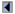Reporting, Appraising, and Integrating Data On Genotype Prevalence and Gene-Disease Associations Table
This website is archived for historical purposes and is no longer being maintained or updated.
TABLE 1: Proposed checklist for reporting and appraising studies of genotype prevalence and gene-disease associations
| Item to be specified | Details by type of study | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype prevalence | Gene-disease associations | ||
| Purpose of study |
Yes
|
Detect associations or estimate magnitude of association
|
|
| Analytic validity of genotyping |
|
|
|
| Types of samples used |
Yes
|
For cases and for controls
|
|
| Timing of sample collection and analysis, by study group* |
Ethnic group†
|
Cases vs. controls†
|
|
| Success rate in extracting DNA, by study group* |
Ethnic group†
|
Cases vs. controls†
|
|
| Definition of the genotype(s) investigated; when there are multiple alleles, those tested for should be specified |
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
| Genotyping method used (reference; for polymerase chain reaction methods—primer sequences,* thermocyle profile,* no. of cycles*) |
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
| Percentage of potentially eligible subjects for whom valid genotypic data were obtained, by study group |
Ethnic group†
|
Cases vs. controls†
|
|
| If pooling was used, strategy for pooling of specimens from cases and controls |
|
Yes
|
|
| Quality control measures* |
Yes
|
Including blinding of
laboratory staff |
|
| Degree of reproducibility between quality control replicates |
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
| Samples from each group of subjects compared (e.g., cases and controls) included in each batch analyzed* |
|
Yes
|
|
| Selection of study subjects |
|
|
|
| Geographic area from which subjects were recruited |
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
| The recruitment period |
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
| Recruitment methods for subjects whose genotypes were determined, such as random population-based sampling, blood donors, and hospitalized subjects with reasons for hospitalization |
Yes
|
Controls†
|
|
| Definition of cases and method of ascertainment |
|
Yes
|
|
| No. of cases recruited from families and methods used to account for related subjects |
|
Yes
|
|
| Exclusion criteria for cases and controls |
|
Yes
|
|
| Recruitment rates |
Where possible by sex, age, and ethnic group
|
For cases and controls
|
|
| Mean age and standard deviation or age range of study subjects, and the distribution by sex |
Yes
|
For cases and controls
|
|
| If the subjects were controls from a case-control study, information on the disease under investigation and any matching criteria such as age, gender, and/or risk factor levels |
Yes
|
|
|
| Ethnic group of study subjects |
Yes |
|
|
| Similarity of sociodemographic (or other) characteristics of subjects for whom valid genotypic data were obtained with characteristics of subjects for whom such data were not obtained* |
|
Yes
|
|
| Steps taken to ensure that controls are noncases* |
|
Yes
|
|
| Confounding, including population stratification |
|
|
|
| Design |
|
Yes
|
|
| If other than a case-family control design, matching for ethnicity or adjustment for ethnicity in analysis |
|
Yes
|
|
| Potential correlates of the genotype identified and taken into consideration in design or analysis |
|
Yes
|
|
| Statistical issues |
|
|
|
| Distinguish clearly a priori hypotheses and hypotheses generated |
|
Yes
|
|
| If haplotypes used, specify how these were constructed |
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
| No. of subjects included in the analysis |
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
| Method of analysis, with reference, and software used to do this |
|
Yes
|
|
| Confidence intervals |
Of genotype frequency
|
Of measures of association with the genotype
|
|
| Assessment of goodness-of-fit of the model used* |
|
Yes
|
|
* Additional information recorded (ideally in Web-based methods register) but not necessarily presented in journal article.
† For example.
- Page last reviewed: June 15, 2009 (archived document)
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir