This article was medically reviewed by Erik Kramer, DO, MPH. Dr. Erik Kramer is a Board-Certified Primary Care Physician at the University of Colorado. With over 15 years of experience, his clinical interests include obesity and weight management, diabetes care, and preventive care, as well as embracing a holistic approach to primary care. He received his Doctorate in Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) from the Touro University Nevada College of Osteopathic Medicine and completed his residency at Central Maine Medical Center. Dr. Kramer is a Diplomate of the American Board of Obesity Medicine.
There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 20,903 times.
Ghrelin is a hormone that causes you to feel hungry, but research has shown that this hormone has other effects on your body. A high level of ghrelin promotes bone formation, inhibits insulin secretion, improves survival rates after a heart attack, prevents muscle atrophy, and may even help to prevent cancer development and metastasis.[1] If you’re looking for ways to increase ghrelin for a specific health concern, there are several strategies you can try, such as modifying your diet and taking supplements. However, keep in mind that these techniques might not work for everyone. Work with your doctor to treat any underlying conditions and make sure this is a safe option for you.
Steps
Changing Your Diet
-
1Follow a low-fat diet. Eating less fat may help to promote an increase in ghrelin. This may be due to the satiety that fat provides. Eating a diet that is high in fat reduces ghrelin. By eating less fat, the hormone may be increased instead. Some low-fat options you might include in your diet are:[2]
- Low-fat cheese, milk, and yogurt
- Lean proteins, such as skinless chicken breast, ground turkey, egg whites, and beans
- Lower fat versions of foods you normally eat, such as baked potato chips, low-fat muffins, and light bread
-
2Try intermittent fasting to raise ghrelin between meals. Some studies have demonstrated a link between going for long periods without food and an increase in ghrelin. To try this strategy, eat all of your meals and snacks during a 10-hour span of the day and then fast for the other 14 hours.[3]
- For example, you could eat all of your meals and snacks between 7:00 am and 5:00 pm, and then fast from 5:00 pm to 7:00 am the following day.
- Set your fasting hours in the evening so you can sleep for most of the time that you’d be hungry.
Warning: An intermittent fasting diet may not be suitable for you if you have diabetes or low blood sugar. Check with your doctor first before you try this strategy.
Advertisement -
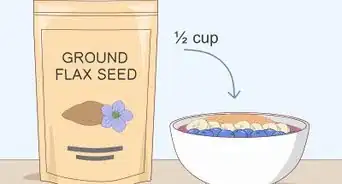
3Eat more high-fiber foods to increase ghrelin if you’re an overweight or obese postmenopausal woman. Consuming more fiber may help to promote an increase in ghrelin between meals. Eat lots of fruits, vegetables, beans, and whole grains to ensure that you’re getting enough fiber. You may also take a daily fiber supplement to promote an increase in ghrelin.[4]
- Aim for 25 grams of fiber per day. If you’re consuming very little fiber now, build up to this amount over a few weeks, such as by adding 1 to 2 servings of a high-fiber food into your diet each day.
-
4Include coriander in your diet as a seasoning. Coriander, also known as cilantro, may help to increase the amount of ghrelin in your system when you consume it regularly. Try using coriander as a seasoning in the foods you make to see if this helps to increase your ghrelin levels.[5]
- Sprinkle freshly chopped coriander onto salads, curries, or grilled chicken.
- Make a salad dressing or marinade for meat or fish using coriander.
-
5Flavor foods with ginger or drink ginger tea. Ginger may also help to increase the amount of ghrelin in your system, so try incorporating more of this spice in your diet. You can season foods with ginger or make yourself a cup of ginger tea once per day.[6]
- Try adding fresh chopped ginger to stir-frys, baked goods, and salad dressings.
- To make ginger tea, peel and chop a 1 in (2.5 cm) piece of ginger and place it into a mug. Then, pour 8 fl oz (240 mL) of boiling water over the ginger and let it steep for 5 to 10 minutes before drinking it.
Taking Supplements
-
