Appendix F2 - Figure 1
Supplement F: Laboratory Guidance
Public Health Guidance for Community-Level Preparedness and Response to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Version 2/3
Figure 1 - SARS-CoV Specimen Testing Guidelines: RT-PCR Testing
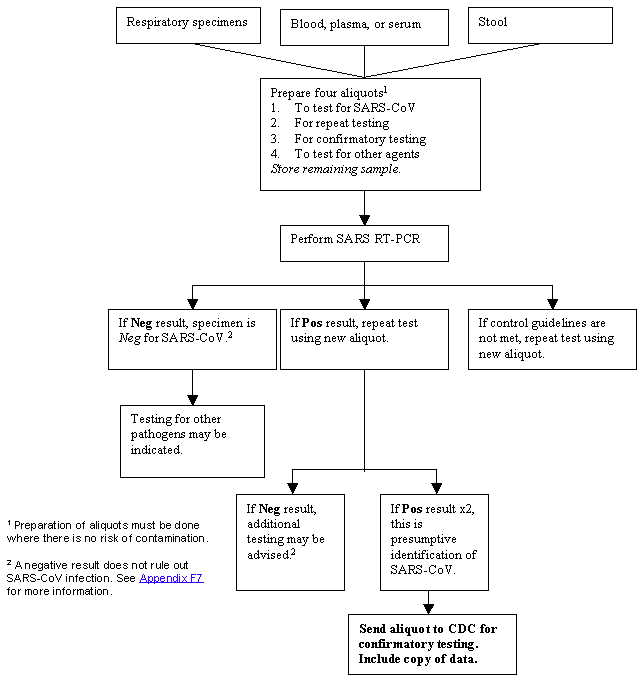
Text version of Figure 1
For Respiratory specimens; Blood, plasma, or serum; and Stool
Prepare four aliquots1
- To test for SARS-CoV
- For repeat testing
- For confirmatory testing
- To test for other agents
Store remaining sample.
Perform SARS RT-PCR
- If Neg result, specimen is Neg for SARS-CoV.2
- Testing for other pathogens may be indicated.
- If control guidelines are not met, repeat test using new aliquot.
- If Pos result, repeat test using new aliquot.
- If Neg result, additional testing may be advised.2
- If Pos result x2, this is presumptive identification of SARS-CoV.
- Send aliquot to CDC for confirmatory testing. Include copy of data.
Footnotes
- Preparation of aliquots must be done where there is no risk of contamination.
- A negative result does not rule out SARS-CoV infection. See Appendix F7 for more information.
Related Pages
- Summary
- I. Rationale and Goals
- II. Lessons Learned
- III. Diagnostic Assays
- IV. CDC's Laboratory Diagnostics Plan
- Appendix F1: Proficiency Testing for Public Health Laboratories Performing SARS-CoV EIA and RT-PCR Diagnostics
- Appendix F2: SARS-CoV Specimen Testing Guidelines: RT-PCR and Serology
- Appendix F3: Guidelines for Clinicians: The Consent Process for SARS-CoV RT-PCR and EIA Testing at CDC and Public Health Laboratories
- Appendix F4: Guidelines for Collecting Specimens from Potential SARS Patients
- Appendix F5: Laboratory Biosafety Guidelines for Handling and Processing Specimens Associated with SARS-CoV
- Appendix F6: Guidelines for Medical Surveillance of Laboratory Personnel Working with SARS-CoV
- Appendix F7: Fact Sheet for Clinicians: Interpreting SARS-CoV Test Results from CDC and Other Public Health Laboratories
- Appendix F8: Guidelines for Laboratory Diagnosis of SARS-CoV Infection
- Page last reviewed: May 3, 2005
- Page last updated: May 3, 2005
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir