull the undergarment on to keep the hernia situated.
-
5Wear the support. Since you should only be using the support with your doctor's recommendation, wear the support for as long as advised. You should understand that pushing the hernia back in will cause temporary relief, but is not a permanent treatment.[2]
- Your doctor may recommend using a hernia support until you're able to get corrective surgery.
Getting Medical Treatment
-
1Know when to get immediate medical attention. If you feel pain, tenderness, or discomfort when you push the hernia, stop pushing and call for medical help. Hernias can block blood flow within the abdomen which can cause a medical emergency. Pain can indicate:
- A hernia that's become trapped in the abdominal wall.
- A hernia that's become twisted and strangulated, which cuts off the blood supply. If this happens, tissue dies and can cause gangrene.
-
2Talk with your doctor. While you can push a hernia back in and use a support to relieve discomfort, surgery is the only permanent treatment for hernias.[3] Discuss whether you'd like to consider this as an option. Keep in mind that most hernias are not medical emergencies, but they can become medical emergencies.
- There are no medications to treat a hernia.
-
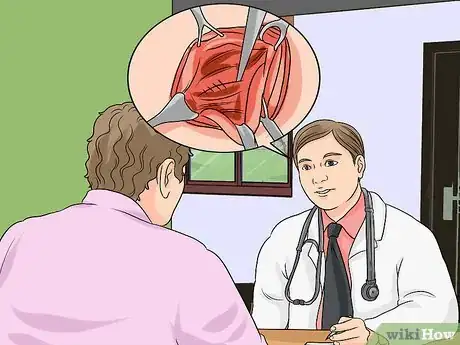
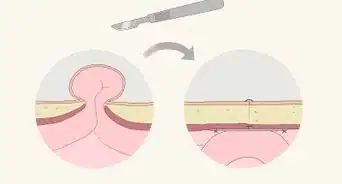
3Get surgery. Your doctor may recommend putting you under general anesthesia and performing open surgery. With this traditional approach, a surgeon opens the abdominal wall and repairs the hernia before closing the wall. Or, your doctor may recommend laparoscopic surgery in which small fiberoptic tools attached with a camera repair the abdominal wall.[4]
- Laparoscopic surgery is less invasive although you'll also need to be under general anesthesia. Recovery time is much shorter than with open surgery.
-
4Follow post-operation recommendations. After surgery, take pain medication and gradually return to your normal activity level within 3 or 4 days. You might feel sore or have nausea (from the anesthesia) which will wear off after a day or two. You should avoid strenuous activity like lifting until your doctor approves.[5]
- Ask your physician when you can resume activities like sex, driving, and exercising.
Identifying and Reducing Your Risk For Hernias
-
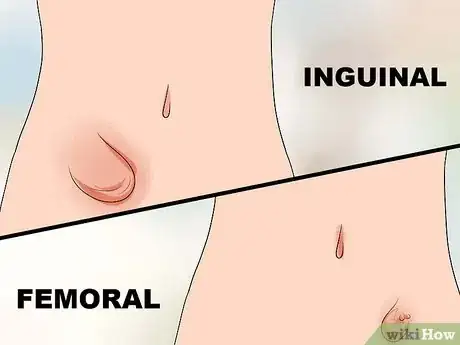
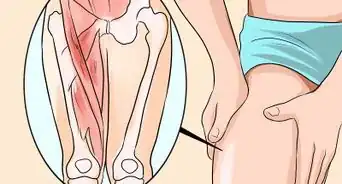
1Consider whether you have an inguinal or femoral hernia. If your hernia is near the groin, determine whether it's located at the inner or outer part of your groin. If it looks like the hernia is at the inner groin (an inguinal hernia), part of the intestines or bladder is forcing through the abdominal wall (or inguinal canal). If it looks like the hernia is at the outer groin, part of the intestines is forcing out into the femoral canal (a femoral hernia).
- Inguinal hernias are the most common type of hernia and they usually occur in older men. Femoral hernias are more common in pregnant or obese women. If you have a femoral hernia, seek medical attention immediately as these are more commonly associated with femoral artery or femoral nerve injury since the canal is much smaller and tighter than other types of hernias.
