This article was medically reviewed by Luba Lee, FNP-BC, MS. Luba Lee, FNP-BC is a Board-Certified Family Nurse Practitioner (FNP) and educator in Tennessee with over a decade of clinical experience. Luba has certifications in Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS), Emergency Medicine, Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS), Team Building, and Critical Care Nursing. She received her Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) from the University of Tennessee in 2006.
This article has been viewed 14,247 times.
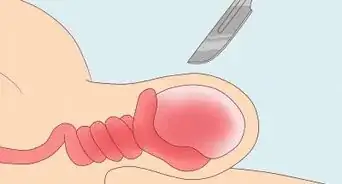
Though there isn’t actually a bone inside of your penis, you can tear or damage the tissue, which is known as a penile fracture. Penile fractures can happen when an erect penis is forced to bend after blunt force during sex, but they can also occur after direct trauma to your penis or after a fall.[1] If you think you may have a penile fracture, there are a few ways you can check to identify it. A penile fracture is a serious injury that needs to be treated immediately so there isn’t any long-term damage. Your doctor will immediately treat your injury, which usually requires surgical repair.
Steps
Recognizing the Signs
-
1Listen for a cracking or popping sound. The majority of penile fractures occur during sexual intercourse and are often accompanied by a characteristic snapping or cracking sound and sensation. If you suddenly feel or hear a cracking sound or sensation in your penis, you may have a fracture.[2]
- For instance, it might sound like the pop or snap of a broken corn cob or glass rod.
- You can fracture your penis by falling on it while it’s erect.
- If you’re having sex and you suffer a penile fracture, stop having sex to prevent long-term damage.
Note: Not all penile fractures occur with a snapping or popping sound. You may not notice that your penis is fractured right away.
-
2Notice if you feel sudden pain in your penis. You're likely worried if your penis hurts. Penile fractures may cause pain that ranges from mild to severe, though you might not notice pain at all. Consider if your pain started during sex or after an impact to your penis to figure out if it could be related to a penile fracture.[3]
- Keep in mind that the degree of your pain may not be related to the severity of your injury. It's possible to have severe pain with a mild injury or mild pain with a serious injury, so always consult a doctor to be sure.
Advertisement -
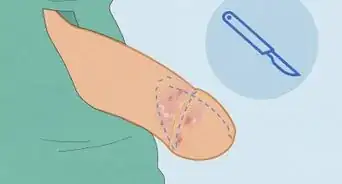
3Look for dark bruising above the injured area. Because a penile fracture is actually a rupture or tear in the tissue of your penis, blood can quickly pool beneath the skin directly above the injury. If you think you’ve injured your penis, examine it for a dark purple bruise to see if it’s fractured.[4]
- Don’t try to push or massage the bruise away or you could further damage your penis.
-
4Check to see if your penis is bent. Another tell-tale sign of a penile fracture is a bend or curve in your penis that wasn’t there before you injured it. Gently examine your penis to see if it looks different or appears damaged.[5]
- It’s possible that you won’t experience pain if you suffer a penile fracture, but if you have a bent penis, it’s likely that you have a fracture.
-
5Take note if you suddenly lose your erection. A distinctive sign of a penile fracture that occurs during sexual intercourse is called “detumescence” and refers to a sudden and rapid loss of your erection. If you’re having sex and you think you may have a penile fracture, check to see if your erection quickly goes away. It could be a sign of a fracture.[6]
- You may not have noticed or felt your penile fracture, so a sudden loss of your erection could be a sign.
-
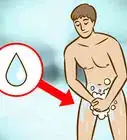
6Keep an eye out for blood leaking from your penis. A penile fracture is actually a tear in the tissue of your penis, which is filled with blood vessels. If you suffer a penile fracture, you may start to have blood leak out of the tip of your penis.[7]
Warning: Blood coming from your penis could also be a sign of another serious medical issue, such as bladder or kidney damage, so it’s imperative that you get immediate medical attention.
-
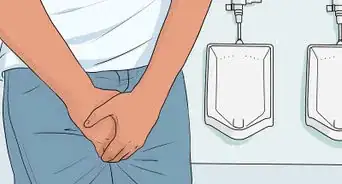
7Find out if you have difficulty urinating. A penile fracture can damage your urethra and make it more difficult for you to urinate. If you feel a pressure or pain when you try to urinate, or if you have to force your urine out, it could be a sign of a fracture.[8]
- Difficulty urinating could be caused by another condition as well.
