Chapter 7
Memory
By Boundless
Sensory memory allows an individual to remember an input in great detail but for only a few milliseconds.
Short-term memory, which includes working memory, stores information for a brief period of recall for things that happened recently.
Long-term memory is used for the storage of information over long periods of time, ranging from a few hours to a lifetime.
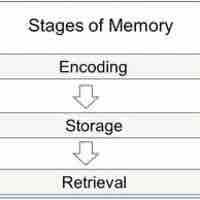
Memory encoding allows an item of interest to be converted into a construct that is stored in the brain, which can later be recalled.
In order to encode information into memory, we must first pay attention, a process known as attentional capture.
Levels-of-processing theory looks at not only how a person receives information, but also what they do with that information.
Memory storage allows us to hold onto information for a very long duration of time—even a lifetime.
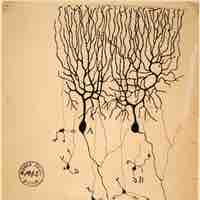
According to network models of memory, the connections between neurons are the source of memories, and the strength of connections corresponds to how well a memory is stored.
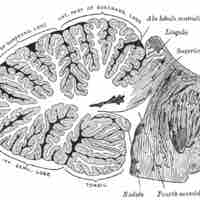
The hippocampus, amygdala, and cerebellum play important roles in the consolidation and manipulation of memory.
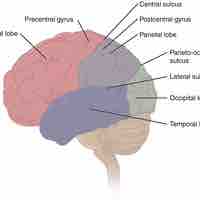
Although the physical location of memory remains relatively unknown, it is thought to be distributed in neural networks throughout the brain.
Memories can be encoded poorly or fade with time; the storage and recovery process is not flawless.
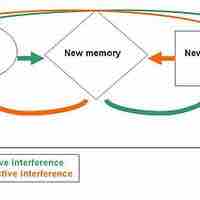
There are many ways in which a memory might fail to be retrieved, or be forgotten.
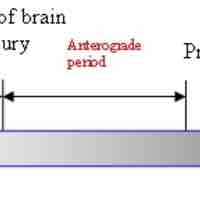
Amnesia, the inability to recall certain memories, often results from damage to any of a number of regions in the temporal lobe and hippocampus.
Memories are not stored as exact replicas of reality; rather, they are modified and reconstructed during recall.
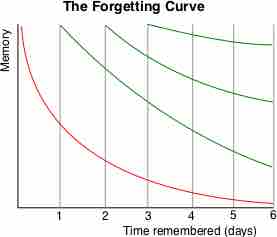
Increasing evidence shows that memories and individual perceptions are unreliable, biased, and manipulable.

Some research indicates that traumatic memories can be forgotten and later spontaneously recovered.