-
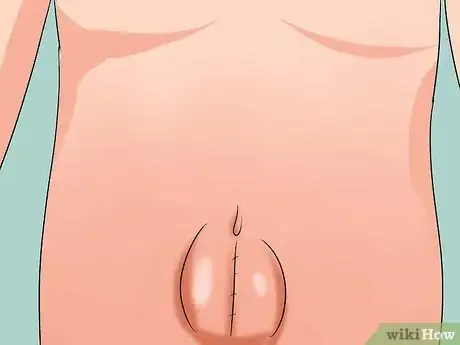
2Determine if you have an umbilical hernia. Umbilical hernias are a noticeable bulge at the belly button or navel. These happen when part of the small intestine pushes through the abdominal wall into the navel area. Umbilical hernias are more common in newborn babies which are usually surgically treated by pediatric surgeons.[6]
- Umbilical hernias also happen in obese women or women who have had multiple pregnancies.
-
3Decide if you have a hiatal hernia. Look for a bulge near your stomach and consider if you have acid reflux disease. These are signs of a hiatal hernia. The bulge is actually your stomach pushing through an opening in your diaphragm where your esophagus enters.[7]
- Other signs of hiatal hernia: heartburn, feeling of food stuck in your throat, feeling full quickly, and, rarely, chest pain, which can be confused with a heart attack.
- Hiatal hernias are more common in women, overweight people, and people over 50 years of age.[8]
-
4Look for an incisional hernia. You might get a hernia following abdominal surgery, especially if you've been inactive. With an incisional hernia, the intestine emerges through a weakened part of the abdomen where you once had surgery.[9]
- Incisional hernias are more common in the elderly or obese.
-
5Exercise and lose weight. You can reduce your risk for hernias by being a healthy weight and staying in shape. Work with a personal trainer or coach who can teach you how to properly exercise your abdominal muscles. You should try to strengthen these muscles to reduce your chances of getting a hernia. Studies have shown that stretching programs, like yoga, may treat inguinal hernias.[10]
- Learn how to lift heavy objects or do weight training before you lift heavy things. This can prevent damage to your abdominal muscles. If lifting, you may want to get help.
-
6Reduce physical stress. Hernias can't be prevented, but you can reduce your risk of developing one. This mainly involves reducing pressure on weakened abdominal walls. Avoid straining or excessive pressure when you use the toilet. To do this, eat fiber and drink plenty of water. These can loosen your stools, preventing constipation or diarrhea, conditions that strain already weak abdominal muscles.
- If you have a cold or allergies, don't be afraid to sneeze or cough. Suppressing these may actually lead to an inguinal hernia.[11] Talk with your doctor if you're sneezing or coughing a lot.
References
- ↑ https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/hernia.html
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/inguinal-hernia/expert-answers/hernia-truss/faq-20058111
- ↑ https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/inguinal-hernia/symptoms-causes/syc-20351547
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments_and_procedures/laparoscopic-surgery/hic_Laparoscopic_Surgery_for_Hernia_Repair
- ↑ http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Inguinalherniarepair/Pages/Recovery.aspx
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/umbilical-hernia/basics/risk-factors/con-20025630
- ↑ https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001137.htm
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases_conditions/hic-hernia/hic-hiatal-hernia
- ↑ https://www.hernia.org/types/incisional-hernia/
About This Article
If you’ve already seen a doctor about your hernia and you’ve got a hernia truss or belt, you should be able to push it back in. First, lie on your back so gravity will help push your hernia down. If you’re using a belt, lie on top of it so you can wrap it around yourself when you’ve pushed the hernia in. All you need to do is gently push the hernia back into your stomach, groin, or belly button. If it hurts, stop and contact your doctor, since there might be a complication with your hernia. Once your hernia’s back inside, fasten your belt or truss to prevent it from coming out again. If your baby has a hernia, don’t try to push it back in yourself in case you accidentally hurt them. For more tips from our Medical co-author, including how to reduce your risk of getting a hernia, read on.



































































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...