-
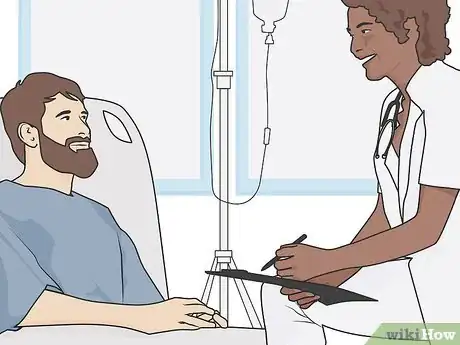
8Get medical attention if you think you have a penile fracture. A penile fracture is a serious injury that can lead to permanent damage and erectile dysfunction if it isn’t treated immediately. If you think you’re experiencing a penile fracture, get to an emergency room as soon as possible.[9]
- Your doctor can rule out other potential causes as well.
- If you’re in too much pain to drive yourself, ask someone to drive you or call an ambulance.
Getting Medical Treatment
-
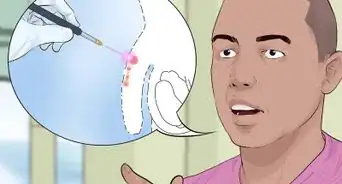
1Ask your doctor for a scan to confirm a fracture. Although your doctor might be able to make a diagnosis based on your symptoms and a physical exam, they may do an imaging test to verify that you have a penile fracture. Your doctor can perform a scan known as a cavernosography, which can tell you if you suffered a penile fracture, even if the injury occurred in the past. They can also perform an ultrasonography, a specialized ultrasound that can scan your penis to identify a fracture.[10]
- If your penis has been hurting, but you don’t show any other signs of a fracture, try getting a scan to be sure.
- Be sure to mention if you’ve been experiencing erectile dysfunction, which can be a sign of a penile fracture.
-
2Try conservative therapy if your doctor recommends it. Although surgery is usually the best way to treat a penile fracture, you might try other non-invasive treatments first if your doctor thinks they might work for you. Talk to your doctor about your unique needs and what treatments you can try. Keep in mind that conservative treatments may increase your risk of complications and permanent damage, so follow your doctor's advice. They may recommend the following conservative treatments:[11]
- Manage pain and swelling by applying an ice pack to your penis.
- Take over-the-counter nonsteroidal inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve) for pain and swelling if your doctor says it's okay.
- Let your doctor insert a Foley catheter to drain your urine while your penis heals.
- Wear compression bandages or a penile splint as instructed by your doctor to help your penis heal properly.
- Take estrogen to help prevent erections if your doctor prescribes them.
- Use an antibiotic if you have an infection.
- Take fibrinolytic agents to dissolve blood clots if they're prescribed.
-
3Agree to surgical repair if you have a fracture. Some mild injuries to your penis may be able to heal up on their own, but fractures require immediate surgical intervention to prevent long-term complications. Don’t delay and agree to surgery if your doctor thinks it’s necessary.[12]
- Surgery consists of using sutures to repair the damaged area.
-
4Follow your doctor’s recommendations as you recover from surgery. It takes around 6 weeks for your penis to fully heal from surgery to repair a fracture, so take all of the medications prescribed by your doctor as directed for the best results. Avoid sexual intercourse or getting an erection until your doctor says it’s safe to avoid reinjuring your penis or rupturing the sutures used to repair the fracture.[13]
- Don’t apply ice or cold to your penis unless your doctor says it’s okay.
- Ask your doctor about any over-the-counter medications before you take them.
- Be sure to tell your doctor right away if your sutures rupture or you reinjure your penis.
Warnings
- A penile fracture is a serious medical emergency that needs to be treated as soon as possible to prevent long-term damage. If you think you have a penile fracture, seek emergency medical treatment.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Penile fractures may cause long-term effects like a curved penis, painful erections, persistent erections, painful intercourse, erectile dysfunction, skin necrosis, fistulas, and scarring that narrows your urethra.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1472832/
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21707-penile-fracture
- ↑ https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/p/penile-trauma
- ↑ https://myhealth.alberta.ca/health/AfterCareInformation/pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=abq3394&
- ↑ https://myhealth.alberta.ca/health/AfterCareInformation/pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=abq3394&
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21707-penile-fracture
- ↑ https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/p/penile-trauma/
- ↑ https://myhealth.alberta.ca/health/AfterCareInformation/pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=abq3394&
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21707-penile-fracture


























































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...