1Use fish oil supplements to promote ghrelin’s anti-inflammatory effects. Omega-3 fatty acids increase ghrelin levels. This may have something to do with the anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3s, since ghrelin also has anti-inflammatory properties. Choose a fish oil supplement or ask your doctor for a recommendation.[7]
- You can also get omega-3s from dietary sources, such as by consuming salmon, mackerel, and walnuts.
-
2Take a daily curcumin supplement to see if this helps your body use ghrelin more efficiently. Curcumin, also known as turmeric, may help to promote the expression of ghrelin so that your body uses it more effectively. This might help reduce oxidative stress. However, be aware that the study was done on diabetic rats, so this might not provide the results you’re looking for.[8]
- You could also season food with turmeric to work it into your diet. Curries often include turmeric in the spice blend, so try making a chicken curry or a vegetable curry.
- You could also drink turmeric, such as in a cup of turmeric tea.
Tip: Make sure to check with your doctor before starting any dietary supplements. Tell your doctor about any over-the-counter or prescription medications you are taking.
-
3Look into cannabis sativa oil if it’s legal where you live. If cannabis sativa oil is legal in your country or state, this might be a good option for increasing your ghrelin levels. Start with a very small dose to see how it affects you and then adjust as needed.[9]
- Be aware that cannabis sativa oil is legal in some states and countries and illegal in others. Find out if this is a legal option before you consider it.
- Cannabis sativa has not been well-researched. Check with your doctor before you decide to try it.[10]
Seeking Medical Treatment
-
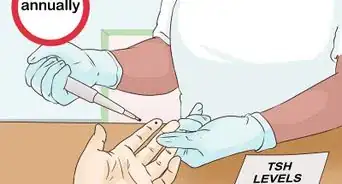
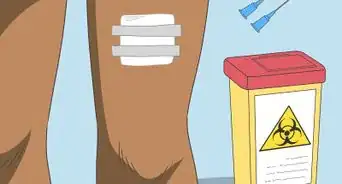
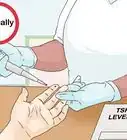
1Get your ghrelin levels checked to see if they’re low. If you’re concerned about your ghrelin levels, work with your healthcare provider to have them checked and develop a plan for improving them. Your doctor can run a blood test to check your ghrelin levels.
- Keep in mind that your doctor might also want to check for other potential causes of your complaints. For example, if you’re struggling to lose weight, your doctor might also check your thyroid.
- Ghrelin levels change and are usually higher at night and lower during the day.
- Western-trained medical providers may not check ghrelin levels since there are no clinical treatments or supplements available.
-
2Talk to your doctor about losing weight if you’re overweight. Being overweight or obese may reduce your ghrelin levels, but losing weight can increase them. Check with your doctor to identify your target weight and develop a plan for achieving it. You’ll need to eat less and incorporate regular exercise to lose weight.[11]
- As your ghrelin levels increase as you lose weight, you may feel extremely hungry.
- Chronically increased levels of ghrelin are usually associated with obesity.
Warning: If you’re already at a healthy weight, losing weight may cause you to become underweight. Don’t attempt to lose weight unless your doctor has recommended it.
-
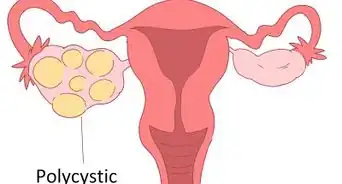
3Get treated for conditions that may decrease ghrelin levels. There are a few medical conditions that can cause your ghrelin levels to be low, but getting treated may help to increase your levels. Seek medical treatment if you have any of the following conditions:[12]
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Metabolic syndrome
- Diabetes type 1 or 2
References
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4049314/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15177945
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15177945
- ↑ https://eje.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/eje/161/1/65.xml
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4587604/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4587604/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23474089
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24036253
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4587604/








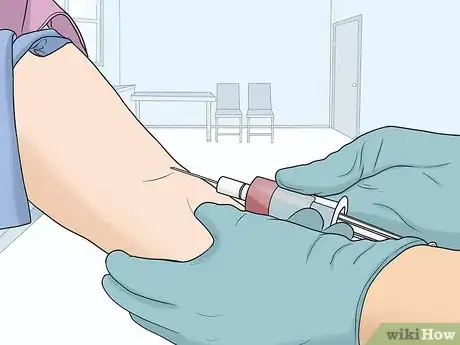








-Step-12-Version-2.webp)














































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...