This article was medically reviewed by Lacy Windham, MD. Lacy Windham, MD, is a Board-Certified Obstetrician & Gynecologist in Cleveland, Tennessee. Dr. Windham attended medical school at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis. Her residency was completed at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, Virginia. She was the recipient of multiple awards during her residency training, including Most Outstanding Resident in Maternal Fetal Medicine, Most Outstanding Resident in Oncology, Most Outstanding Resident Overall, and Special Award in Minimally Invasive Surgery.
This article has been viewed 22,980 times.
Protecting your body’s ability to create children is not just limited to women. Men can also have concerns about their fertility, and both men and women can take steps to protect their fertility. Infertility, or your inability to have children, is not inevitable and can be prevented by practicing safe sex and making lifestyle adjustments.[1]
Steps
Practicing Safe Sex
-
1Use protection when having sexual intercourse. Both men and women should always use condoms or a form of protection when having sex to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Practice safe sex by always using protection, even if you are in a monogamous relationship. This will prevent unplanned pregnancy and allow you and your partner to plan ahead for a family.
-
2Get tested often for STIs. STIs like chlamydia and gonorrhoea can be contracted by men and women. These diseases are the leading causes of infertility, and have limited symptoms so they can be difficult to detect. Ensure you are STI free by getting tested at least yearly especially if you are not married, not in a monogamous relationship or have many sexual partners.
- If left untreated, chlamydia and gonorrhoea can damage a woman’s fallopian tubes, which can make it more difficult to conceive.
-
3See your doctor for regular check ups. Regular visits to your doctor will help you detect and treat any conditions that may affect your fertility. Women should visit their ob-gyn annually for fertility tests and other health tests. Men should also discuss any fertility issues with their doctor, especially if they have an undescended testicle or experience a loss of testicular size.[2]
- If you have been trying to conceive for a year or more by having regular, unprotected sex, and are still not pregnant, you should talk to your doctor. As well, if you are a woman over the age of 35 who has been trying to conceive for six months, you should speak to your doctor about fertility testing. Both men and women should be tested for fertility issues in the event of difficulty conceiving to determine the possible cause or causes.[3]
- Be aware of your family history. If your mother went through early menopause (before the age of 40), you may not want to wait until age 35 to start trying for pregnancy.
Adjusting Your Lifestyle
-
1Understand how age factors into your fertility. For women, there is a decrease in fertility as they advance in age. While you and your partner are the ones who should decide the best time, if any, to have children, you are more likely to conceive in your twenties and early thirties. An older woman’s eggs are not fertilized as easily as a younger woman’s eggs, and may not develop normally even after fertilization occurs. As well, men are most fertile in their early twenties.[4]
- Fertility in men declines gradually at around 40 years old. However, most men can father children into their 50s and beyond.
- Women are more likely to have fertility issues when they are over 35. Women over 35 are also less likely to get pregnant as a result of fertility treatments, and are more like to have a miscarriage if they do become pregnant.
- Women concerned about their future fertility may want to take additional steps to protect their ovarian reserve, that is, the number of remaining eggs that can produce children.
-
2Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise. If you are trying to conceive or are considering pregnancy in the near future, you should try to maintain a healthy weight for your age and height. Being underweight or overweight can lower your fertility.[5]
- This is especially important for women, as being overweight or obese can increase your risk of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which can cause infertility.
- To determine if you are at the ideal weight for your age and height, use a Body Mass Index calculator. If you are overweight, you should work on losing weight in a healthy and sustainable way.
-
3Stop smoking or cut down on smoking. There are many health risks related to smoking, one of which is negative affects on your fertility. Women who smoke are more likely to get menopause earlier than women who do not smoke, and are more likely to experience ovarian failure.[6] As well, men who smoke risk affecting their virility by damaging their sperm, decreasing their sperm’s motility, and decreasing their sperm production.
-
4Reduce your alcohol consumption. If you are trying to get pregnant, avoid drinking any alcohol to prevent harming a developing baby. If you are planning on getting pregnant in the near future, avoid drinking excessively and drink no more than one or two units of alcohol once or twice a week.[7]
- Men should also be wary of drinking excessively. You may damage your sperm if you exceed three to four units of alcohol (or two standard drinks) a day.
-
5Limit your exposure to harmful toxins. If you are in a profession that exposes you to high levels of potentially harmful toxins or chemicals, you may be at risk of developing fertility issues. Dental assistants, industrial workers, agricultural workers, and hair stylists are all at risk of reduced fertility due to the chemicals involved in their day to day work.[8]
- You should also avoid exposure to radiation and glycol ester, a chemical found in some paints. These substances can both negatively affect your fertility.
-
6Avoid taking steroids. Men can protect their fertility by avoiding drugs such as steroids or marijuana. These can lead to negative impacts on your virility and lessen your chances of producing viable sperm.[9]
-
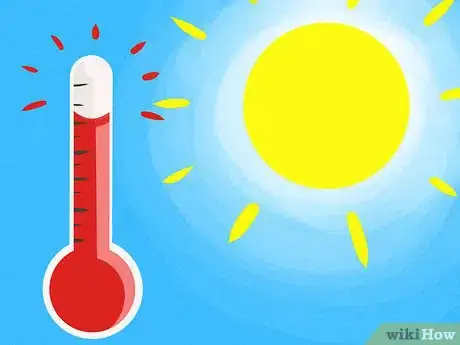
7Minimize your exposure to heat. A man’s testicles should always be one to two degrees cooler than the rest of his body to prevent slow sperm production. Avoid prolonged exposure to direct heat, such as sitting in a hot tub or a hot bath. If your occupation requires long hours of sitting, or you wear clothing that retain heat, including tight underwear, this can raise the temperature of your testicles and affect your sperm count.[10]
- Opt for short soaks in a hot bath or a hot tub, try to go for walks throughout the day if your job requires a lot of sitting down, and wear loose underwear.
References
- ↑ https://www.reproductivefacts.org/globalassets/asrm/asrm-content/learning--resources/patient-resources/protect-your-fertility3/asrm_brochure.pdf
- ↑ https://www.reproductivefacts.org/globalassets/asrm/asrm-content/learning--resources/patient-resources/protect-your-fertility3/asrm_brochure.pdf
- ↑ http://www.nhs.uk/Livewell/Fertility/Pages/Protectyourfertility.aspx
- ↑ https://newsinhealth.nih.gov/2015/07/pregnancy-problems
- ↑ https://www.nhs.uk/common-health-questions/pregnancy/how-can-i-increase-my-chances-of-getting-pregnant/
- ↑ https://www.reproductivefacts.org/globalassets/asrm/asrm-content/learning--resources/patient-resources/protect-your-fertility3/asrm_brochure.pdf
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/getting-pregnant/in-depth/female-fertility/art-20045887?pg=2
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/getting-pregnant/in-depth/female-fertility/art-20045887?pg=2
- ↑ https://www.reproductivefacts.org/globalassets/asrm/asrm-content/learning--resources/patient-resources/protect-your-fertility3/asrm_brochure.pdf
-Step-3-Version-2.webp)
-Step-2-Version-2.webp)